Abstract
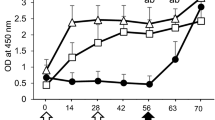
The encephalitogenic potential of rabies vaccines prepared from nervous tissue is a result of the presence of myelin basic protein. Vaccines prepared from duck embryos are economical and efficient, but, occasionally, cases of allergic encephalomyelitis have been reported. An improved rabies vaccine has been developed that contains the classical Pitman Moore strain of rabies virus grown in embryonated duck eggs. This vaccine has been highly purified and enriched in immunologically effective rabies virus glycoprotein antigen. We have searched for the presence of myelin basic protein using sensitive radioimmunological and immunoblotting techniques. Whereas the classical duck embryo rabies vaccine contained small amounts of myelin basic protein, in the improved purified duck embryo rabies vaccine, none could be detected.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bachmann G., Steffen R., Glück R., Wegmann A., and Schär M. (1985) Präexpositonelle Tollwutschutzimpfung mit einer neuen Entenembryovakzine.Schweiz. Med. Wochenschr. 115, 863–865.
Bürgisser P. (1983)Mise au point d’un dosage radioimmunologique de la protéine basique de la myéline dans le liquide céphalorachidien et dans le tissu nerveux. Application à la clinique et à la recherche. Thèse, Université de Lausanne, Switzerland, pp. 182.
Bürgisser P., Matthieu J.-M., de Tribolet N., and Gautier E. (1982) Dosage de la protéine basique de la myéline dans le liquide céphalo-rachidien au cours d’affections neurologiques.Schweiz. Med. Wochenschr. 112, 643–647.
Ferguson M., Seagroatt V. and Schild G. C. (1984) A collaborative study on the use of single radial immunodiffusion for the assay of rabies virus glycoprotein.J. Biol. Stand. 12, 283–294.
Glück R. and Germanier R. (1984)Immunogenicity of two different conformations of rabies glycoproteins. 6th International Congress of Virology, Sendai, Japan.
Glück R., Keller H., Mischler R., Wegmann A., and Germanier R. (1983) New aspects concerning the immunogenicity of rabies vaccines produced in animal brains (duck embryo), inRabies in the Tropics (E. Kuwert, C. Mérieux, H. Koprowski, K. Bögel, (eds.), Springer Verlag, Berlin, 181–188 (1985).
Glück R., Wegmann A., Germanier R., Keller H., Hess M. W., Kraus-Ruppert R., and Wandeler A. I. (1984) A new, highly immunogenic duck embryo rabies virus.Lancet 8381, i, 844–845.
Hilfenhaus J., Köhler R., Barth R., Majer M., and Mauler R. (1976) Large-scale purification of animal viruses in the RK-mod 1 zonal ultra-zentrifuge.J. Biol. Stand. 4, 263–271.
Keller H., Glück R., Wegmann A., and Wandeler A. I. (1984) Immunogenität einer neuen, hochgereinigten, hochkonzentrierten Tollwut-Entenembryo-vakzine.Schweiz. Med. Wochenschr. 114, 648–653.
Kies M. W., Alvord, Jr. E. C. (1959) Encephalitogenic activity in guinea pigs of water soluble protein fractions of nervous tissue, inAllergic Encephalomyelitis (Kies M. W. and Alvord, Jr. E. C., eds.) Charles C. Thomas, Springfield, Ill.
Laemmli U. K. (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4.Nature 227, 680–685.
Lowry O. H., Rosebrough N. J., Farr A. L., and Randall R. J. (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent.J. Biol. Chem. 193, 265–275.
Rivers T. M., Sprunt D. H., and Berry G. P. (1933) Observations on attempts to produce acute disseminated encephalomyelitis in monkeys.J. Exp. Med. 58, 39–53.
Rivers T. M. and Schwentker F. F. (1935) Encephalomyelitis accompanied by myelin destruction experimentally produced in monkeys.J. Exp. Med. 61, 689–701.
Roboz-Einstein E. and Henderson N. (1959) Preparation and properties of water soluble proteins from bovine cord with “allergic” encephalomyelitis activity, inAllergic Encephalomyelitis (Kies M. W. and Alvord, Jr. E. C., eds.) Charles C. Thomas, Springfield, Ill.
Towbin H., Stahelin T., and Gordon J. (1979) Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: Procedure and some applications.Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 76, 4350–4354.
Wegmann A., Glück R., and Keller H. (September 1984) Importance of booster vaccination on day 90 with modern rabies vaccines.Lancet 8404, ii, 702.
WHO Expert Committee on Rabies (1984) Seventh Report. Techn. Rep. Ser. 709.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Glück, R., Matthieu, J.M., Wegmann, A. et al. Absence of myelin basic protein in an improved purified duck embryo rabies vaccine. Neurochemical Pathology 4, 69–75 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03160186
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03160186