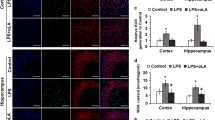
Abstract
Pro-inflammatory molecules induce glial activation and the release of potentially detrimental factors capable of generating oxidative damage, such as nitric oxide (NO) and superoxide anion (O2 ·−. Activated glial cells (astrocytes and microglia) are associated to the inflammatory process in neurodegenerative diseases. A strong inflammatory response could escape endogenous control becoming toxic to neurons and contributing to the course of the disease. We evaluated in a hippocampal cells-microglia co-culture model, if the pro-inflammatory condition induced by lipopolysaccharide + interferon-γ (LPS+IFN-γ) promoted damage directly or if damage was secondary to glial activation. In addition, we explored the effect of the anti-inflammatory cytokine transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1), and pro-inflammatory cytokines, interleukin-1β (IL-1β) and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) on the regulation of the inflammatory response of microglia. We found that LPS+IFN-γ-induced damage on hippocampal cultures was dependent on the presence of microglial cells. In hippocampal cultures exposed to LPS+IFN-γ, TGF-β1 was induced whereas in microglial cell cultures LPS+IFN-γ induced the secretion of IL-1β. TGF-β1 and IL-1β but not TNF-α decreased the NO production by 70–90%. PD98059, an inhibitor of MAP kinase (MEK), reduced the IFN-γ-induced NO production by 40%. TGF-β1 and IL-1β reduced the IFN-γ-induced phosphorylation of ERK1,2 by 60% and 40%, respectively. However, the effect of IL-1β was observed at 30 min and that of TGF-β1 only after 24 h of exposure. We propose that acting with different timing, TGF-β1 and IL-1β can modulate the extracellular signal-regulated kinase ERK1,2, as a common element for different transduction pathways, regulating the amplitude and duration of glial activation in response to LPS+IFN-γ. Cross-talk among brain cells may be key for the understanding of inflammatory mechanisms involved in pathogenesis of neurodegenerative diseases.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akiyama H, S Barger, S Barnum, B Bradt, J Bauer, G Cole, N Cooper, P Eikelenboom, M Emmerling, B Fiebich, C Finch, S Frautschy, W Griffin, H Hampel, M Hull, G Landreth, L Lue, R Mrak, I Mackenzie, P McGeer, M O’Banion, J Pachter, G Pasinetti, C Plata-Salaman, J Rogers, R Rydel, Y Shen, W Streit, R Strohmeyer, I Tooyoma, F Van Muiswinkel, R Veerhuis, S Walker, B Wegrzyniak, G Wenk and T Wyss-Coray (2000) Inflammation and Alzheimer’s disease.Neurobiol. Aging 21, 383–421.
Basu A, J Krady and S Levinson (2004) Interleukin-1: A master regulator of neuroinflammation.J. Neurosci. Res. 78, 151–156.
Benveniste E, V Nguyen and G O’Keefe (2001) Immunological aspects of microglia: relevance to Alzheimer’s disease.Neurochem. Int. 39, 381–391.
Blanchette J, M Jaramillo and M Olivier (2003) Signalling events involved in interferon-γ-inducible macrophage nitric oxide generation.Immunology 108, 513–522.
Bruce-Keller A, J Keeling, J Keller, F Huang, S Camondola and M Mattson (2000) Antiinflammatory effects of estrogen on microglial activation.Endocrinol.141, 3646–3656.
Cáceres A, G Banker, O Steward, L Binder and M Payne (1984) MAP2 is localized to the dendrites of hippocampal neurons which develop in culture.Brain Res. 315, 314–318.
Chao CC, S Hu and PK Peterson (1995) Modulation of human microglial cell superoxide production by cytokines.J. Leukoc. Biol. 58, 35–70.
Ding M, B St. Pierre, J Parkinson, P Medberry, J Wong, N Rogers, L Ignaro and J Merril (1997) Inducible nitric-oxide synthase and nitric oxide production in human foetal astrocytes and microglia.J. Biol. Chem. 272, 11327–11335.
Flanders K, R Ren and C Lippa (1998) Transforming growth factor-betas in neurodegenerative disease.Prog. Neurobiol.54, 71–85.
Giulian D and T Baker (1986) Characterization of ameboid microglia isolated from developing mammalian brain.J. Neurosci. 6, 2163–2178.
