Abstract
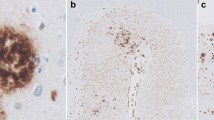
Apolipoprotein J (apoJ), also known as clusterin and SP-40,40, binds soluble beta-amyloid (Aβ and is up-regulated in the Alzheimer’s disease (AD) brain. In the present study we classified apoJ-immunopositive Aβ deposits in AD temporal cortex, and found apoJ-immunoreactive plaques were often associated with dystrophic neurites. Quantitative immunohistochemical analysis of five AD brains showed that 29% of Aβ deposited in the parenchyma was associated with apoJ. Of Aβ deposits with apoJ immunopositivity, 71% were associated with phospho-tau-positive dystrophic neurites in the surrounding tissue. Conversely, 64% of phospho-tau-labeled neuritic deposits were labeled with apoJ. ApoJ was found at the core of these deposits, and co-localized with the amyloid staining agent thioflavine-S. To test the direct effects of apoJ on tau metabolism, we treated cells in culture with apoJ-containing conditioned media, and we injected apoJ-containing media into the rat hippocampus. Using both systems, we observed increases in levels of tau and phosphorylated tau. Our findings demonstrate that apoJ immunopositivity strongly correlates with the presence of amyloid and associated neuritic dystrophy in the neuropil of AD temporal cortex, and supports a model where extracellular apoJ facilitates the conversion of diffuse Aβ deposits into amyloid and enhances tau phosphorylation in neurites surrounding these plaques.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alonzo NC, BT Hyman, GW Rebeck and SM Greenberg (1999) Progression of cerebral amyloid angiopathy: accumulation of amyloid-ß40 in affected vessels.J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 57, 353–359.
Augustinack JC, A Schneider, EM Mandelkow and BT Hyman (2002) Specific tau phosphorylation sites correlate with severity of neuronal cytopathology in Alzheimer’s disease.Acta Neuropathol. 103, 26–35.
Bales KR, T Verina, DJ Cummins, Y Du, RC Dodel, J Saura, CE Fishman, CA DeLong, P Piccardo, V Petegnief, B Ghetti and SM Paul (1999) Apolipoprotein E is essential for amyloid deposition in the APPV717F transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96, 15233–15238.
Boggs LN, KS Fuson, M Baez, L Churgay, D McClure, G Becker and PC May (1996) Clusterin (Apo J) protects againstin vitro amyloid-beta(1-40) neurotoxicity.J. Neurochem. 67, 1324–1327.
Burns MP, WJ Noble, V Olm, K Gaynor, E Casey, J LaFrancois, L Wang and K Duff (2003) Co-localization of cholesterol, apolipoprotein E and fibrillar Aß in amyloid plaques.Mol. Brain Res. 110, 119–125.
Cho HS, BT Hyman, SM Greenberg and GW Rebeck (2001), Quantification of apoE domains in Alzheimer disease brain suggests a role for apoE in Aß aggregation.J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 60, 342–349.
Choi-Miura NH, Y Ihara, K Fukuchi, M Takeda, Y Nakano, T Tobe and M Tomita (1992), SP-40,40 is a constituent of Alzheimer’s amyloid.Acta Neuropathol. 83, 260–264.
Cruz L, B Urbanc, SV Buldyrev, R Christie, T Gómez-Isla, S Havlin, M McNamara, HE Stanley and BT Hyman (1997) Aggregation and disaggregation of senile plaques in Alzheimer disease.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94, 7612–7616.
Cummings BJ, CJ Pike, R Shankle and CW Cotman (1996) Beta-amyloid deposition and other measures of neuropathology predict cognitive status in Alzheimer’s disease.Neurobiol. Aging 17, 921–933.
DeMattos RB, MA O’Dell, M Parsadanian, JW Taylor, JAK Harmony, KR Bales, SM Paul, BJ Aronow and DM Holtzman (2002) Clusterin promotes amyloid plaque formation and is critical for neuritic toxicity in a mouse model for Alzheimer’s disease.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99, 10843–10848.
