Abstract
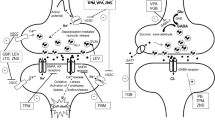
Degenerative diseases of the central nervous system (CNS) frequently have a predilection for specific cell populations. An explanation for the selective vulnerability of particular neuronal populations and the mechanisms of cell death remains, as yet, elusive. Partial elucidation of the processes underlying the selective action of neurotoxic substances such as iron, 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA), glutamate, kainic acid, quinolinic acid or l-methyl-4-phenyl-l,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP), has revealed possible molecular mechanisms for neurodegeneration. Hypotheses regarding the neurotoxic mechanisms of these substances have evolved based on our understanding of the pathogenesis of cell death in neurodegenerative disorders and have been the rationale for neuroprotective approaches. Various experimental models have demonstrated that monoamine oxidase type B (MAO-B) inhibitors and dopamine agonists exert a neuroprotective effect at the cellular, neurochemical and functional levels, however as yet it has not been possible to demonstrate an unequivocal neuroprotective effect of these substances in clinical studies. This does not suggest, however, that the pathogenetic processes underlying neurodegenerative disorders are not amenable to neuroprotective treatment.
This chapter briefly reviews the mechanisms underlying dopaminergic cell death in Parkinson’s disease (PD) as an example of a neurodegenerative disorder and discusses preclinical approaches which attempt to demonstrate the neuroprotective effects of representative drugs in experimental models of this disorder. The problems associated with carrying out clinical neuroprotective studies aimed to demonstrate neuroprotection in PD are also discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alam, Z.I., Jenner, A., Daniel, S.E., Lees, A.J., Cairns, N., Marsden, CD., Jenner, P. and Halliwell, B. (1997) Oxidative DNA damage in the parkinsonian brain: An apparent selective increase in 8-hydroxyguanine levels in substantia nigra.J. Neurochem. 69, 1196–1203.
Altman, J. (1992) Programmed cell death: the paths to suicide.TiPS 15, 278–280.
Arendt, T., Bigl, V., Arendt, A. and Tennstedt, A. (1983) Loss of neurons in the nucleus basalis of Meynert in Alzheimer’s disease, paralysis agitans and Korsakoff’s disease.Acta Neuropathol. Berlin 61, 101–108.
Aubin, N., Curet, O., Deffois, A. and Carter, C. (1998) Aspirin and salicylate protect against MPTP-induced dopamine depletion in mice.J. Neurochem. 71, 1635–1642.
Becker, G., Seufert, J., Bogdhan, U., Reichmann, H. and Reiners, K. (1995) Degeneration of substantia nigra in chronic Parkinson’s disease visualized by transcranial color-coded real-time sonography.Neurology 45, 182–184.
Ben-Shachar, D., Eshel, G., Finberg, J.P.M. and Youdim, M.B.H. (1991) The iron chelator desferrioxamine (desferal) retards 6-hydroxydopamine-induced degeneration of nigro-striatal neurons.J. Neurochem. 56, 1441–1444.
Berg, D., Becker, G., Zeiler, B., Tucha, O., Hofmann, E., Preier, M., Benz, P., Jost, W., Reiners, K. and Lange, K.W. (1999) Vulnerability of the nigrostriatal system as detected by transcranial ultrasound.Neurology 53, 1026–1031.
Bezard, E., Stutzmann, J.M., Imbert, C, Boraud, T., Boireau, A. and Gross, C.E. (1998) Riluzole delayed appearance of parkinsonian motor abnormalities in a chronic MPTP monkey model.Eur. J. Pharmacol. 356, 101–104.
Blanchet, P.J., Konitsiotis, S., Hyland, K., Arnold, L.A., Pettigrew, K.D. and Chase, T.N. (1998) Chronic exposure to MPTP as a primate model of progressive parkinsonism: A pilot study with a free radical scavenger.Exp. Neurol. 153, 214–222.
