Abstract
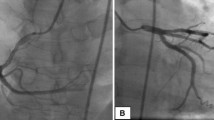
Patients with essential thrombocythemia (ET) are at increased risk of developing arterial thrombosis. We report a case of a 36-year-man with unstable angina in the presence of occlusion of two coronary arteries with insufficient collateral perfusion. We also found essential thrombocythemia in this patient. The patient underwent coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG). Ten days before surgery, the aspirin was replaced by a prophylactic dose of low-molecular-weight heparin. Postoperative follow-up was complicated by pulmonary embolisms and a cardiac tamponade. We conclude that ET is a risk factor for coronary heart disease that should be treated with aspirin. If a patient needs CABG, aspirin should be continued because of the high risk of thromboembolic events in the high-risk ET patients. (Neth Heart J 2010;18:378-80.)


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schafer AI. Thrombocytosis. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:1211-9.
Hehlmann R, Jahn M, Baumann B, Köpcke W. Essential thrombocythemia: clinical characteristics and course of 61 cases. Cancer. 1988; 61:2487-96.
Tefferi A, Fonseca R, Pereira D, Hoagland H. A long-term retrospective study of young women with essential thrombocythemia. Mayo Clin Proc. 2001;76:22.
Watson KV, Key N. Vascular complications of essential thrombocythaemia: A link to cardiovascular risk factors. Br J Haematol. 1993;83:198.
Ruggeri M, Tosetto A, Rodeghiero F, Finazzi G, Barbui T. The management of ‘low risk’ and ‘intermediate risk’ patients with primary thrombocythemia. Br J Haematol. 1999;106:834.
Harrison CN, Campbell PJ, Buck G, Wheatley K, East CL, Bareford D, et al. Hydroxyurea compared with anagrelide in high-risk essential thrombocythemia. N Engl J Med 2005;353:33-45.
Ruggeri M, Rodeghiero F, Tosetto A, Castaman G, Scognamiglio F, Finazzi G, et al.; for the Gruppo Italiano Malattie Ematologiche dell'Adulto (GIMEMA) Chronic Myeloproliferative Diseases Working Party. Postsurgery outcomes in patients with polycythemia vera and essential thrombocythemia: a retrospective survey. Blood. 2008;111:666-71.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
B.E. Schölzel Department of Cardiology, St. Antonius Hospital, PO Box 2500, 3430 EM Nieuwegein, the Netherlands
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schölzel, B.E., Endeman, H., Dewilde, W. et al. Cardiac surgery in a patient with essential thrombocythemia: a case report. NHJL 18, 378–380 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03091797
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03091797