Abstract
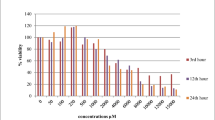
It is well-known that fumonisin B1 (FB1) stimulates apoptosis in a variety of cell types and tissues but the apoptotic potential of other fumonisins and fumonisin metabolites has not been investigated. In our studies we exposed human proximal tubule-derived cells (IHKE cells) to FB1, fumonisin B2 (FB2), hydrolyzed fumonisin B1 (HFB1) and N-palmitoyl-hydrolyzed fumonisin B1 (N-Pal-HFB1) and investigated caspase 3 activation and DNA fragmentation. Only exposure to 10 μmol/L FB1 for 24h led to a significantly increased activity of caspase 3 and to DNA fragmentation. All other compounds tested did not show any significant activation of caspase 3 activity. Further we examined wether a sphinganine accumulation is correlated with the induction of apoptosis in IHKE cells. Therefore we developed a liquid chromato-graphy/electrospray ionization-tandem-mass spectrometry(HPLC-MS/MS)-method using phytosphingosine as an internal standard to determine sphinganine- and sphingosine concentrations in incubated IHKE cells. Whereas a significant increase of sphinganine was observed with all substrates, sphingosine levels remained unchanged. This shows that FB1 exposure leads to apoptosis in a sphinganine-independent mechanism.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Merrill AH, Liotta DC, Riley RT (1996) Fumonisins: Naturally occurring inhibitors of ceramide synthase. Trends in Cell Biology 6: 218–223.
Tolleson WH, Dooley KL, Sheldon WG, Thurman J, Bucci TJ, Howard PC (1996) The mycotoxin fumonisin induces apoptosis in cultured human cells and in livers and kidneys of rats. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 392: 237–250.
Humpf H-U, Schmelz EM, Meredith FI, Vesper H, Vales TR, Wang E, Menaldino DS, Liotta DC, Merrill AH (1998) Acylation of naturally occurring and synthetic 1-deoxysphinganines by ceramide synthase — Formation of N-palmitoyl-aminopentol produces a toxic metabolite of hydrolyzed fumonisin, AP(1), and a new category of ceramide synthase inhibitor. J. Biol. Chem. 273: 19060–19064.
Tveito G, Hansteen I, Dalen H, Haugen A, (1989) Immortalization of normal human kidney epithelial cells by nickel (II). Cancer Res. 49: 1829–1835.
Tolleson WH, Couch L, Melchior WB, Jenkins GR, Muskhelishvili M, Muskhelishvili L, McGarrity LJ, Domon O, Morris SM, Howard PC (1999) Fumonisin B1 induces apoptosis in cultured human keratinocytes through sphinganinine accumulation and ceramide depletion. Int. J. Onc. 14: 833–843.
Schmelz EM, Dombrink-Kurtzman MA, Roberts PC, Kozutsumi Y, Kawasaki T, Merrill AH (1998) Induction of apoptosis by fumonisin B1 in HT29 Cells is mediated by accumulation of endogenous free shingoid bases. Tox. Appl. Pharm. 148: 252–260.
Hartl M, Humpf H-U (1999) Simultaneous determination of fumonisin B1 and hydrolized fumonisin B1 in corn products by liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 47: 5078–5083.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seefelder, W., Humpf, HU., Schwerdt, G. et al. Induction of apoptosis in cultured human proximal tubule cells by fumonisins and fumonisin metabolites. Mycotox Res 17 (Suppl 1), 107–111 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03036723
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03036723