Blum-Degen, D., Müller, T., Kuhn, W., Gerlach, M., Przuntek, H. and Riederer, P. (1996) Interleukin-1β and interleukin-6 are elevated in the cerebrospinal fluid of Alzheimer’s andde novo Parkinson’s disease patients.Neurosci. Lett. 202, 17–20.
Blum-Degen, D., Haas, M., Pohli, S., Harth, R., Römer, W., Oettel, M., Riederer, P. and Götz, M.E. (1998) Scavestrogens protect IMR 32 cells from oxidative stress-induced cell death.Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 152, 49–55.
Boireau, A., Dubedat, P., Bordier, F., Peny, C, Miquet, J.-M., Durand, G., Meunier, M. and Doble, A. (1994) Riluzole and experimental parkinsonism: Antagonism of MPTP-induced decrease in central dopamine levels in mice.NeuroReport 5, 2657–2660.
Carboni, S., Melis, F., Pani, L., Hadjiconstantinou, M. and Rossetti, Z. (1990) The non-competitive NMDA-receptor antagonist MK-801 prevents the massive release of glutamate and aspartate from rat striatum induced by 1-methy-4-phenyl-l,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridinium (MPP+).Neurosci. Lett. 117, 129–133.
Carrillo, M.-C, Kanai, S., Nokubo, M. and Kitani, K. (1991) (-)Deprenyl induces activities of both Superoxide dismutase and catalase but not of glutathione peroxidase in the striatum of young male rats.Life Sci. 48, 517–521.
Carvey P.M., Pieri, S. and Ling, Z.D. (1997) Attenuation of levodopa-induced toxicity in mesencephalic cultures by pramipexole.J. Neural Transm. 104, 209–228.
Cassarino, D.S., Fall, C.P., Smith, T.S. and Bennett, J.P. (1998) Pramipexole reduces reactive oxygen species productionin vivo andin vitro and inhibits the mitochondrial permeability transition produced by the Parkinsonian neurotoxin methylpyridinium ion.J. Neurochem. 71, 295–301.
Chan, P., Dimonte, D.A., Langston, J.W. and Janson, A.M. (1997) (+)MK-801 does not prevent MPTP-induced loss of nigral neurons in mice.J. Pharmacol. Exp. They. 280, 439–446.
Chen, T.S., Koutsilieri, E. and Rausch, W.D. (1995). MPP+ selectively affects calcium homeostasis in mesencephalic cell cultures from embryonal C57/BL mice.J. Neural Transm. (P.-D.-Sect.) 100, 153–163.
Chiueh, C.C., Miyake, H. and Peng, M.T. (1993) Role of dopamine autoxidation, hydroxyl radical generation and calcium overload in underlying mechanism involved in MPTP-induced parkinsonism.Adv. Neurol. 60, 251–258.
Clow, A., Hussain, T., Glover, V., Sandier, M., Dexter, D.T. and Walker, M. (1991) (-)-Deprenyl can induce soluble superoxide dismutase in rat striata.J. Neural Transm. (Gen. Sect.) 86, 77–80.
Clow, A., Freestone, C, Lewis, E., Dexter, D., Sandler, M. and Glover, V. (1993) The effect of pergolide and MDL 72974 on rat brain CuZn Superoxide dismutase.Neurosci. Lett. 164, 41–43.
Cohen, G. (1987) Monoamine oxidase, hydrogen peroxide, and Parkinson’s disease.Adv. Neurol. 45, 119–125.
Dexter, D.T., Holley, A.E., Flitter, W.D., Slater, T.F., Wells, ER., Daniel, S.E., Lees, A.J., Jenner, P. and Marsden, C.D. (1994) Increased levels of lipid hydroperoxides in the parkinsonian substantia nigra: An HPLC and ESR study.Mov. Disord. 9, 92–97.
Double, K.L., Maywald, M., Schmittel, M., Riederer, P. and Gerlach, M. (1998)In vitro studies of ferritin iron release and neurotoxicity.J. Neurochem. 70, 2492–2499.