Dickson DW, HA Crystal, C Bevona, W Honer, I Vincent and P Davies (1995) Correlations of synaptic and pathological markers with cognition of the elderly.Neurobiol. Aging 16, 285–304.
Ghiso J, E Matsubara, A Koudinov, NH Choi-Miura, M Tomita, T Wisniewski and B Frangione (1993) The cerebrospinal fluid soluble form of Alzheimer’s amyloid beta is complexed to SP40,40 (apolipoprotein J), an inhibitor of the complement membrane attack complex.Biochem. J. 293, 27–30.
Giannakopoulos P, E Kovari E, LE French, I Viard, PR Hof and C Bouras (1998) Possible neuroprotective role of clusterin in Alzheimer disease: a quantitative immunocytochemical study.Acta Neuropathol. 95, 387–394.
Gómez-Isla T, HL West, GW Rebeck, SD Harr, JH Growdon, JJ Locascio, TT Perls, LA Lipsitz and BT Hyman (1996) Clinical and pathological correlates of apolipoprotein E epsilon-4 in Alzheimer’s disease.Ann. Neurol. 39, 62–70.
Hammad SM, S Ranganathan, E Loukinova, WO Twal and WS Argraves (1997) Interaction of apolipoprotein J-amyloid beta-peptide complex with low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein-2/megalin. A mechanism to prevent pathological accumulation of amyloid beta-peptide.J. Biol. Chem. 272, 18644–18649.
Han BH, RB DeMattos, LL Dugan, JS Kim-Han, RP Brendza, JD Fryer, M Kierson, J Cirrito, K Quick, JAK Harmony, BJ Aronow and DM Holtzman (2001) Clusterin contributes to caspase-3-independent brain injury following neonatal hypoxia-ischemia.Nat. Med. 7, 338–343.
Hardy J (1997) The Alzheimer family of diseases: many etiologies, one pathogenesis?Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94, 2095–2097.
Harr SD, L Uint, R Hollister, BT Hyman and AJ Mendez (1996) Brain expression of apolipoproteins E, J, and A-I in Alzheimer’s disease.J. Neurochem. 66, 2429–2435.
Holtzman DM, KR Bales, T Tenkova, AM Fagan, M Parsadanian, LJ Sartorius, B Mackey, J Olney, D McKeel, D Wozniak and SM Paul (2000a) Apolipoprotein E isoform-dependant amyloid deposition and neuritic degeneration in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97, 2892–2897.
Holtzman DM, AM Fagan, B Mackey, T Tenkova, L Sartorius, SM Paul, K Bales, KH Ashe, MC Irizarry and BT Hyman (2000b) Apolipoprotein E facilitates neuritic and cerebrovascular plaque formation in an Alzheimer’s disease model.Ann. Neurol. 47, 739–747.
Irizarry MC, BS Cheung, GW Rebeck, SM Paul, KR Bales and BT Hyman (2000), Apolipoprotein E affects the amount, form, and anatomical distribution of amyloid ß-peptide deposition in homozygous APPV717F transgenic mice.Acta Neuropathol. 100, 451–458.
Kida E, NH Choi-Miura and KE Wisniewski (1995) Deposition of apolipoproteins E and J in senile plaques is topographically determined in both Alzheimer’s disease and Down’s syndrome brain.Brain Res. 685, 211–216.
Kindy MS and DJ Rader (1998) Reduction in amyloid A formation in apolipoprotein-E-deficient mice.Am. J. Pathol. 152, 1387–1395.
Matsubara E, B Frangione and J Ghiso (1995) Characterization of apolipoprotein J-Alzheimer’s amyloid-beta interaction.J. Biol. Chem. 270, 7563–7567.
