Summary
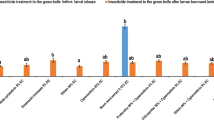
The present studies deal with the bioassay of the persistence of insecticidal spray deposits on the cotton plant usingP. gossypiella as the test insect. Field-infested bolls were the main source for moth culture. Persistence studies were made by releasing moths in cages kept over treated cotton plants in pots. Mortality counts were taken every 24 hours till the residues lost their toxicity completely. Exposure period was 12 hours. A complete record of climatic conditions was maintained for the experimental period. 0·2% DDT and lindane, 0·1% endrin and gusathion persisted for 144, 96, 120 and 96 hours respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brazzel, T. R. and Gaines, J. C.Jour. Eco. Ent., 1959,52 (2), 301.
Ivy, E. E., Brazzel, J. R., Scales, A. L. and Martin, D. F. Ibid., 1955,48 (3), 293–95.
Mistric, W. J. (Jr.) and Martin, D. F. Ibid., 1956,49 (6), 760–63.
Robertson, O. T... Ibid., 1948,41 (1), 120–21.
Siddiqi A. A... Ibid., 1945,17 (2), 241–44.
—————.. Ibid., 1956,18 (1), 45–48.
Sloan, M. J., Rawlins, W. A. and NortonJour. Eco. Ent., 1951,44 (5), 691–700.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Part of a thesis submitted by the principal author to the Faculty of the Post-Graduate School, Indian Agricultural Research Institute, in partial fulfilment of the requirements for the M.Sc. Degree.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haque, M.M., Venkatraman, T.V. Preliminary studies on the bioassay of degree of persistence of insecticidal spray deposits on cotton plant in pink bollworm control. Proc. Indian Acad. Sci. 54, 94–99 (1961). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03051585
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03051585