Erdö, S.L. and Schäfer, M. (1991) Memantine is highly potent in protecting cortical cultures against excitotoxic cell death evoked by glutamate and N-methyl-D-aspartate.Eur. J. Pharmacol. 198, 215–217.
Feiten, D.L., Feiten, S.Y., Fuller, R.W., Romano, T.D., Smalstig, E.B., Wong, D.T. and Clemens, J.A. (1992) Chronic dietary pergolide preserves nigrostriatal integrity in aged- Fischer-344 rats.Neurobiol. Aging 13, 339–351.
Ferger, B., Spratt, C, Teismann, P., Seitz, G. and Kuschinsky K. (1998) Effects of cytisine on hydroxyl radicalsin vitro and MPTP-induced dopamine depletionin vivo.Eur. J. Pharmacol. 360, 155–163.
Gassen, M., Glinka, Y, Pinchasi, B. and Youdim, M.B.H. (1996) Apomorphine is a highly potent free radical scavenger in rat brain mitochondrial fraction.Eur. J. Pharmacol. 308, 219–225.
Gassen, M., Gross, A. and Youdim, M.B.H. (1998) Apomorphine enantiomers protect cultured pheochromocytoma (PC 12) cells from oxidative stress induced by H2O2 and 6-hydroxydopamine.Mov. Disord. 13, 242–248.
Gerlach, M., Riederer, P., Przuntek, H. and Youdim, M.B.H. (1991) MPTP mechanisms of neurotoxicity and their implications for Parkinson’s disease.Eur. J. Pharmacol. (Mol. Pharmacol. Sect.) 208, 273–286.
Gerlach, M., Riederer, P. and Youdim, M.B.H. (1992) The molecular pharmacology of L-deprenyl.Eur. J. Pharmacol. (Mol. Pharmacol. Sect.) 226, 97–108.
Gerlach, M., Ben-Shachar, D., Riederer, P. and Youdim, M.B.H. (1994) Altered brain metabolism of iron as a cause of neurodegenerative diseases?J. Neurochem. 63, 793–807.
Gerlach, M., Riederer, P. and Youdim, M.B.H. (1995) Neuroprotective therapeutic strategies: comparison of experimental and clinical results.Biochem. Pharmacol. 50, 1–16.
Gerlach, M. and Riederer, P. (1996) Animal models of Parkinson’s disease: an empirical comparison with the phenomenology of the disease in man.J. Neural Transm. 103, 987–1041.
Gerlach, M., Riederer, P. and Youdim, M.B.H. (1996a) Molecular mechanisms for neurodegeneration: Synergism between reactive oxygen species, calcium and excitotoxic amino acids.Adv. Neurol. V 69, 77–194.
Gerlach, M., Youdim, M.B.H. and Riederer, P. (1996b) Pharmacology of selegiline.Neurology 47(Suppl. 3): S137-S145.
Gerlach, M. and Riederer, P. (1999) Time sequences of dopaminergic cell death in Parkinson’s disease. Indications for neuroprotective studies.Adv. Neurol. 80, 219–225.
Giulian, D., Vaca, K. and Corpuz, M. (1993) Brain glia release factors with opposing actions upon neuronal survival.J. Neurosci. 13, 29–37.
Götz, M.E., Künig, G., Riederer, P. and Youdim, M.B.H. (1994) Oxidative stress: free radical production in neural degeneration.Pharmac. Ther. 63, 37–122.
Graham, D.G., Tiffany, S.M., Bell, W.R. and Gutknecht, W.F. (1978) Autooxidation versus covalent binding quinones as the mechanism of toxicity of dopamine, 6-hydroxydopamine and related compounds towards C1300 neuroblas- toma cellsin vitro. Mol. Pharmacol. 14, 644–653.
Grünblatt, E., Mandel, S., Berkuzki, T. and Youdim, M.B.H. (1999) Apomorphine protects against MPTP-induced neurotoxicity in mice.Mov. Disord. 14, 612–618.
