Abstract
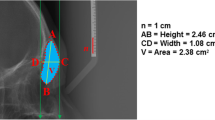
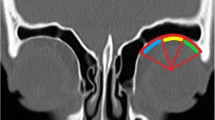
Considering the importance of frontal sinus from the view of otolaryngologist, 200 adults, constituting 100 males and 100 females, xray were studied. Mean frontal sinus size was found to be 14. 81 ± 8. 04 (SD) sq. cm., range O to 32. 7 sq. cm in males and 13. 02 ± 7. 11 (SD) sq. cm — range O to 38. 3 sq. cm. Bilateral asymmetry was found and the mean of bigger frontal sinus was much larger than the average of the smaller ones (highly significant, p < 0. 001.) both in males and females. Absence of one frontal sinus was in 7 percent cases and in 2 percent cases there was bilateral absence.
Similar content being viewed by others
Referencs
Blaney, S. P. A. (1986): An allometric study of the frontal sinus in Gorilla, Pan and Pongo,Folia primatologica,47: 81–96
Blaney, S. P. A. (1990): Why paranasal sinuses?Journal of Laryngology and Otology,104: 690–693.
Diamant, M. (1940): Otitis and pneumatization of mastoid bone.Acta Otolaryngologica, Supplement 41: 10.
Flottes, L., Clerc, P., Rui, R., Devilla, F. (1960): Laphysiologie des sinus. (societe Francaise D’Oto-Rhino-Laryngologie), Libraire Arnette, Paris, Cited from Blanton and Biggs, 1968.
Galen (130-201 AD): De Uau Partium 1x, 2 et. Seq (Kuhn) III P. 169. Translation available by M. Tallmadge May 1968, Cornell University Press.New York.
Kurata, T. (1938): Quoted by Diamant (1940) Lang, J. (1981): Clinical Anatomy of the Head. Barlin: Springer Verlag.
Pickard, B. H. (1987): The complications of sinusitis, in Scott-Borwn’s Otolaryngology, 5th edn Vol. 4, Butterworths, London, pp 206.
Schenck, N. L. (1975): Frontal Sinus disease: III experimental and clinical factors in failure of the frontal Osteoplastic operation.,The Laryngoscope,85: 76–92
Shea, B. T. (1985): On aspects of skull form in African apes and orangutans with implications for hominid evolution. AmericalnJournal of Physical Arthropology. 68: 329–342.
Takahashi, R. (1983): The formation of human paranasal sinuses.Acta Otolaryngologica, Supplement 408.
Vesalius, A. (1542): De Humani Corporis Fabrica, Lib 1, Cap. VI–IX. cited from Wright, P. 168, 1914
Wilson, P. S. and Grocutt, M. (1990): Mucosal thickening on sinus X-rays and its significance.Journal of Laryngology and Otology,104: 694–695
Wright, J. (1914): A history of Laryngology and Rhinology. 2nd edition, Lea and Febigeri:New York.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sen, M.K., Samaddar, R.R. Variation in the size of frontal sinus in adults : A radiographic planimetric study. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 45, 13–15 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03051617
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03051617