Abstract
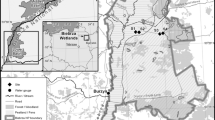
In a ground-water discharge fen that supports species-rich herbaceous vegetation, the chemistry of the shallow ground water was monitored over two distinct periods. The fen is situated on a thick sandy aquifer in a region that is known for its acid soils. An irrigation ditch supplies the aquifer with alkaline water just upstream of the fen. Three water types of different origin contribute to the hydrochemical pattern in the fen. Recently infiltrated acid ground water is present on higher grounds, neutral-to-alkaline irrigation water discharges at the upper fen margin, and deep ground water that is rich in iron discharges in the lower parts. The soil chemistry and species distribution are in accordance with this pattern: rich fen at the upper margin and poor fen in lower parts. However, we detected considerable hydrochemical variability due to varying influence of water types and temporal acidification of the shallow ground water. The latter leads to anionic dominance shifts from HCO3 to SO4 2− and the release of base cations in the soil solution. This hydrochemical variability is an additional source of environmental heterogeneity and may thus be partly responsible for the species richness.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Boeye, D. 1992. Hydrologie, hydrochemie en ecologie van een grondwaterafhankelijk veen. Ph.D. Dissertation. University of Antwerp, Antwerp, Belgium.
Boeye, D. and R. F. Verheyen. 1992. The hydrological balance of a groundwater discharge fen. Journal of Hydrology 137:149–163.
Bultot, F. and G. L. Dupriez. 1974. L’évapotranspiration potentielle des bassins hydrographiques en Belgique. Institut Royal Meteorologique de Belgique, Brussels, Belgium. Publications, Série A, No 85.
Cnudde, J. P. 1978. Hydrogeologische studie van het plassengebied te Mol. State University of Ghent, Ghent, Belgium.
De Langhe, J.-E., V. Westhoff, and R. D’Hose. 1979. De plantengroei van het Buitengoor te Mol (Antwerpen). Dumortiera 12:10–13.
Gilvear, D. J., R. Andrews, J. H. Tellam, J. W. Lloyd, and D. N. Lerner. 1993. Quantification of the water balance and hydrogeological processes in the vicinity of a small groundwater-fed wetland, East Anglia, UK. Journal of Hydrology 144:311–334.
Greerberg, A. E., R. Rhodes Trussel, and L. S. Clesceri. 1985. Standard methods for the examination of water and waste water, 16th ed. APHA, AWWA, WPCF, Washington, DC, USA.
Karlin, E. F. and L. C. Bliss. 1984. Variation in substrate chemistry along microtopographical and water-chemistry gradients in peatlands. Canadian Journal of Botany 62:142–153.
Kemmers, R. H. and P. C. Jansen. 1985. Hydrologie in relatie tot de beschikbaarheid van vocht en voedingsstoffen voor natuurlijke begroeiingen. Cultuurtechnisch Tijdschrift 24:195–211.
Kirchner, J. W. 1992. Heterogeneous geochemistry of catchment acidification. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 56:2311–2327.
Krajenbrink, G. J. W., D. Ronen, W. Van Duijvenboden, M. Margaritz, and D. Wever. 1988. Monitoring of recharge quality under woodland. Journal of Hydrology 98:83–102.
LaZerte, B. D. 1993. The impacts of drought and acidification on the chemical exports from a minerotrophic conifer swamp. Biogeochemistry 18:153–175
Lembrechts, J. and D. van Straaten. 1982. Gradient investigation of a peat-bog (Buitengoor-Meergoor/Mol, Belgium). 1. Physical and chemical investigation of surface water and soil. Bulletin de la Société Royale de Botanique de Belgique 115:325–336.
Malmer, N. 1986. Vegetational gradients in relation to environmental conditions in northwestern European mires. Canadian Journal of Botany 64:375–383.
McGlynn, J. A. 1974. Examination of waters: evaluation of methods for selected characteristics. Australian Water Resources Council, Australian Government Publishing Service, Canberra, Australia, Technical Paper No 8.
Meade, R. and T. H. Blackstock. 1988. The impact of drainage on the distribution of rich-fen plant communities in two Anglesey basins. Wetlands 8:159–177.
Pedroli, B. 1990. Classification of shallow groundwater types in a Dutch coversand landstape. Journal of Hydrology 115:361–375.
Romesburg, H. C. 1984. Cluster analysis for researchers. Lifetime Learning Publications, Belmont, CA, USA.
Rosenqvist, I. Th. 1990. From rain to lake: water pathways and chemical changes. Journal of Hydrology 116:3–10.
Ruiz, F., V. Gomis, and P. Blasco. 1990. Application of factor analysis to the hydrogeochemical study of a coastal aquifer. Journal of Hydrology 119:169–177.
Schafran, G. C. and C. T. Driscoll. 1990. Porewater acid/base chemistry in near-shore regions of an acidic lake. The influence of groundwater inputs. Biogeochemistry 11:131–150.
Siegel, D. I. and P. H. Glaser, 1987. Groundwater flow in a bogfen complex, Lost River Peatland, northern Minnesota. Journal of Ecology 75:743–754.
Sneath, P. H. A. and R. R. Sokal. 1973. Numerical taxonomy: principles and practice of numerical classification. W. H. Freeman, San Francisco, CA, USA.
Tyler, C. 1981. Soil acidity and distribution of species on tussocks and interspaces in Schoenus vegetation of south and southeast Sweden. Vegetatio 44:25–35.
Vangenechten, J. H. D. 1980. Interrelations between pH and other physico-chemical factors in surface waters of the Campine of Antwerp, (Belgium): with special reference to acid moorland pools. Archive für Hydrobiologie 90:265–283.
van Straaten, D. and J. Lembrechts. 1982. Gradient investigation of a peat-bog (Buitengoor-Meergoor/Mol, Belgium). 2. Phytosociological description. Bulletin de la Société Royale de Botanique de Belgique 115:337–356.
van Wirdum, G. 1991. Vegetation and hydrology of floating richfens. Ph.D. Dissertation. University of Amsterdam. Datawyse, Maastricht, The Netherlands.
Vitt, D. H. and W. L. Chee. 1990. The relationship of vegetation to surface water chemistry and peat chemistry in fens of Alberta, Canada. Vegetatic 89:87–106.
Wassen, M. J. 1990. Water flow as a major landscape ecological factor in fen development. Ph.D. Dissertation., University of Utrecht. Utrecht. The Netherlands.
Wassen, M. J., A. Barendregt, M. C. Bootsma, and P. P. Schot. 1989. Groundwater chemistry and vegetation gradients from rich fen to poor fen in the Naardermeer (the Netherlands). Vegetatio 79:117–132.
Westhoff, V. and A. J. Den Held. 1975. Plantengemeenschappen in Nederland. Thieme & Cie. Zutphen, The Netherlands.
Wheeler, B. D. 1988. Species richness, species rarity and conservation evaluation of rich-fen vegetation in lowland England and Wales. Journal of Applied Ecology 25:331–353.
Wilcox, D. A., R. J. Shedlock, and W. H. Hendrickson. 1986. Hydrology, water chemistry and ecological relations in the raised mound of Cowles Bog. Journal of Ecology 74:1103–1117.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boeye, D., Clement, L. & Verheyen, R.F. Hydrochemical variation in a ground-water discharge fen. Wetlands 14, 122–133 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03160628
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03160628