Hagihara, M., Fujishiro, K., Takahashi, A., Naoi, M. and Nagatsu, T. (1989) Cyclosporin A, an immune suppressor, enhanced neurotoxicity of N-methyl-4-pheny 1-1,2,3,6- tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) to mice.Neurochem. Int. 15, 249–254.
Hall, S., Rulledge, J.H. and Schallert, T. (1992) MRI brain iron and 6-hydroxydopamine experimental Parkinson’s disease.J. Neurol. Sci. 113, 198–208.
Halliwell, B. (1992) Reactive oxygen species and the central nervous system.J. Neurochem. 59, 1609–1623.
Hantraye, P., Brouillet, E., Ferrante, R., Palfi, S., Dolan, R., Matthews, R.T. and Beal, M.F. (1996) Inhibition of neuronal nitric oxide synthase prevents MPTP-induced parkinsonism in baboons.Nature Med. 2, 1017–1021.
Hara, H., Yokota, K., Shimazawa, M. and Sukamoto, T. (1993) Effect of KB-2796, a new diphenylpiperazine Ca2+ antagonist, on glutamate-induced neurotoxicity in rat hippocampal primary cell cultures.Jap. J. Pharmacol. 61, 361–365.
Harper, S., Bilsland, J., Young, L., Bristow, L., Boyce, S., Mason, G., Rigby, M., Hewson, L., Smith, D. and O’Donnell, R. (1999) Analysis of the neurotrophic effects of GPI-1046 on neuron survival and regeneration in culture andin vivo.Neuroscience 88, 257–267.
Heikkila, R.E. and Cohen, G. (1978) Further studies on generation of hydrogen peroxide by 6-hydroxydopamine: Potentiation by ascorbic acid.Mol. Pharmacol. 8, 241–248.
Hou, J.G.G., Lin, L.F.H. and Mytilineou, C. (1996) Glial cell linederived neurotrophic factor exerts neurotrophic effects on dopaminergic neuronsin vitro and promotes their survival and regrowth after damage by l-methyl-4-phenylpyridi-nium.J. Neurochem. 66, 74–82.
Itzhak, Y. and Ali, S.F. (1996) The neuronal nitric oxide synthase inhibitor, 7-nitroindazole, protects against methamphet-amine-induced neurotoxicityin vivo.J. Neurochem. 67, 1770–1773.
Jellinger, K. (1989) Pathology of Parkinson’s syndrome. In: Calne, D.B. (Ed.),Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology, Vol. 88 (Berlin Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag) pp. 47–112.
Jenner, P. and Olanow, C.W. (1996) Oxidative stress and the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease.Neurology 47, S161-S170
Kerr, J.F.R., Wyllie, A.H. and Currie, A.R. (1972) Apoptosis: A basic biological phenomenon with wide-ranging implications in tissue kinetics.Br. J. Cancer 265, 239–245.
Kinloch, R.A., Treherne, J.M., Furness, L.M. and Hajimohamadreza, I. (1999) The pharmacology of apoptosis.TiPS 20, 35–42.
Kitamura, Y, Itano, Y, Kubo, T. and Nomura, Y. (1994) Suppressive effect of FK-506, a novel immunosuppressant, against MPTP-induced dopamine depletion in the striatum of young C57/BL/6 mice.J. Neuroimmunol. 50, 221–224.
Kitamura, Y, Kohno, Y, Nakazawa, M. and Nomura, Y. (1997) Inhibitory effects of talipexole and pramipexole on MPTP-induced dopamine reduction in the striatum of C57BL/6N mice.Jap. J. Pharmacol. 74, 51–57.
Klivenyi, P., St Clair, D., Wermer, M., Yen, H.C., Oberley, T., Yang, L.C. and Beal, M.F. (1998) Manganese Superoxide dismutase overexpression attenuates MPTP toxicity.Neurobiol. Disease 5, 253–258.
