Abstract
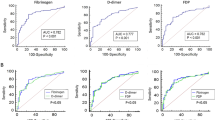
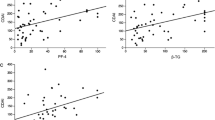
Pathological roles of coagulation and fibrinolytic system are suggested in the progressive and destructive articular lesions of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). In the present study, we simultaneously and serially determined recently available molecular markers of coagulation (thrombin-antithrombin III complex; TAT) and fibrinolysis/fibrinogenolysis [fibrin/fibrinogen degradation products (FDP),d-dimer and FDP-E], and compared their circulating levels with conventional indicators for the disease activity of RA in 31 patients. Either TAT,d-dimer or FDP-E levels well correlated with Lansbury activity index (LAI), erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and C-reactive protein (CRP) levels. Compared with CRP levels, these hemostatic markers more strongly associated with LAI. In addition, the molecular marker levels correlated with each other in RA patients. The hemostatic markers were further determined on at least two different occasions in 14 RA patients. Percentage changes of thed-dimer level significantly associated with those of LAI, as observed between LAI and ESR or CRP levels. Our results clearly indicate excessive coagulation and fibrinolysis in active RA patients. Among the molecular markers determined,d-dimer was considered to be especially useful as a clinical indicator for disease activity of RA.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ronday HK, Smith HH, Van Muijen GNPet al.: Difference in expression of the plasminogen activation system in synovial tissue of patients with rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis.Br J Rheumatol 35: 416–423, 1996.
Gabazza EC, Taguchi O, Yamakami Tet al.: Correlation between clotting and collagen metabolism markers in rheumatoid arthritis.Thromb Haemostas 71: 199–202, 1994.
Lau CS, McLaren M, Hanslip Jet al.: Abnormal plasma fibrinolysis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and impaired endothelial fibrinolytic response in those complicated by vasculitis.Ann Rheum Dis 52: 643–649, 1993.
Motohashi Y, Nakazawa T, Kojima A: Analysis of blood coagulation and fibrinolysis in rheumatoid arthritis using the urokinase activated thromboelastography.Ryumachi 32: 123–130, 1992 (in Japanese).
Weinberg JB, Pippen AMM, Greenberg CS: Extravascular fibrin formation and dissolution in synovial tissue of patients with osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Rheum 34: 996–1005, 1991.
Kawakami M, Kawagoe M, Harigai Met al.: Elevated plasma levels of α2-plasmin inhibitor-plasmin complex in patients with rheumatic diseases.Arthritis Rheum 32: 1427–1433, 1989.
Conn DL, McDuffie FC, Kazmier FJet al.: Coagulation abnormalities in rheumatoid disease.Arthritis Rheum 19: 1237–1243, 1976.
Inoh M, Tokuda M, Kiuchi Het al.: Evaluating systemic lupus erythematosus disease activity using molecular markers of hemostasis.Arthritis Rheum 39: 287–291, 1996.
Inamo Y, Pemberton S, Tuddenham EGDet al.: Increase of activated factor VIIa and haemostatic molecular markers in juvenile chronic arthritis.Br J Rheumatol 34: 466–469, 1995.
Beckham JC, Caldwell DS, Peterson BLet al.: Disease severity in rheumatoid arthritis: relationships of plasma tumor necrosis factor-α, soluble interleukin 2-receptor, soluble CD4/CD8 ratio, neopterin, and fibrind-dimer to traditional severity and functional measures,J Clin Invest 12: 353–361, 1992.
Arnett FC, Adworthy SM, Bloch DAet al.: The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Rheum 31: 315–324, 1988.
Steinbroker O, Traeger CH, Batterman RC: Therapeutic criteria in rheumatoid arthritis.J Am Med Ass 140: 659–662, 1949.
Lansbury J: Methods for evaluating rheumatoid arthritis. InArthritis and Allied Conditions, 7th edn (Hollander JL, McCarty DJ, Eds), pp. 269–291. Lea and Febiger, Philadelphia, 1966.
Pelzer H, Schwarz A, Heimburger N: Determination of human thrombin-antithrombin III complex in plasma with an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.Thromb Haemostas 59: 101–106, 1988.
Elms MJ, Bunce IH, Bundesen PGet al.: Measurement of crosslinked fibrin degradation products —an immunoassay using monoclonal antibodies.Thromb Haemostas 50: 591–594, 1983.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Ichikawa, Y., Hoshina, Y., Horiki, T. et al. Molecular markers of coagulation and fibrinolysis as indicators for the disease activity of rheumatoid arthritis. Japanese Journal of Rheumatology 7, 173–181 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03041239
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03041239