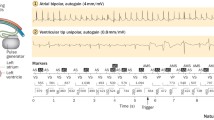
Abstract
The diagnostic programmes of modern pacemakers have increased our knowledge of atrial tachyarrhythmias (ATAs) in chronically paced patients. These programmes also support the evaluation of the effects of pharmacological treatment of ATAs. The success of interruption and/or prevention of ATAs with pacemakers depends strongly on the diagnostic accuracy and the properties of the pacing algorithms, their individual programming and the site and configuration of the pacing leads. Atrial septum pacing can be beneficial in patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation and prolonged P wave duration. Recent large-scale studies on preventive and interruptive atrial pacing of ATAs show modestly positive or no results. Therefore, atrial pacing therapy for ATAs should be considered cautiously, serving as an adjuvant to pharmacological treatment rather than as a primary intervention. This also applies for pacing interventions for ATAs in cardiac resynchronisation therapy. The pacemaker algorithms for the detection of ATAs and atrial lead configuration are crucial for the success of pacemaker-mediated prevention or interruption of ATAs. The success of these interventions is dependant on future improvements of pacemaker technology. (Neth Heart J 2008;16 (suppl 1): S20-S24.)
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Israel CW, Barold SS. Pacemaker systems as implantable cardiac rhythm monitors. Am J Cardio l2001;88:442-5.
de Voogt WG, van Hemel NM, van de Bos AA, Koistinen J, Fast JH. Verification of pacemaker automatic mode switching for the detection of atrial fibrillation and atrial tachycardia with Holter recording. Europace 2006;8:950-61.
Israel CW, Barold SS. Failure of atrial flutter detection by a pacemaker with a dedicated atrial flutter detection algorithm. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol 2002;25:1274-7.
Goethals M, Timmermans W, Geelen P, Backers J, Brugada P. Mode switching failure during atrial flutter: the ‘2:1 lock-in’ phenomenon. Europace 2003;5:95-102.
de Voogt W, van Hemel N, Willems A, Visser J, Chitre Y, Bornzin G, et al. Far-field R-wave reduction with a novel lead design: experimental and human results. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol 2005;28:782-8.
van Hemel NM, Wohlgemuth P, Engbers JG, Lawo T, Nebaznivy J, Taborsky M, et al. Form analysis using digital signal processing reliably discriminates far-field R waves from P waves. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol 2004;27:1615-24.
Guyomar Y, Thomas O, Marquie C, Jarwe M, Klug D, Kacet S, et al. Mechanisms of onset of atrial fibrillation: a multicenter, prospective, pacemaker-based study. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol 2003;26:1336-41.
Waldo AL, Feld GK. Inter-relationships of atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter mechanisms and clinical implications. J Am Coll Cardiol 2008;51:779-86.
Bailin SJ, Adler S, Giudici M. Prevention of chronic atrial fibrillation by pacing in the region of Bachmann's bundle: results of a multicenter randomized trial. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 2001;12:912-7.
Padeletti L, Pieragnoli P, Ciapetti C, Colella A, Musilli N, Porciani MC, et al. Randomized crossover comparison of right atrial appendage pacing versus interatrial septum pacing for prevention of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation in patients with sinus bradycardia. Am Heart J 2001;142:1047-55.
de Voogt WG, Van Mechelen R, Van Den BA, Scheffer M, van Hemel NM, Koistinen J. A technique of lead insertion for low atrial septal pacing. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol 2005;28:639-46.
Padeletti L, Santini M, Boriani G, Botto G, Ricci R, Spampinato A, et al. Duration of P-wave is associated with atrial fibrillation hospitalizations in patients with atrial fibrillation and paced for bradycardia. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol 2007;30:961-9.
Padeletti L, Purerfellner H, Adler SW, Waller TJ, Harvey M, Horvitz L, et al. Combined efficacy of atrial septal lead placement and atrial pacing algorithms for prevention of paroxysmal atrial tachyarrhythmia. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 2003;14:1189-95.
De Voogt W, Van Hemel N, de Vusser P, Mairesse GH, Van Mechelen R, Koistinen J, et al. No evidence of automatic atrial overdrive pacing efficacy on reduction of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Europace 2007;9:798-804.
Lellouche N, De Diego C, Vaseghi M, Buch E, Cesario DA, Mahajan A, et al. Cardiac resynchronization therapy response is associated with shorter duration of atrial fibrillation. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol 2007;30:1363-8.
Padeletti L, Musilli N, Porciani MC, Colella A, Di Biase L, Ricciardi G, et al. Atrial fibrillation and cardiac resynchronization therapy: the MASCOT study. Europace 2004;5(Suppl 1):S49-S54.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Department of Cardiology, St. Lucas Andreas Hospital, Amsterdam, the Netherlands
University Utrecht, Utrecht, the Netherlands
W.G. de Voogt St. Lucas Andreas Hospital, J. Tooropstraat 164, 1061 AE Amsterdam, the Netherlands
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Voogt, W.G., van Hemel, N.M. Clinical application of pacemakers in atrial tachyarrhythmias. NHJL 16, 18–22 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03086200
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03086200