Summary and Conclusions
-
(1)
As shown by the effect of death, resistance of the muscle to alternating current of low frequency is a measure of the permeability of the cell.
-
(2)
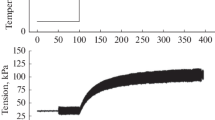
Permeability is high at low and high temperatures; frog muscle if heated beyond 35°C. and mammalian muscle beyond 40°C, is irreparably damaged, the resistance being permanently lowered.
-
(3)
Cations such as potassium, calcium, ammonium, magnesium increase the resistance of the muscle in small concentrations.
-
(4)
Anions such as Cl, Br, I, NO3, SCN, CN increase the resistance of the muscle in small concentrations.
-
(5)
Drugs and narcotics such as adrenaline, caffeine, novocaine, chloral hydrate, ether, chloroform, ethyl alcohol, butyl alcohol, octyl alcohol increase the resistance in small and decrease it in large concentrations.
-
(6)
Inhibition and narcosis are associated with increased resistance or decreased permeability. Increased excitability to ions without is associated with an opposite change. Excitability to electric current is increased with diminished permeability.
-
(7)
For excitation an optimum permeability is necessary.
-
(8)
The resistance of frog skin is higher than that of muscle.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achelis, J. D.Pfluger’ls Arch., 1932, 320, 412.
Blinks, L. R.Annual Rev. Physiol, 1942,1, 4.
Bozzler, E. J. CellComp. Physiol, 1935,6, 217
Bozzler, E.J. Cell. Comp. Physiol., 1935,6, 217.
— and Cole, S. —, 1935,6, 229.
Buchthal, F.Skand. Arch. Physiol, 1934,68, 187.
Duboisson, M.Arch. int. Physiol, 1934,38, 85.
—J. Physiol, 1937,89, 132.
Ebbecke, U.Pfluger’s Arch., 1922, 195, 555.
Fenn, W. O., and Cobb, D.Amer. J. Physiol, 1936, 115, 345.
Gelhorn, E., and Gelhorn, H.Pfluger’s Arch., 1928, 221 247
Gerard, R. W.Annual Rev. Physiol, 1942,4, 329.
Gokhale, S. K., and Singh, I.J. Physiol, in the Press.
Guttman, S. A., and Wilbur, D. T.Amer. Jour. Physiol, 1936, 194, 115.
Heilbrunn, L. V.Outline of General Physiology, London.
Harris, D. T.Proc. Roy. Soc, B, 1925, 399, 110.
Hemingway, A., and Collins, D. A.Amer. J. Physiol, 1932,99, 338.
Hill, A. V.J. Physiol, 1910,40, 190.
Hogben, L., and Gordon, E.J. F.xpt. Biol, 1930,7, 269.
McCIendon, J. F.Amer. J. Physiol, 1912,29, 302.
— —, 1927,82, 585.
—Science, 1936,84, 184.
Nernst, W.Golt. Nachr. Math. Phys. Kl., 1899. Quoted from Hill, A. V.,J. Physiol, 1910,40, 190.
Osterhout, W. J. V.Science, 1912,37, 111.
Ray, G. B., and Rapport, D.,Amer. J. Physiol., 1927, 80, 126.
Rao, M. S., and Singh, I.J. Physiol, 1940, 98, 12.
Rosenbleuth, A., and Cannon, W. B.Amer. J. Physiol, 1936, 414, 116.
Singh, I.J. Phvsiol, 1936,89, 10.
—, 1937,89, 8.
—, 1938a,91, 398.
—, 1938b,92, 62.
—, 1938c,92, 232.
—, 1938d,92, 241.
—, 1938e,94, 1.
—, 1938f,94, 322
—, 1939a,96, 1.
—, 1939b,96, 367.
—, 1940,98, 155.
—, 1940,98, 155.
—Ind. Journ. Med. Res., 1942a,30, 449.
—, 1942b,36, 29.
—Proc. Ind. Acad. Sci., 1943a,17, 13.
—, 1943b,17, 20.
—Curr. Sci., 1943c,12, 56.
—, 1943d,12, 57.
—, 1943e,12, 83.
—Proc. Ind. Acad. Sci., 1943f,17, 143.
—, 1943g,17, 149.
—, 1943h,18, 53.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by Prof. A. Subba Rau,b.a., d.sc. (Lond.),f.r.m.s., f.a.sc.
We wish to thank Dr. R. N. Ghosh of the Physics Department, University of Allahabad, for his help and advice; we also wish to thank the Vice-Chancellor for lending the apparatus needed.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, I., Singh, I. The electrical resistance of unstriated muscle and other tissues and its relation to permeability and excitability. Proc. Indian Acad. Sci. 18, 58–71 (1943). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03049649
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03049649