Giulian D and M Corpuz (1993) Microglial secretion products and their impact on the nervous system.Adv. Neurol.59, 315–320.
Giulian D and J Ingemann (1988) Colony-stimulating factors as promoters of ameboid microglia.J. Neurosci. 8, 4707–4717.
Giulian D, K Vaca and M Corpuz (1993) Brain glial release factors with opposing actions upon neuronal survival.J. Neurosci. 13, 29–37.
Giulian D, J Li, X Li, J George and P Rutecki (1994) The impact of microglia-derived cytokine upon gliosis in the CNS.Dev. Neurosci. 16, 128–136.
Gleizes P, J Munger, I Nunes, J Harpel, R Mazzieri, I Noguera and D Rifkin (1997) TGF-β latency: biological significance and mechanisms of activation.Stem Cells 15, 190–197.
Han I-O, K-W Kim, J-H Ryu and W-K Kim (2002) p38 Mitogen-activated protein kinase mediates lipopolysaccharide, not inter-feron-γ, -induced inducible nitric oxide synthase expression in mouse BV2 microglial cells.Neurosci. Lett. 325, 9–12.
Hazuda D, R.L. Webb, P Simon and P Young (1998) Purification and characterization of human recombinant precursor interleukin 1 beta.J. Biol. Chem. 264, 1689–1693.
Henrich-Noack P, J Prehn and J Krieglstein (1996) TGF-β1 protects hippocampal neurons against degeneration caused by transient global ischemia.Stroke 27, 1609–1614.
Herrera-Molina R and R von Bernhardi (2005) Transforming growth factor-β1 produced by hippocampal cells modulates microglial reactivity in culture.Neurobiol. Dis. 19, 229- 236.
Hu S, WS Sheng, PK Peterson and CC Chao (1995) Cytokines modulation of murine microglial cell superoxide production.Glia 13, 45–50.
Kaur Ch, A-J Hao, Ch-H Wu and E-A Ling (2001) Origin of microglia.Microsc. Res. Tech. 54, 2–9.
Lee S, W Liu, C Brosnan and D Dickinson (1994) GM-CSF promotes proliferation of human fetal and adult microglia in primary cultures.Glia 12, 309–318.
Lieb K, S Engels and B Fiebich (2003) Inhibition of LPS-induced iNOS and NO synthesis in primary rat microglial cells.Neurochem. Int. 42, 131–137.
Ling E and W Wong (1993) The origin and nature of ramified and amoeboid microglia: a historical review and current concepts.Glia 7, 9–18.
Marcus J, S Karackattu, M Fleegal and C Summers (2003) Cytokine-stimulated inducible nitric oxide synthase expression in astroglia: role of Erk Mitogen-activated protein kinase and NF-κB.Glia 41, 152–160.
Martin L, C Pardo, L Cork and D Price (1994) Synaptic pathology and glial responses to neuronal injury precede the formation of senile plaques and amyloid deposits in the aging cerebral cortex.Am. J. Pathol. 145, 1358–1381.
McCartney-Francis N and S Wahl (2002) Dysregulation of IFN-γ signaling pathways in the absence of TGF-β1.J. Immunol.169, 5941–5947.
McGeer P and E McGeer (1995) The inflammatory response system of brain: implications for therapy of Alzheimer and other neurodegenerative diseases.Brain Res. Rev. 21, 195–218.
McGeer P and E McGeer (2001) Inflammation, autotoxicity and Alzheimer disease.Neurobiol. Aging 22, 799–809.
Meda L, P Baron and G Scarlato (2001) Glial activation in Alzheimer’s disease: the role of Aβ and its associated proteins.Neurobiol. Aging 22, 885–893.
Mrak R, J Sheng and S Griffin (1995) Glial cytokines in Alzheimer’s disease.Human Pathology 26, 816–823
Munger J, J Harpel, P Gleizes, R Mazzieri, I Nunes and D Rifkin (1997) Latent transforming growth factor-β: structural features and mechanisms of activation.Kidney Int. 51, 1376–1382.
O’Brien M, L Lenke, J Lou, K Bridwell and M Joyce (1994) Astrocyte response and transforming growth factor-beta localization in acute spinal cord injury.Spine 19, 2321–2329.
Patel AJ, S Gunasekera, A Jen and H Rohan (1996) Beta-amyloid-mediated inhibition of redox activity (MTT reduction) is not an indicator of astroglial degeneration.NeuroReport 7, 2026–2030.
