Abstract
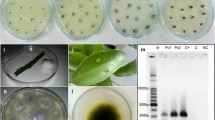
Several species ofColletotrichum occur in maturing bark ofCoffea arabica branches in Kenya. TheColletotrichum population inhabits the bark tissue external to the developing phellogens in the cortex. TheColletotrichum species are unable to invade green bark tissue, where the phellogen has not yet been differentiated, while colonization ceases on the phelloderm of the true bark.
Only one of theColletotrichum species discussed in this paper,C. coffeanum, can infect green coffee berries. Shortly after the initiation of the first phellogen in the cortex the parasite is in a small area in the bark. It cannot be found in bark tissues where more phellogens have been formed and where the colour of the bark has changed from yellow-green to brown or black.
From the bark ofC. liberica trees, grown in Kenya, andC. arabica cv. ’lsBourbon’, grown in greenhouses in the Netherlands one of the saprophytic components of theColletotrichum population could be isolated.
It was impossible to induce ddie-back symptoms or mere infection by inoculation of green internodes even after wounding of live branches ofC. arabica with any of theColletotrichum components colonizing the bark. It is suggested that die-back systems of coffee in Kenya are primarily caused by unfavourable growing conditions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bock, K. R., 1956. Investigations on the coffee berry disease. Laboratory studies. E. Afr. agric. J. 22: 97–103.
Bock, K. R., 1963. The control of coffee berry disease in Kenya. Emp. J. exp. Agric. 31: 97–107.
Butler, E. J., 1918. Fungi and diseases in plants. Calcutta.
Butt, D. J. & Butters, B. 1966. The control of coffee berry disease in Uganda. Proc. 1st. Spec. Meeting on Coffee Research, E. Afr. Common Serv. Org., Nairobi, Kenya.
Gibbs, J. N., 1969. Inoculum sources for coffee berry disease. Ann. appl. Biol. 64: 515–522.
Gray, P., 1954. The Microtomist’s formulary and guide. Blackiston Co. Inc.
Griffiths, E. & Gibbs, J. N., 1969. Early season sprays for the control of coffee berry disease. Ann. appl. Biol. 64: 523–532.
Gutierrez, L. H. de, 1954. Muerte descendente causada porColletotrichum en las plantas de Café en el almacigo y su combate por medio de aspersion en Turrialba, Costa-Rica. Turrialba 4: 115–123.
Hindorf, H., 1970.Colletotrichum spp. isolated fromCoffea arabica L. in Kenya. (in press).
Macdonald, J., 1926. A preliminary account of a disease of green coffee berries in Kenya Colony. Trans. Br. mycol. Soc. 11: 145–154.
Macdonald, J., 1937. Coffee in Kenya. Diseases of coffee. Dep. Agric., Kenya: 151–164.
Meiffren, M., 1957. Les Maladies du Caféier en Côte d’Ivoire. Centre. Rech. agron. Bingerville: 67–72.
Mendes da Ponte, A., 1966. Spraying of Arabica coffee with calcium superphosphates for the control of coffee berry disease normally attributed toColletotrichum coffeanum Noack. Kenya Coff. 31: 21–22.
Mulder, D. & Hocking, D., 1967. Hypothesis to explain to explain the uneven distribution of coffee berry disease in areas of endemic occurrence. Meded. Rijksfac. Landb Wet. Gent 32: 729–734.
Muller, R. A., 1964. L’anthracnose des baies du caféier d’Arabie (Coffea arabica), due àColletotrichum coffeanum Noack, au Cameroun. I.F.C.C. Bull. no. 6.
Nicholls, W., 1969. The progress of bark formation in Arabica Coffee. Kenya Coff. 34: 429–434.
Noack, D., 1901. Die Krankheiten des Kaffeebaumes in Brasilien. III.Colletotrichum coffeanum n.sp. Z. Pfl. Krankh. PflPath. PflSchutz 11: 202.
Nutman, F. J. & Roberts, F. M. 1960. Investigations on a disease ofCoffea arabica caused by a form ofColletotrichum coffeanum Noack. I. Some factors affecting infection by the pathogen. Trans. Br. mycol. Soc. 43: 489–505.
Nutman, F. J. & Roberts, F. M., 1961. Investigations on a disease ofCoffea arabica caused by a form ofColletotrichum coffeanum Noack. III. The relation between infection of bearing wood and disease incidence. Trans. Br. mycol. Soc. 44: 511–521.
Nutman, F. J. & Roberts, F. M. 1969. Seasonal variations in the sporulating capacity of the fungus causing coffee berry disease. Ann. appl. Biol. 64: 85–99.
Rayner, R. W., 1948. Latent infection inCoffea arabica L. Nature, Lond. 161: 245–246.
Rayner, R. W., 1952. Coffee berry disease — A survey of investigations carried out up to 1950. E. Afr. agric. J. 17: 130–158.
Saccas, A. M. & Charpentier, J. 1969. L’anthracnose des caféiers Robusta et Excelsa, due àColletotrichum coffeanum Noack, en République Centra-africaine. I.F.C.C. Bull. no. 9.
Small, W., 1926. On the occurrences of a species ofColletotrichum. Trans. Br. mycol. Soc., 11: 122–137.
Thorold, C. A., 1945. Elgon die-back disease of Coffee. E. Afr. agric. J. 10: 198–206.
Vermeulen, H., 1968. Screening fungicides, for the control of coffee berry disease in Kenya. Expl Agric. 4: 255–261.
Vermeulen, H., 1970. Coffee berry disease in Kenya. II. The role ofGlomerella cingulata in theColletotrichum population, colonizing the bark ofCoffea arabica. Neth. J. Pl. Path. 76: 285–292.
Wallis, J. A. N. & Firman, I. D. 1965. Spraying Arabica coffee for the control of coffee berry disease. Ann. appl. Biol. 55: 139–148.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vermeulen, H. Coffee berry disease in Kenya. I. Colletotrichum spp. colonizing the bark of Coffea arabica. Neth. J. Pl. Path. 76, 277–284 (1970). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03041357
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03041357