Abstract
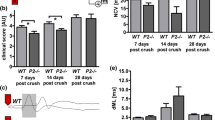
The large myelin-associated glycoprotein isoform (L-MAG) protein and small myelin-associated glycoprotein isoform (S-MAG) protein were demonstrated after sciatic nerve crush injury in mice by an immunoblotting technique using specific antibodies to the L-MAG protein and the S-MAG protein, respectively. Immunoblots indicated a rapid decrease in expression of both isoform proteins in the crushed sciatic nerves to <10% of the control side. By 13 d after injury, L-MAG protein expression had quickly recovered to 100% of the control level. Following the increase in L-MAG protein expression, S-MAG protein expression recovered to 100% by 20 d after injury. It has been reported that the developmental maximum expression of L-MAG protein precedes that of S-MAG protein in both central and peripheral nervous system (CNS and PNS). Our previous work demonstrated that L-MAG mRNA was characteristically induced at the time of most active myelination, including remyelination in the CNS. We here have shown the expression of L-MAG protein precedes that of S-MAG protein during active remyelination in the PNS. This suggests that it plays an important role in the early stage of myelin formation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Edwards A. M., Braun P. E., and Bell J. C. (1989) Phosphorylation of myelin-associated glycoprotein in vivo and in vitro occurs only in the cytoplasmic domain of the large isoform.J. Neurochem. 52, 317–320.
Figlewicz D. A., Wood D. A., and Millar D. B. (1983) In vivo study of demyelination and remyelination following sciatic nerve crush.J. Neurochem. 41, S31.
Fujita N., Sato S., Kurihara T., Inuzuka T., Takahashi Y., and Miyatake T. (1988) Developmentally regulated alternative splicing of brain myelin-associated glycoprotein mRNA is lacking in the quaking mouse.FEBS Lett. 232, 323–327.
Fujita N., Ishiguro H., Sato S., Kurihara T., Kuwano R., Sakimura K., Takahashi Y., and Miyatake T. (1990a) Induction of myelin-associated glycoprotein mRNA in experimental remyelination.Brain Res. 513, 152–155.
Fujita N., Sato S., Ishiguro H., Inuzuka T., Baba H., Kurihara T., Takahashi Y., and Miyatake T. (1990b) The large isoform of myelin-associated glycoprotein is scarcely expressed in the quaking mouse brain.J. Neurochem. 55, 1056–1059.
Gupta S. K., Poduslo J. F., Dunn R., Roder J., and Mezei C. (1990) Myelin-associated glycoprotein gene expression in the presence and absence of schwann cell-axonal contact.Dev. Neurosci. 12, 22–33.
Inuzuka T., Fujita N., Sato S., Baba H., Nakano R., Ishiguro H., and Miyatake T. (1991) Expression of the large myelin-associated glycoprotein isoform during the development in the mouse peripheral nervous system.Brain Res. 562, 173–175.
Laemmli U. K. and Favre M. (1973) Maturation of the head of bacteriophage T4.I. DNA packing events.J. Mol. Biol. 80, 575–600.
Lai C., Brown M. A., Nave K.-A., Noronha A. B., Quarles R. H., Bloom F. E., Milner R. J., and Sutcliffe J. G. (1987) Two forms of 1B236/myelin-associated glycoprotein, a cell adhesion molecule for postnatal neural development, are produced by alternative splicing.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 84, 4337–4341.
Lowry O. H., Rosebrough N. J., Farr A. L., and Randall R. J. (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent.J. Biol. Chem. 193, 265–275.
Mitchell L. S., Griffith I. R., Morrison J. A., Barrie D., Kirkham D., and McPhilemy K. (1990) Expression of myelin protein gene transcripts by schwann cells of regenerating nerve.J. Neurosci. Res. 27, 125–135.
Quarles R. H., Everly J. L., and Brady R. O. (1973) Myelin-associated glycoprotein: a developmental change.Brain Res. 58, 506–509.
Quarles R. H. (1984) Myelin-associated glycoprotein in development and disease.Dev. Neurosci. 6, 285–303.
Towbin H., Staehelin T., and Gordon J. (1979) Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gel to nitrocellulose, sheets: procedure and applications.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 76, 4350–4354.
Willison H. J., Trapp B. D., Bacher J. D., and Quarles R. H. (1988) The expression of myelin-associated glycoprotein in regenerating cat sciatic nerve.Brain Res. 444 10–16.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Inuzuka, T., Sato, S., Fujita, N. et al. Expression of myelin-associated glycoprotein isoforms after sciatic nerve crush injury in mice. Molecular and Chemical Neuropathology 20, 191–196 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03160072
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03160072