Knoll, J. (1987) R-(-)-deprenyl (Selegiline, Movergan®) facilitates the activity of the nigrostriatal dopaminergic neuron.J. Neural Transm. 25(Suppl.), 45–66.
Knoll, J. (1988) The striatal dopamine dependency of life span in male rats, longevity study with (-)deprenyl.Mech. Ageing Dev. 46, 237–262.
Koutsilieri, E., Ocallaghan, J.F.X., Chen, T.S., Riederer, P. and Rausch, W.-D. (1994) Selegiline enhances survival and neurite outgrowth of MPP+-treated dopaminergic neurons.Eur. J. Pharmacol. (Mol. Pharmacol. Sect.) 269, R3-R4.
Koutsilieri, E., Chen, T.-S., Rausch, W.-D. and Riederer, P. (1996) Selegiline is neuroprotective in primary brain cultures treated with l-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium.Eur. J. Pharmcol. (Mol. Pharmacol. Sect.) 306, 181–186.
Krüger, R., Vieira-Säcker, A.M.M., Kuhn, W., Müller, T., Woitalla, D., Schöls, L., Przuntek, H., Epplen, J.T. and Riess, O. (1999) Analysis of the Parkin deletion in sporadic and familial Parkinson’s disease.J. Neural Transm. 106, 159–163.
Kuhn, W. and Müller, Th. (1995) Neuroimmune mechanisms in Parkinson’s disease.J. Neural Transm. 46(Suppl.), 229–233.
Kupsch, A., Loeschmann, P., Sauer, H., Arnold, G., Renner, P., Pufal, D., Burg, M., Wachtel, H., Ten Bruggencate, G. and Oertel, W.H. (1992) Do NMDA receptor antagonists protect against MPTP-toxicity? Biochemical and immuno-cytochemical analyses in black mice.Brain Res. 592, 74–83.
Kupsch, A., Gerlach, M., Pupeter, S.C., Sautter, J., Dirr, A., Arnold, G., Opitz, W., Przuntek, H., Riederer, P. and Oertel, W.H. (1995) The calcium channel blocker nimodipine prevents MPTP-induced neurotoxicity at the nigral, but not at the striatal level in mice.NeuroReport 6, 621–625.
Kupsch, A., Sautter, J., Schwarz, J., Riederer, P., Gerlach, M. and Oertel, W.H. (1996) l-Methyl-4-phenyl-l,2,3,6-tetrahydro-pyridine-induced neurotoxicity in non-human primates is antagonized by pretreatment with nimodipine at the nigral, but not at the striatal level.Brain Res. 741, 185–196.
Kupsch, A., Sautter, J., Götz, M.E., Breithaupt, W., Schwarz, J., Youdim, M.B.H., Riederer, P., Gerlach, M. and Oertel, W.H. (1999) MAO-inhibition and MPTP-induced neurotoxicity in the non-human primate: Comparison of rasagiline (TVP 1012) with selegiline.J. Neural Transm. (submitted).
Lange, K.W., Löschmann, P.A., Sofic, E., Burg, M., Horowski, R., Kalreram, K.T., Wachtel, H. and Riedevev, P. (1993) The competitive NMOA antagonist CPP protect substantia nigra neurons from MPTP-induced degeneration in primates.Naunyu Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 34, 586–592.
Lapchak, P.A., Gash, D.M., Collins, F., Hilt, D., Miller, P.J. and Araujo, D.M. (1997) Pharmacological activities of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF): Preclinical development and application to the treatment of Parkinson’s disease.Exp. Neurol. 145, 309–321.
Leist, M. and Nicotera, P. (1998) Calcium and neuronal death.Rev. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 132, 79–125.
Martinovits, G., Melamed, E., Cohen, O., Rosemthal, J. and Uzzan, A. (1986) Systemic administration of antioxidants does not protect mice against the dopaminergic neurotoxicity of l-methyl-4-phenyl-l,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine.Neurosci. Lett. 69, 192–197.