Matsubara E, C Soto, S Governale, B Frangione and J Ghiso (1996) Apolipoprotein J and Alzheimer’s amyloid beta solubility.Biochem. J. 316, 671–679.
McGeer PL, T Kawamata and DG Walker (1992) Distribution of clusterin in Alzheimer brain tissue.Brain Res. 579, (1992) 337–341.
Nakai M, T Kawamata, T Taniguchi, K Maeda and C Tanaka (1996) Expression of apolipoprotein E mRNA in rat microglia.Neurosci. Lett. 211, 41–44.
Namba Y, M Tomonaga, H Kawasaki, E Otomo and K Ikeda (1991) Apolipoprotein E immunoreactivity in cerebral amyloid deposits and neurofibrillary tangles in Alzheimer’s disease and kuru plaque amyloid in Creutzfeld-Jakob disease.Brain Res. 541, 163–166.
Nishida K, AJ Quantock, A Dota, NH Choi-Miura and S Kinoshita (1999) Apolipoproteins J and E co-localise with amyloid with amyloid in gelatinous drop-like and lattice type I corneal dystrophies.Br. J. Ophthalmol. 83, 1178–1182.
Paxinos G and C Watson (1997)The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates (Academic Press: New York).
Pitas RE, JK Boyles, SH Lee, D Foss and RW Mahley (1987) Astrocytes synthesize apolipoprotein E and metabolize apolipoprotein E-containing lipoproteins.Biochem. Biophys. Acta 917, 148–161.
Qiu Z, Strickland DK, Hyman BT, and GW Rebeck (2002) ?2-Macroglobulin exposure reduces calcium responses toN-methyl-D-aspartate via low density lipoprotein recepor-related protein in cultured hippocampal neurons.J. Biol. Chem. 277, 14459–14466.
Sasaki K, K Doh-ura, Y Wakisaka and T Iwaki (2002) Clusterin/apolipoprotein J is associated with cortical Lewy bodies: immunohistochemical study in cases with ?-synucle-inopathies.Acta Neuropathol. 104, 225–230.
Scheuner D, C Eckman, M Jensen, X Song, M Citron, N Suzuki, TD Bird, J Hardy, M Hutton, W Kukull, E Larson, E Levy-Lahad, M Viitanen, E Peskind, P Poorkaj, G Schellenberg, R Tanzi, W Wasco, L Lannfelt, D Selkoe and S Younkin (1996) Secreted amyloid beta-protein similar to that in the senile plaques of Alzheimer’s disease is increasedin vivo by the presenilin 1 and 2 and APP mutations linked to familial Alzheimer’s disease.Nat. Med. 2, 850–852.
Schnell SA, WA Staines and MW Wessendorf (1999) Reduction of lipofuscin-like autofluorescence in fluorescently labeled tissue.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 47, 719–730.
Selkoe DJ (1998) The cell biology of ß-amyloid precursor protein and presenilin in Alzheimer’s disease.Trends Cell Biol. 8, 447–453.
Stoltzner SE, TJ Grenfell, C Mori, KE Wisniewski, TM Wisniewski, DJ Selkoe and CA Lemere (2002) Temporal accrual of complement proteins in amyloid plaques in Down’s syndrome with Alzheimer’s disease.Am. J. Pathol. 156, 489–499.
Thal DR, U Rüb, C Schultz, I Sassin, E Ghebremedhin, K Del Tredici, E Braak and H Braak (2000) Sequence of Aß-protein deposition in the human medial temporal lobe.J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 59, 733–748.
Wisniewski T and B Frangione (1992) Apolipoprotein E: a pathological chaperone protein in patients with cerebral and systemic amyloid.Neurosci. Lett. 135, 235–238.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martin-Rehrmann, M.D., Hoe, HS., Capuani, E.M. et al. Association of apolipoprotein J-positive β-amyloid plaques with dystrophic neurites in alzheimer’s disease brain. neurotox res 7, 231–241 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03036452
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03036452