Abstract
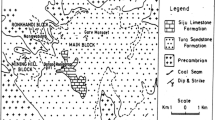
In the Jharia Coalfield, Bihar, dykes and sills of mica lamprophyre are common and have thermally metamorphosed the coal seams in contact into natural coke. Petrological study of the metamorphosed zones of the coal seams in the south-eastern extremity of the coalfield has been carried out. Four petrologically distinct zones designated as natural coke, coked coal, affected coal and unaffected coal are traced, when studied away from the contact. Chemically, a marked increase of volatiles and decrease of ash is recorded away from the seam-igneous contact. Phosphorus content is quite high in the natural coke ash.
The natural coke is characterised by numerous mineral-filled or empty vacuoles and strongly anisotropic, highly-reflecting nature of the fused matrix having physically unaltered fusinite embedded. The fused matrix is of mosaic appearance and consists of ill-defined units varying from one to fifty microns size. In the coked coal, the size and number of vacuoles has considerably reduced, and so also, the anisotropism and mosaic appearance of the matrix, accompanied by an increase in size of the units around fifty microns. The affected coal is distinctly folded, though minutely, and is micro-laminated, the lamination being due to occurrence of vitrinite layers and sheets with interbedaed fusinite, semifusinite, resinite and micrinite. The vesicles occur here and there. Resinite is seen in cleats and as coalesced films migrated along the bedding. The unaffected coal is a typical banded bituminous coal. The natural coke formation is discussed. Graphite is concluded to be absent.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. S. I. R. O...Seventeenth Annual Report, Division of Coal Research, Australia, 1965, p. 11.
Clegg, K. E... “Metamorphism of coal by peridotite dikes in Southern Illinois,”Ill. St. Geol. Sur. Rep. Investg., 1955,178, 18.
Dormans, H. N. M., Huntjens, F. J. and van Krevelen, D. V. “Chemical structure and properties of coal—XX. Composition of the individual macerals (vitrinites, fusinites, micrinites and exinites),”Fuel, 1957,36 (3), 321–39.
Ganju, P. N. and Pant, I. D... “Effects of a mica-peridotite dyke on the Dishergarh seam in the Sodepur Colliery, Raniganj Coalfield,”Proc. Ind. Acad. Sci., 1962,55 (6)B, 307–19.
Hoehne, K... “Neue Spuren von Rotliegend—intrusive vulkanismus in kohlenflozen des Saarkarbons,”Brennstoff-Chemie, 196243 (1), 10–16.
Marshall, C. E... “The alteration of coal seams by the intrusion of some of the igneous dykes in the Northumberland and Durham coalfield,”Trans. Inst. Min. Engg., 1936,91, 235–60.
—————.. “Petrology of Natural coke,”Fuel, 1945,24, 120–26.
Mukherjee, B... “Studies on the petrological and electrical conductivity characters of Jharia—XIV. Seam coal, affected by igneous intrusive, from Keshargarh colliery, Dhanbad District, Bihar,”Jour. Geol. Soc. Ind., 1962,3, 119–24.
Pareek, H. S... “Petrological characteristics of Barakar coal, metamorphosed by lamprophyre sill in Jharia coalfield, India,” in Scientific Communications,Econ. Geol., 1964,59, 926–29.
Sanyal, S. P. .. “Petrology and differential thermal analysis of natural coke from parts of Jharia coalfield, Bihar,” Research papers in petrology,Geol. Sur. Ind., 1964, 159–73.
Stach, E... “Ein geologischer Koks im Saarkarbon,”Zeits Deuts. Geol Gesellsch, 1951,103, 233–37.
—————.. “Mikroskopie Naturalischer Kokse,” in H. Freund,Hand buch der Mikroskopie in der Technik, 1952,2, Tome 1, 411–43’ Umschau-Verlag, Frankfurt.
Taylor, G. H... “The behaviour of the petrological components of coal in carbonization,”Fuel, 1957,36, 221–35.
Ueji, T... “On the microscopical study of thin sections of coal, metamorphosed by intrusives (in Japanese),”Jap. Mem. College of Engg., Kyoto Imp. Univ., 1932,7, 632–37.
—————.. “Intrusive rocks and their influence on coal seams, Chikuho Coalfield (in Japanese),” Ibid., 1936,9, 163–89.
Whitaker, J. W. ..Indian Coals, Their Nature and Composition, Fuel Research Institute, 1949.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by Mr. B. Rama Rao,f.a.sc.
Published with the kind permission of the Director-General, Geological Survey of India.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pareek, H.S. Petrological characteristics of barakar coal seams, metamorphosed by lamprophyre sill in the Jharia coalfield, Bihar. Proc. Indian Acad. Sci. 63, 261–270 (1966). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03052002
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03052002