Abstract
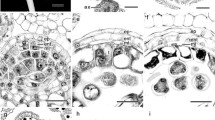
InBlainvillea rhomboidea, Cass. the floral parts arise in acropetalous succession. The archesporium consists of two linear rows. of cells In the fully formed anther there is an epidermis, an endothecium, a middle layer, a tapetum and two linear rows of microspore mother cells. Tapetal cells become binucleate and are of the plasmodial type. Microspore tetrads are isobilateral, tetrahedral and decussate. Exine of the pollen grain is echinate. Shedding is at the three-celled stage as in the majority of Compositae. Endothecium shows faint fibrillar thickenings at the time of anther dehiscence.
Ovules are anatropus, unitegmic and tenuinucellate. A hypodermal archesporial cell directly functions as the megaspore mother cell. Embryo sac development is of the Polygonum type. More than one megaspore in the tetrad show signs of development. Organised embryo sac is six-celled with only two antipodals. A secondary multiplication of nuclei in the antipodal cells results in a variable number of nuclei.
Endosperm is of theab initio cellular type.
Embryogeny conforms to Asterad type.
Fruit wall has a thick layer of tannin cells in the hypodermal layers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
*Afzelius, K... “Embryologische und Zytologische Studdien inSenecio und verwandten Gattungen,”Acta Horti. Bergiani., 1924,8, 123–219.
Bhargava, H. R... “Contributions to the Morphology ofEclipta erecta,”Proc. Ind. Acad. Sci., 1935,1, 325–36.
Davis, G. L... “Embryological studies in compsitae. IV. Sporogenesis, gamete-genesis and embryogeny inBrachycome ciliaris (Labill) LessAust. J. bot.‘ 1964,12, 142–51.
—————.. “The Embryology ofEpaltes australis, Less,”Proc. Linn. Soc. NSW., 1968,93, 184–92.
----- ..Systematic Embryology of Angiosperms London, 1966.
Deshapande, P. K... “Contribution to the embryology ofBidens biternata (B. pilosa),”J. Indian bot. Soc., 1964b,43, 149–57.
*Fagerlind.. “Kritische und rividierende unter suchungen uber das vorkommen des Adoxa (Lillium) Typus.”Acta Horti. Bergiani., 1939,13, 1–49.
Gho h, R. B... “A contribution to the life history ofWedelia calendulacea,”J. Indian bot Soc., 1962,41, 197–206.
Hjelmqvist, H. .. “The embryo sac development inTridax triloba.”Bot. Notiser, 1951, Pp. 180–87.
*Harling, G... “Embryological studies in compositae 1–3,,”Acta. Horti. Bergiani, 1951,16, 1–120.
*—————.. “The embryo sac development inVittadania triloba.”Svensk. bot. Tidsk., 1954,48, 489–96.
Kapil, R. N., and Sethi, S. B... “Gametogenesis and Seed development inAinsliaea aptera.”Phytomorphology, 1962,12, 222–34.
Maheswari Devi, H... “Embryological studies in compositae. III.Gerbera iamesoni,”Proc. Ind. Acad. Sci., 1957,46, 68–74.
—————.. “Embryological studies in compositae. IVHeliantheae.”Proc. Ind. Acad. Sci., 1963,58, 274–90.
*Martinoli, G... “Contributoal embryologia delle Asteraceae—I–III,”Nuovo. Gior. Bot. Ital, N.S., 1939,46, 259–98.
Maheswari, P. and Roy, K... “The embryo sac and embryo ofTridax procumbens.”Phytomorphology, 1952,2, 245–53.
Misra, S... “Floral morphology of compositae. I. The flower and gametophytes ofFlaveria repanda.”J. Indian bot. Soc., 1957,36, 503–12.
Schnarf Karl. .. “Vergleichende Embryologie der Angiospermen,” Berlin, 1931.
Sundara Rajan, S... “Embryological studies in compositae—Floral morphology, Sporogenesis and Gametogenesis inEmilia sonchifolia,”Curr. Sci., 1968a,37, 26–28.
—————.. “Observations on Female Gametogenesis inSynedrella nodiflora,” Ibid., 1968b,37, 385–86.
Venkateswarulu, J. and Maheswari Devi, H. “Embryological studies in compositae. II.Helenieae,”Proc. Nat. Inst. Sci. India, 1955b,21, 149–61.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by Prof. L. Narayana Rao,f.a.sc.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sundara Rajan, S. Embryological studies in compositae. Proc. Indian Acad. Sci. 75, 167–176 (1972). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03045526
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03045526