Abstract
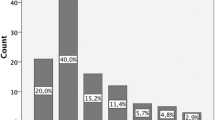
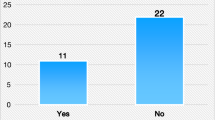
Forty cases of external ear trauma have been studied during a period of three years from Jan ’2001 to December 2004. It was observed that accidental trauma to the auricle may result in laceration, partial or complete loss of auricle. Injury of the tympanic membrane, temporal bone or facio maxillary region may be associated with auricular trauma. All wounds of auricle carry a risk of infection leading to perichondritis. Principles of successful treatment are conservation of tissue and prevention of infection.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brent BD: Ear reconstruction. In Grabb & Smiths Plastic Surgery 5 th Ed., 1997.
Brent BD:Auricular Repair with autogenous Rib Cartilage Grafts. Two decades of experience with 600 cases.Plastic Reconstructive Surgery, Sep90 (3)355–374, 1992.
Bardsley AF, Mercer DM:The Injured ear, a review of 50 cases.Br. J. Plast. Surgery Oct 36 (4)466–69, 1983.
Brandt F.A.: Human bites of the ear: Plastic Reconstructive Surgery 43–130, 1969.
Brown JB, Cannon B, Lischan C, Davis W:Surgical substitutions for losses of the external ear:Surg. Gynaecol. Obst 84:192, 1947
Clemons JE, Connelly MV:Reattachment of an almost totally avulsed ear:Plast. Reconstructive Surg. 65:93, 1980.
Conserve JM:Reconstruction of the auricle Part I, Plast. Recons. Surg. 65:820, 1980
Destro MW, Speranzine MB:Total Reconstruction of the auricle after traumatic amputation.Plast. Reconst. Surgery Nov94 (6)859–64, 1994.
Grabb WC, Dingman Ro:The fate of amputated tissues in the head and neck following replacement:Plastic Reconstructive Surg. 49:28, 1972
Lovejong & Smith: Otology: 5 th Edition Sobt-Brown’s Otolaryngology, 1970
Lee & Mcllwain: Otology — 5 th Edition: Scot Brow’s Otolaryngology, 1985
McDowell F:Successful replantation of a severed half ear:Plast. Reconstructive Surg. 48:281, 1971
M. M. Paparella MD: Year Book of Otolaryngo. Head & Neck Surgery, Page 58, 2001.
Pennington, Sai and Pelly: Otology: 6thEdition Scot Brown’s Otolaryngology, 1980.
Renner, Gregory, Lane, Robert V:Auricular Reconstruction: an update.Current opinion in Otolaryngology and Head & Neck Surgery, Aug12 (4)277–780, 2004.
Selesnick S, Nguyen TP, Eisenman DJ:Surgical treatment of acquired external auditory canal atresia.Am. J. Otol. 19 (2):123–30 (ISSN:0192-9763),1998.
Willer, Ledereich and de Vreis: Otology 6thEdition: Scot Brown’s Otolaryngology, 1992.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, K., Goswami, S.C. & Baruah, D.K. Auricular trauma and its management. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 58, 232–234 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03050826
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03050826