Pfeiffer S, A Gorren, K Schmidt, E Werner, B Hanser, D Bohle and B Mayer (1997) Metabolic fate of peroxynitrite in aqueous solution.J. Biol. Chem. 272, 3465–3470.
Pyo H, I Jou, S Jung, S Hong and E-H Joe (1998) Mitogen-activated protein kinases activated by lipopolysaccharide and β-amyloid in cultured rat microglia.NeuroReport 9, 871–874.
Ramírez G, R Toro, H Döbeli and R von Bernhardi (2005) Protection of rat primary hippocampal cultures from Aβ cytotoxicity by pro-inflammatory molecules is mediated by astrocytes.Neurobiol Dis. 19, 243–254.
Rook G (1985) A simple method for the solubilisation of reduced NBT, and its use as a colorimetric assay.J. Immunol. Methods 82, 161–167.
Rothwell N and G Luheshi (2000) Interleukin 1 in the brain: biology, pathology and therapeutic target.Trends Neurosci. 23, 618–625.
Schubert P, T Morino, H Miyazaki, T Ogata, Y Nakamura, C Marchini and S Ferroni (2000) Cascading glia reactions: a common pathomecanism and its differentiated control by cyclic nucleotide signalling.Ann. NY. Acad. Sci. 903, 24–33.
Shappell N (2003) Ergovaline toxicity on CACO-2 cells as assessed by MTT, alamar blue and DNA assays.In vitro Cell Dev. Biol-animal 39, 329–335.
Sheng J, S Bora, G Xu, D Borchelt, D Price and V Koliatos (2003) Lipopolysaccharide-induced-neuroinflammation increases intra-cellular accumulation of amyloid precursor protein and amyloid beta peptide in APPswe transgenic mice.Neurobiol. Dis. 14, 133–145.
Van Eldik L (2001) Glia and Alzheimer’s disease.Neurochem. Int. 39, 329–331.
Vegeto E, C Bonincontro, G Polli, A Sala, S Viappiani, F Nardi, A Brusadelli, B Viviani, P Ciana and A Maggi (2001) Estrogen prevents the lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response in microglia.J. Neurosci. 21, 1809–1818.
Vincent V, F Tielders and A Van Dam (1997) Inhibition of endotoxin induced nitric oxide synthase production in microglial cells by the presence of astroglial cells: a role for transforming growth factor β.Glia 19, 190–198.
von Bernhardi R and J Eugenín (2004) Microglial activity to - amyloid is modulated by astrocytes and pro-inflammatory factors.Brain Res. 1025, 186–193.
von Bernhardi R, G Ramírez, H Matile and H Döbeli (2001) Immobilized APP constructs: a tool for thein vitro screening of glial cells reactivity.Europ. J. Neurosci. 14, 946–956.
von Bernhardi R, K Saud and R Herrera-Molina (2004) Modulation of the production of NO and O2-induced by IFN-γ in glial cells by anti- and pro-inflammatory cytokines: the role of ERK and STAT pathways. Shanghai Int. Conf. Physiol. Biophys. Abstract book, p 127.
Weiner H and D Selkoe (2002) Inflammation and therapeutic vaccination in CNS diseases.Nature 420, 879–884.
Zhu Y, S Roth-Eichhorn, N Braun, C Culmsee, A Rami and J Krieglstein (2000) The expression of transforming growth factor-beta 1 (TGF-β1) in hippocampal neurons: a temporary upregulated protein level after transient forebrain ischemia in the rat.Brain Res. 866, 286–298.
Zhu Y, G Yang, B Ahlemeyer, L Pang, X Che and C Culmsee (2002) Transforming growth factor-ß1 increases bad phosphorylation and protects neurons against damage.J. Neurosci. 22, 3898–3909.
Zhu Y, C Culmsee, S Klumpp and J Krieglstein (2004) Neuroprotection by transforming growth factor-β1 involves activation of nuclear factor-κB through phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinase/Akt and mitogen-activated protein kinase extracellular-signal regulated kinase 1,2 signaling pathways.Neuroscience 123, 897–906.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saud, K., Herrera-Molina, R. & Von Bernhardi, R. Pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines regulate the ERK pathway: Implication of the timing for the activation of microglial cells. neurotox res 8, 277–287 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03033981
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03033981