Abstract
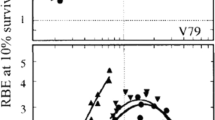
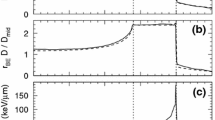
A new treatment planning program was developed for the heavy ion therapy facility at GSI, which is tailored to the special needs for an active beam delivery using a magnetic raster scanner. It also includes a biological model for the estimation of biological effective dose for carbon ions and realizes a fully biological treatment planning. Biological effective dose distributions and RBE maps can be displayed and assessed from the graphical user interface.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Haberer T, Becher W, Schardt D, et al. Magnetic scanning system for heavy ion therapy. Nucl Instr Meth 1993;A330:296–305.
Krämer M, Jäkel O. Therapy planning for heavy ion irradiation. In: Amaldi U, Larsson B, Lemoigne Y, Eds. Advances in Hadrontherapy. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1997:351–58.
Jäkel O, Krämer M. Treatment planning for heavy ion irradiation. Physica Medica 1998;XIV S.1:52–62.
Jäkel O, Krämer M, Hartmann GH, et al. Treatment planning for the heavy ion facility at GSI. Strahlenther Onkol 1999, this issue.
Tsuji H, Miyamoto T, Mizoe J, et al. A. Phase I/II dose escalation study with carbon ions at NIRS. Physica Medica 1998;XIV S.1:70–5.
Kraft G. RBE and its interpretation. Strahlenther Onkol 1999, this issue.
Scholz M, Kraft G. Track structure and the calculation of biological effects of heavy charged particles. Adv Space Res 1996;18:5–14.
Scholz M, Kellerer AM, Kraft-Weyrather W, et al. Computation of cell survival in heavy ion beams for therapy. Radiat Environ Biophys 1997; 36:59–66.
Haberer T. Entwicklung eines magnetischen Strahlführungssystems zur tumorkonformen Strahlentherapie mit schweren geladenen Teilchen. In: GSI, Ed. GSI-Report GSI-94-09. Darmstadt, 1994.
Heinrich W, Wiegel B, Kraft G. ß. Zeff, dE/dx, range and restricted energy loss of heavy ions in the region 1–1000 MeV/u. In: GSI, Ed. GSI-Report GSI-91-30. Darmstadt, 1991.
Gademann G, Schlegel W, Bürkelbach J, et al. Dreidimensionale Bestrahlungsplanung— Untersuchungen zur klinischen Integration. Strahlenther Onkol 1993;169:159–167.
Bendl R. Virtuelle Therapiesimulation. In: Schlegel W, Bortfeld T, Stein J., Eds. Dreidimensionale Strahlentherapieplanung. Heidelberg: DKFZ, 1995:31–42.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jäkel, O., Debus, J., Krämer, M. et al. Treatment planning for light ions: How to take into account Relative Biological Effectivness (RBE). Strahlenther Onkol 175 (Suppl 2), 12–14 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03038877
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03038877