Abstract
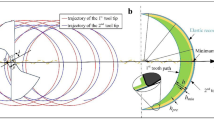
A study for investigating the geometric characteristics of the side wall, which is generated by the flat end-milling process, is carried out through experiments and geometrical analysis. For this research, flat surfaces of prismatic parts are considered. It is assumed that the change of material removal per tooth causes the change of tool deflection. Under this assumption, it is verified that the milled surface geometry is directly affected by the amount of material removal per tooth. Analytical models for predicting the location, size, and depth of the geometrically defected zone are also developed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Budak, E. and Altintas, Y., 1994., “Peripheral Milling Conditions for Improved Dimensional Accuracy,”Int. J. Mach. Tools Manu., Vol. 34, No. 7, pp. 907–918.
Cho, H. D. and Yang, M. Y., 1992, “A Study on the Prediction of Tool Deflection and Precision Machining in Ball End Milling Process,”KSME Journal, Vol. 16, No. 9, pp. 1669–1680.
Choi, J. G. and Yang, M. Y., 1998, “In-Process Prediction of the Surface Error Using an Identification of Cutting Depths in End Milling Operation by Simulating Surface,”J. of KSPE, Vol. 15, No. 2, pp. 114–123.
Kim, Y. H. and Ko, S. L., 2001, “Improvement of the Accuracy in Cornering Cut Using End Mill,”KSME Journal, Vol. 25/A, No. 3, pp. 399–407.
Ko, S. L., Lee, S. K. and Bae, S. M., 2001, “Study on the Design of End Mill Geometry,”J. of KSPE, Vol. 18, No. 8, pp. 24–30.
Lee, S. K. and Ko, S. L., 1999, “Analysis on the Precision Machining in End Milling Operation by Simulating Surface Generation,”J. of KSPE, Vol. 16, No. 4, pp. 229–236.
Rowe, W. B. and Barash, M. M., 1964, “Computer Method for Investigating the Inherent Accuracy of Centerless Grinding,”Int. J. Mach. Tool Des. Res., Vol. 4, pp. 91–116.
Ryu, S. H., Choi, D. K. and Chu, C. N., 2003, “Optimal Cutting Condition in Side Wall Milling Considering Form Accuracy,”J. of KSPE, Vol. 20, No. 10, pp. 31–39.
Seo, T. I. and Cho, M. W., 1999a, “Tool Trajectory Generation Based on Tool Deflection Effects in Flat-End Milling Process (I)—Tool Path Compensation Strategy—,”KSME International Journal, Vol. 13, No. 10, pp. 738–751.
Seo, T.I. and Cho, M. W., 1999b, “Tool Trajectory Generation Based on Tool Deflection Effects in Flat-End Milling Process (II)—Prediction and Compensation of Milled Surface Errors—,”KSME International Journal, Vol. 13, No. 12, pp. 918–930.
Tlusty, J., Smith, S. and Zamudia, C., 1990, “New NC routines for Quality in Milling,”Annals of CIRP, Vol. 39/1, pp. 517–521.
Yoon, J. H., Cheong, M. S. and Lee, H. C., 2003, “A Study on Transition of Dimension Error and Surface Precision in High Speed Machining of Al-alloy,”J. of KSMTE, Vol. 9, No. 3, pp. 96–102.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, K. Unavoidable geometric errors in the side walls of end-milled parts —Flat surface—. J Mech Sci Technol 21, 48–56 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03161711
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03161711