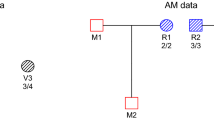
Abstract
During clearing work in the loft of a two-family-house the corpses of two neonates were found wrapped in textile material. Both corpses were strongly mummified so that a postmortem interval of some years could be assumed. The police investigations to clarify the parentage included persons which had lived in this house during the last 10 years. Altogether six persons were involved, four women and two men. A comparative DNA analysis using 7 STR systems (ACTBP2, TH01, CD4, VWA, FGA, FES, F13B) resulted in a parentage probability for one man and one woman of W=99.993% for both children. When confronted with this results a confession was made for the 5-and 6-year-old offences.
Zusammenfassung
Zwei Neugeborenenleichen wurden in Tücher eingewickelt bei Aufräumarbeiten auf dem Dachboden eines Zweifamilienhauses gefunden. Beide Leichen befanden sich in einem stark mumifizierten Zustand, so daß von einer mehrjährigen postmortalen Liegezeit auszugehen war. Die polizeiliche Ermittlungsarbeit zur Klärung der Elternschaft erstreckte sich auf Personen, die in den vergangenen zehn Jahren in dem Haus wohnten. Insgesamt wurde ein engerer Kreis von sechs Personen ermittelt, vier Frauen und zwei Männer. Die vergleichende DNA-Untersuchung mit sieben STR-Systemen (ACTBP2, TH01, VWA, CD4, FGA, FES, F13B) ergab für eine Mann-Frau-Kombination aus den sechs untersuchten Personen eine Elternschaftswahrscheinlichkeit für beide Kinder von 99,993%. Erst mit diesem Ergebnis konfrontiert, erfolgte ein Geständnis der fünf bzw. sechs Jahre zurückliegenden Tathandlungen.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Alper B, Meyer E, Schürenkamp M, Brinkmann B (1995) HumFES/FPS and HumF13B: Turkish and German population data. Int J Legal Med 108:93–95
Budowle B, Chakraborty R, Giusti AM, Eisenberg AJ, Allen RC (1991) Analysis of the variable number of tandem repeats locus D1S80 by the polymerase chain reaction, followed by high resolution polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Am J Hum Genet 48:137–144
Gill P, Ivanov PI, Kimpton C, Piercy R, Benson N, Tully G, Evett I, Hagelberg E, Sullivan K (1994) Identification of the remains of the Romanov family by DNA analysis. Nat Genet 6:130–135
Günther S, Herold J, Patzelt D (1995) Extraction of high quality DNA from bloodstains using diatoms. Int J Legal Med 108:154–156
Hochmeister M, Budowle B, Borer UV, Eggmann U, Comey CT, Dirnhofer R (1991) Typing of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) extracted from compact bone from human remains. J Forensic Sci 36:1649–1661
Höss M, Pääbo S (1993) DNA extraction from pleistocene bones by silica-based purification method. Nucleic Acids Res 21:3913–3914
Möller A, Wiegand P, Grüschow C, Seuchter SA, Baur MP, Brinkmann B (1994) Population data and forensic efficiency values for the microsatellite systems Hum VWA. HumMBP and HumFABP. Int J Legal Med 106:183–189
Pääbo S (1989) Ancient DNA: extraction, characterization, molecular cloning, and enzymatic amplification. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:1939–1943
Wiegand P, Bajanowski T, Brinkmann B (1992) Möglichkeiten der DNA-Typisierung an exhumierten Leichengeweben. Rechtsmedizin: 3:10–13
Wiegand P, Bajanowski T, Brinkmann B (1993a) DNA typing of debris from fingernails. Int J Legal Med: 106:81–84
Wiegand P, Budowle B, Rand S, Brinkmann B (1993b) Forensic validation of the STR systems SE33 and TC11. Int J Legal Med 105:315–320
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wiegand, P., Kleiber, M. DNA-Typisierung von mumifizierten Neugeborenen zur Feststellung der Elternschaft. Rechtsmedizin 7, 95–97 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03042366
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03042366