McGeer, PL., Itagaki, S., Boyes, B.E. and McGeer, E.G. (1988) Reactive microglia are positive for HLA-DR in the substantia nigra of Parkinson’s and Alzheimers’ disease brains.Neurology 38, 1285–1291.
Meldrum, B. and Garthwaite, J. (1990) Excitatory amino acid neurotoxicity and neurodegenerative disease. In: Lodge, and Collingridge, G. (Eds.),The Pharmacocology of Excitatory Amino Adds: A TiPS Special Report (Cambridge: Elsevier), pp. 54–62.
Mihatsch, W., Russ, H., Gerlach, M., Riederer, P. and Przuntek, H. (1991) Treatment with antioxidants does not prevent loss of dopamine in the striatum of MPTP-treated common marmoset: Preliminary observations.J. Neural Transm. (P.-D.Sect.) 3, 73–78.
Monteiro, H.P. and Winterbourn, C.C. (1989) 6-Hydroxydopa- mine releases iron from ferritin and promotes ferritin-dependent lipid peroxidation.Biochem. Pharmacol. 38, 4177–4182.
Morrish, P.K., Sawle, G.V. and Brooks, D.J. (1996) An [18F]dopa- PET and clinical study of the rate of progression in Parkinson’s disease.Brain 119, 585–591.
Muralikrishnan, D. and Mohanakumar, K.P. (1998) Neuroprotection by bromocriptine against l-methyl-4-phenyl-l,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine-induced neurotoxicity in mice.FASEB J. 12, 905–912.
Nishibayashi, S., Asanuma, M., Kohno, R., Gomez-Vargas, M. and Ogawa, N. (1996) Scavenging effects of dopamine agonists on nitric oxide radicals.J. Neurochem. 67, 2208–2211.
Ogawa, N., Tanaka, K., Asanuma, M., Kawai, M., Masumizu, T., Kohno, M. and Mori, A. (1994) Bromocriptine protects mice against 6-hydroxydopamine and scavenges hydroxyl free radicalsin vitro. Brain Res. 657, 207–213.
Oishi, T., Hasegawa, E. and Murai, Y. (1991) Sulfhydryl drugs reduce neurotoxicity of l-methyl-4-phenyl-l,2,3,6-tetrahy- dropyridine (MPTP) in the mouse.J. Neural Transm. (P.-D.Sect.) 6, 45–52.
Olney, J.W. (1978) Neurotoxicity of excitatory amino acids. In: McGeer, E.G. and Olney, J.W. (Eds.),Kainic Acid as a Tool in Neurobiology (New York: Raven Press), pp. 95–121.
Olney, J.W. (1989) Excitatory amino acids and neuropsychiatrie disorders.Biol. Psychiatry 26, 505–525.
Opacka-Juffry, J., Wilson, A.W. and Blunt, S.B. (1998) Effects of pergolide treatment onin vivo hydroxyl free radical formation during infusion of 6-hydroxydopamine in rat striatum.Brain Res. 810, 27–33.
Otto, D. and Unsicker, K. (1990) Basic FGF reserves chemical and morphological deficits in thenigostriatal system of MPTP-treated mice.J. Neurosci. 10, 1912–1921.
Pattichis, K., Louca, L.L., Clow, A. and Glover, V. (1995) Effects of pergolide, (-)-deprenyl and thioridazine on soluble SOD, catalase and glutathione peroxidase in rat striata.Med. Sci. Res. 23, 733–735.
Perry, T.L., Yong, V.W., Clavier, R.M., Jones, K., Wright, J.M., Foulks, J.G. and Wall, R.A. (1985) Partial protection from the dopaminergic neurotoxin N-methyl-4-phenyl-l,2,3,6-tetra- hydropyridine by four different antioxidants in mouse.Neurosci. Lett. 60, 109–114.
Przedborski, S., Kostic, V., Jackson-Lewis, V, Naini, A.B., Simonetti, S., Fahn, S., Carlson, E., Epstein, C.J. and Cadet, J.L. (1992) Transgenic mice with increased Cu/Zn- superoxide dismutase activity are resistant to N-methyl-4- phenyl-l,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine-induced neurotoxicity.J. Neurosci. 12, 1658–1667.
