Abstract
Aim
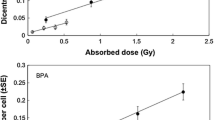
Further experiments were performed to explain a difference in chromosomal aberration yield found between samples cultivated immediately after fission neutron irradiation and samples which were cultivated with 96 h delay after irradiation.
Material and Method
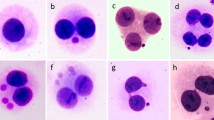
Human peripheral blood samples were irradiated in mixed fission neutron/gamma field (1800 s) and biological effect assessed in the mean of analysis of unstable chromosome aberrations with a time delay in culturing cells of 12, 24, 48, and 96 h. Additional measurements were performed on irradiated and blank blood samples with the aim to detect any increase in α and β activity after fission neutron irradiation. No difference was found. Results were compared to theoretically calculated values of the α and β activity released from natural radioactive isotopes.
Result and Conclusion
As a conclusion it is shown that in our experimental conditions the secondary effects resulting from nuclear transformations of natural or induced radioactive isotopes, recoil reactions and accompanying α, β, and γ radiation are not the reason for the increase observed in chromosomal aberration yield in blood samples cultured with a time delay of at least 24 hours.
Zusammenfassung
Ziel
Um Differenzen in der Chromosomaberration zu erkennen, wurden weitere Experimente durchgeführt.
Material und Methode
Es wurden zwei Kulturen angelegt: unmittelbar nach der Bestrahlung mit Spaltneutronen und 96 Stunden nach der Bestrahlung. Die Proben von menschlichem peripherem Blut wurden in einem Mischfeld aus Neutronen-/Gammastrahlen für 1800 s bestrahlt und die biologischen Strahleneffekte mit Hilfe der instabilen Chromosomaberration nach einer Lagerung von 12, 24, 48 und 96 Stunden untersucht. Messungen an bestrahltem und nichtbestrahltem Blut zeigten keinen Anstieg der α- und β-Aktivität. Die Resultate wurden mit den theoretisch berechneten α- und β-Aktivitäten der natürlichen Isotopen verglichen.
Ergebnis und Schlußfolgerung
Das Ergebnis der Experimente zeigte, daß Sekundäreffekte, die aus der Kernumwandlung von natürlichen oder induzierten radioaktiven Stoffen resultieren, und die begleitende α- β- und γ-Strahlung nicht die Ursache für das beobachtete Ansteigen der Chromosomaberration in Blutproben, die nach mindestens 24 Stunden kultiviert wurden, sind.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Balasem, A., H. A. Al-Jobouri, A. S. Ali, J. Abdul-Khaliq: Radiation-induced chromosomal aberrations in simulated internal contamination with radioactive caesium. Radiat. Prot. Dosim 42 (1992), 323–326.
Balzer-Kubiczek, E. K., G. H. Harrison: Lack of dose rate modification (0.0049 vs. 0.12 Gy/min) of fission-neutron-induced neoplastic transformation in C3H/10T1/2 cells. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 59 (1991), 1017–1026.
Brenner, D. J., E. J. Hall: The inverse dose-rate effect for oncogenic transformations by neutrons and charged particles: a plausible interpretation consistent with published data. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 58 (1990). 745–758.
Browne, E., R. B. Firestone: Table of radiactive isotopes. Wiley & Sons Inc., New York, 1986, p 32/2 and 35.
Eisenbud, M. Environmental radioactivity, from natural, industrial and military sources, Academic Press, Inc., Orlando, Florida 1987.
Elkind M. M.: Enhanced neoplastic transformation due to protrected exposure of fission-spectrum neutrons: biophysical model. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 59 (1991), 1467–1474.
Erdtmann, G.: Neutron activation tables. Verlag Chemie, New York 1976, p. 29 und 30.
Fajgelj, A., D. Horvat, B. Pucelj: Chromosome aberrations induced in human lymphocytes by U-235 fission neutrons: II. Evaluation of the effect of the induced Na-24 activity on the chromosomal aberration yield. Strahlenther. Onkol. 168 (1992), 406–411.
Fajgelj A, A. Lakoski, D. Horvat, I. Remec, J. Škrk, P. Stegnar: Chromosome aberrations induced in human lymphocytes by U-235 fission neutrons: I. Irradiation of human blood samples in the “dry cell” of the TRIGA Mark II nuclear reactor. Strahlenther. Onkol. 167 (1991), 661–666.
Fajgelj, A., J. Rant, D. Kavšek, A. Trkov, J. Škrk: An improved set-up for fission neutron irradiation in the “dry cell” of the TRIGA Mark II reactor in Ljubljana. Proc. of the Nuclear Society of Slovenia Annual Meeting, Rogaška Slatina (Slovenia), September, 1994.
Hill, C. K., F. M. Buonaguro, C. P. Myers, A. Han, E. E. Elkind: Fission-spectrum neutrons at reduced dose rates enhanced neoplastic transformation. Nature 298 (1985), 67–69.
Holmberg, K., A. M. Meijer, G. Auer, B. Lambert: Delayed chromosomal instability in human T-lymphocyte clones exposed to ionizing radiation. 10th Congress of Radiation Research, Würzburg, Germany 27.8,-1.9. 1995.
International Atomic Energy Agency: Biological domestry chromosomal aberration analysis for dose assessment IAEA Technical Report Series No. 260, Vienna 1986.
Iyengar, G. V., W. E. Kollmer, H. J. Bowen: The elemental composition of human tissue and body fluids: a compilation of values for adults. Verlag Chemie, Weinheim 1978.
Seelemann-Eggebert, W. G., Pfenning, H. Munzel, H. Klewe-Nebenius: Chart of the nuclides, 5th ed., Kernforschungs-Zentrum Karlsruhe GmbH 1981.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fajgelj, A., Horvat, D. & Škrk, J. Chromosome aberrations induced in human lymphocytes by U-235 fission neutrons. Strahlenther. Onkol. 173, 91–97 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03038928
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03038928