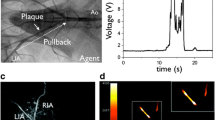
Abstract
There is increasing evidence that presence and location of neovascular vasa vasorum play an important role in atherosclerotic plaque pathogenesis and stability. This paper describes a method to detect vasa vasorum with high contrast and high spatial resolution. It uses second harmonic or subharmonic intravascular ultrasound, in combination with ultrasound contrast agents. The same technology in combination with targeted contrast agents is suited for molecular imaging. The potential for vasa vasorum imaging is illustrated using an atherosclerotic animal model and the potential for molecular imaging is illustrated using phantom experiments.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schoenhagen P, Ziada KM, Vince DG, Nissen SE, Tuzcu EM. Arterial remodeling and coronary artery disease: the concept of “dilated” versus “obstructive” coronary atherosclerosis J Am Coll Cardiol 2001;38:297-306.
Nicholls SJ, Sipahi I, Schoenhagen P, Crowe T, Tuzcu EM, Nissen SE. Application of intravascular ultrasound in anti-atherosclerotic drug development. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2006;5:485-92.
Nissen SE, Yock P. Novel pathophysiological insights and current clinical applications. Intravascular ultrasound. Circulation 2001;103:604-16.
Glaser R, Selzer F, Faxon DP, Laskey WK, Cohen HA, Slater J, et al. Clinical progression of incidental, asymptomatic lesions discovered during culprit vessel coronary intervention. Circulation 2005;111:143-9
Schaar JA, Muller JE, Falk E, Virmani R, Fuster V, Serruys PW, et al. Terminology for high-risk and vulnerable coronary artery plaques – Report of a meeting on the vulnerable plaque. Santorini, Greece, 2003.
Muller JE, Tawakol A, Kathiresan S, Narula J. New opportunities for identification and reduction of coronary risk - Treatment of vulnerable patients, arteries, and plaques. J Am Coll Cardiol 2006;47:Suppl:C2-6.
Virmani R, Burke AP, Farb A, Kolodgie FD. Pathology of the vulnerable plaque. J Am Coll Cardiol 2006;47:C13-8.
Schaar JA, de Korte CL, Mastik F, Strijder C, Pasterkamp G, Boersma E, et al. Characterizing vulnerable plaque features with intravascular elastography. Circulation 2003;108:2636-41.
Nair A, Kuban BD, Tuzcu EM, Schoenhagen P, Nissen SE, Vince DG. Coronary plaque classification with intravascular ultrasound radiofrequency data analysis. Circulation 2002;106:2200-6.
Ultrasound contrast agents: basic principles and clinical applications echocardiography. Goldberg BB, Raichlen JS, Forsberg F (editors). Martin Dunitz. 2001.
de Jong N, Frinking PJA, Buoakaz A, Ten Cate FJ. Detection procedures of ultrasound contrast agents. Ultrasonics 2000;38:87-92.
Gorce JM, Arditi M, Schneider M. Influence of bubble size distribution on the echogenicity of ultrasound contrast agents - A study of SonoVue™. Invest Radiol 2000;35:661-71.
Cachard C, Finet G, Bouakaz A, Tabib A, Francon D, Gimenez G. Ultrasound contrast agents in intravascular echography: An in vitro study. Ultrasound Med Biol 1997;23:705-17.
Goertz DE, Cherin E, Needles A, Karshafian R, Duckett A, Burns PN, et al. High frequency nonlinear b-scan imaging of microbubble contrast agents. IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectr Freq Control 2005;52:65-79.
Goertz DE, Frijlink ME, de Jong N, van der Steen AF. Nonlinear intravascular ultrasound contrast imaging. Ultrasound Med Biol 2006;32:491-502.
Frijlink ME, Goertz DE, van Damme LC, Krams R, van der Steen AFW. Intravascular ultrasound tissue harmonic imaging in vivo. IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectr Freq Control 2006;53:1844-52.
Zamir M, Silver MD. Vasculature in the walls of human coronary arteries. Arch Pathol Lab Med 1985;109:659-62.
Barger AC, Beeuwkes R, Lainey LL, Silverman KJ. Hypothesis: vasa vasorum and neovascularization of coronary arteries. A possible role in the pathophyiology of atherosclerosis. N Engl J Med 1984;310:175-7.
Zhang Y, Cliff WJ, Schoefl GI, Higgins G. Immunohistochemical study of intimal microvessels in coronary atherosclerosis. Am J Pathol 1993;143:164-73.
Kwon HM, Sangiorgi G, Ritman EL, McKenna C, Holmes DR, Schwartz RS, et al. Enhanced coronary vasa vasorum neovascularization in experimental hypercholesterolemia. J Clin Invest 1998;101:1551-6.
Kumamoto M, Nakashimi Y, Sueishi K. Intimal neovascularization in human coronary atherosclerosis- its origin and pathophysiological significance. Hum Pathol 1995;26:450-6.
de Boer OJ, van der Wal AC, Teeling P, et al. Leucocyte recruitment in rupture prone regions of lipid-rich plaques: a prominent role for neovascularization? Cardiovascular Res 1999;41:443-9.
Moulton KS, Vakili K, Zurakowski D, Soliman M, Butterfield C, Sylvin E, et al. Inhibition of plaque neovascularization reduces macrophage accumulation and progression of advanced atherosclerosis. Proc Nat Acad Sciences 2003;100;4736-41.
