Summary and Conclusions
-
(1)
Plain muscle is capable of great changes in viscosity. The viscosity of plain muscle is about 100 to 1,000 times that of striated muscle and its movements correspondingly slower.
-
(2)
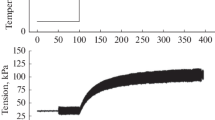
The viscosity of plain muscle increases as a result of tonic contraction, but is decreased during active contraction.
-
(3)
Hydrogen ions increase the viscosity; the optimum pH is 7·8, change on either side increasing the viscosity. The excitability is maximum at this pH.
-
(4)
Substances that decrease the rate of relaxation, increase the viscosity; plain muscle is thus able to keep up tension without expenditure of energy. During active contraction, viscosity decreases to facilitate movement.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hill, A. V.Proc. Roy. Soc., 1926,B 100, 108.
Bayliss, L. E.J. Physiol., 1928,65, 1.
Rao, M. S., and Singh, I., — 1940,98, 12.
Singh, I. —, 1938,92, 383.
Winton, F. R. —, 1937,88, 429.
Singh, I. —, 1938,94, 1.
Bozzler, E. —, 1930,69, 442.
Levin, A., and Wyman, J.Proc. Roy. Soc., 1927,B 101, 218.
Winton, F. R.J. Physiol., 1930,69, 393.
Bouchaert, J. P., Capellen, L., and Blende, J. de —, 1930,69, 473.
Singh, I.Ind. Journ. Med. Res., July 1942,30, 449.
Gasser, H. S., and Hill, A. V.Proc. Roy. Soc., 1924,B 96, 398.
Fenn, W. O., and Marsh, B. S.J. Physiol., 1935,85, 277.
Singh, I. —, 1938,91, 398.
— —, 1938,92, 62.
— —, 1938,92, 241.
— —, 1938,94, 322.
— —, 1939,94, 1.
— —, 1939,96, 367.
— —, 1940,98, 155.
--Ibid., in the Press.
--Ind. Journ. Med. Res., October 1942. In the Press.
--Nature. In the Press.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by Lt.-Col. S. S. Sokhey, i.m.s., f.a.sc.
An erratum to this article is available at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/BF03049911.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, I. The effect of hydrogen ions and tonic contraction on the viscosity of unstriated muscle. Proc. Indian Acad. Sci. 17, 13–19 (1943). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03046187
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03046187