Kolodgie FD, Gold HK, Burke AP, Fowler DR, Kruth HS, Weber DK, et al. Intraplaque hemorrhage and progression of coronary Atheroma. N Engl J Med 2002;349:2316-25.
Milei J, Parodi JC, Alonso GF, et al. Carotid rupture and intraplaque hemorrhage: Immunophenotype and role of cells involved. Am Heart J 1998;136: 1096-105.
Barger AC, Beeuwkes R. Rupture of vasa vasorum as trigger of acute myocardial infarction. Am J Cardiol 1990;66:G41-3.
Tenaglia AN, Peters KG, Sketch MH, et al. Neovascularization in atherectomy specimens from patients with unstable angina: Implications for pathogenesis of unstable angina. Am Heart J 1998;135:10-4.
Mofidi R, Crotty TB, McCarthy P, et al. Association between plaque instability, angiogenesis and symptomatic carotid occlusive disease. Br J Surg 2001;88:945-50.
Schaar JA, Muller JE, Falk E, Virmani R, Fuster V, Serruys PW, et al. Terminology for high-risk and vulnerable coronary artery plaques. Eur Heart J 2004;25:1077-82.
Moreno PR, Purushothaman R, Fuster V, Echeverri D, Truszczynska H, Sharma SK, et al. Plaque neovascularization is increased in ruptured atherosclerotic lesions of human aorta - Implications for plaque vulnerability. Circulation 2004;110:2032-8.
Jorgensen SM, Demirkaya O, Ritman EL. Three-dimensional imaging of vasculature and parenchyma in intact rodent organs with X-ray micro-CT. Am J Physiol 1998;275:H1103-4.
Herrmann J, Lerman LO, Rodriguez-Porcel M, Holmes DR, Richardson DM, Ritman EL, et al. Coronary vasa vasorum neovascularization precedes epicardial endothelial dysfunction in experimental hypercholesterolemia. Cardiovasc Res 2001;51:762-6.
Kerwin W, Hooker A, Spilker M, et al. Quantitative magnetic resonance imaging analysis of neovasculature volume in carotid atherosclerotic plaque. Circulation 2003;107:851-6.
Feinstein SB. The powerful microbubble: from bench to bedside, from intravascular indicator to therapeutic delivery system, and beyond. Am J Physiol 2004;287:H450-7.
Casscels W, Haasan G, Vasegi MF, et al. Plaque blush, branch location, and calcification are angiographic predictors of progression of mild to moderate coronary stenosis. Am Heart J 2003;145:813-20.
Li W, van der Steen AFW, Lancee CT, Cespedes EI, Bom N. Blood flow imaging and volume flow quantitation with intravascular ultrasound. Ultrasound Med Biol 1998;24:203-14.
Carlier SG, Kakadiaris A, Dib N, et al. Vasa vasorum imaging: a new window to the clinical detection of vulnerable atherosclerotic plaques. Curr Atherosclerosis Reports 2005;7:164-9.
Goertz DE, Frijlink ME, Tempel D, van Damme LC, Krams R, Schaar JA, et al. Contrast harmonic intravascular ultrasound: a feasibility study for vasa vasorum imaging. Invest Radiol 2006;41:631-8.
Villanueva FS, Jankowski RJ, Klibanov AL, Brandenburger GH, Wagner WR. Microbubble targeted to intercellular adhesion molecule-1 bind to activated coronary endothelial cells. Circulation 2004;98:1-5.
Demos SM, Alkan-Onyuksel H, Kane BJ, Ramani K, Nagaraj A, Greene R, et al. In vivo targeting of acoustically reflective liposomes for intravascular and transvascular ultrasonic enhancement. J Am Coll Cardiol 1999; 33:867-75.
Goertz DE, van Wamel A, Frijlink ME, de Jong N, van der Steen AFW. Nonlinear Imaging of Targeted Microbubbles with Intravascular Ultrasound. IEEE Ultrasonics Symp., Rotterdam, 2005:2003-6.
van der Steen AFW, Baldewsing RA, Degertekin FL, Emelianov S, Frijlink ME, Furukawa Y, et al. IVUS beyond the horizon. EuroIntervention 2006;2:132-42.
van der Steen AFW, Goertz D. Kontiki revisited. Eur J Echocardiog. In press 2007.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Biomedical Engineering Department, Erasmus Medical Centre, Rotterdam, the Netherlands and Interuniversity Cardiology Institute of the Netherlands
Biomedical Engineering Department, Erasmus Medical Centre, Rotterdam, the Netherlands
Biomedical Engineering Department, Erasmus Medical Centre, Rotterdam, the Netherlands, Interuniversity Cardiology Institute of the Netherlands and Physics of Fluids, University of Twente, Enschede, the Netherlands
Biomedical Engineering Department, Erasmus Medical Centre, Rotterdam, the Netherlands and Interuniversity Cardiology Institute of the Netherlands
Correspondence to: A.F.W. van der Steen Biomedical Engineering,Thorax Centre Ee 23.02, Erasmus Medical Centre, PO Box 2040, 3000 CA Rotterdam, the Netherlands
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goertz, D.E., Frijlink, M.E., Krams, R. et al. Vasa vasorum and molecular imaging of atherosclerotic plaques using nonlinear contrast intravascular ultrasound. NHJL 15, 77–80 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03085959
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03085959