Przedborski, S., Jackson-Lewis, V, Yokoyama, R., Shibata, T., Dawson, V.L. and Dawson, T.M. (1996) Role of neuronal nitric oxide in l-methyl-4-phenyl-l,2,3,6-tetrahydropyri- dine (MPTP)-induced dopaminergic neurotoxicity.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93, 4565–4571.
Reinhard Jr., J.F., Carmichael, S.W. and Daniels, A.J. (1990) Mechanisms of toxicity and cellular resistance of 1-methyl-4-phenyl-l,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine and 1-methyl- 4-phenylpyridiniumin adrenomedullary chromaffin cell cultures.J. Neurochem. 55, 311–320.
Riederer, P. and Wuketich, S. (1976) Time course of nigrostriatal degeneration in Parkinson’s disease: A detailed study of influential factors in human brain amine analysis.J. Neural Transm. 38, 277–301.
Rodnitzky, R.L. (1999) Can calcium antagonists provide a neuroprotective effect in Parkinson’s disease?Drugs 57, 845–849.
Rollema, K., Kuhr, W.G., Kranenborg, G., DeVries, J. and Van den Berg, C. (1988) MPP+ induced efflux of dopamine and lactate from rat striatum have similar time courses as shown byin vivo brain dialysis.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 245, 858–866.
Römer, Vf., Oettel, M., Droescher, P. and Schwarz, S. (1997) Novel “scavestrogens” and their radical scavenging effects, iron-chelating, and total antioxidative activities: Δ8,9-dehydro derivatives of 17α-estradiol and 17β-estradiol.Steroids 62, 304–310.
Rossetti, Z.I., Sotgiu, A., Sharp, D.E., Hadjiconstantinou, M. and Neff, N.H. (1988) l-Methyl-4-phenyl-l,2,3,6-tetrahy- dropyridine (MPTP) and free radicalsin vitro. Biochem. Pharmacol. 37, 4573–4574.
Saiardi, A., Bozzi, Y, Baik, J.H. and Borrelli, E. (1997) Antiproliferate role of dopamine: Loss of D2 receptors causes hormonal dysfunction and pituitary hyperplasia.Neuron,19, 115–126.
Sano, M., Ernesto, C, Thomas, R.G., Klauber, M.R., Schafer, K., Grundman, M., Woodbury, P., Growdon, J., Cotman, D.W., Pfeiffer, E., Schneider, L.S. and Thal, L.J. (1997) A controlled trial of selegiline, alpha-tocopherol, or both as treatment for Alzheimer’s disease.New Engl. J. Med. 336, 1216–1222.
Sautter, J., Kupsch, A., Earl, CD. and Oertel, W.H. (1997) Degeneration of pre-labelled nigral neurons induced by intrastriatal 6-hydroxydopamine in the rat: Behavioural and biochemical changes and pretreatment with the calciumentry blocker nimodipine.Experimental Brain Res. 117, 111- 119.
Schulz, J.B., Henshaw, D.R., Matthews, R.T. and Beal, M.F. (1995a) Coenzyme Q(10) and nicotinamide and a free radical spin trap protect against MPTP neurotoxicity.Exp. Neurol. 132, 279–283.
Schulz, J.B., Matthews, R.T., Jenkins, B.G., Ferrante, R.J., Siwek, D., Henshaw, D.R., Cipolloni, P.B., Mecocci, P., Kowall, N.W., Rosen, B.R. and Beal, M.F. (1995b) Blockade of neuronal nitric oxide synthase protects against excitotoxicityin vivo.J. Neurosci. 15, 8419–8429.
Sershen, H., Reith, M.E.A., Hashim, A. and Lajtha, A. (1985) Protection against l-methyl-4-phenyl-l,2,3,6-tetrahydro-pyrdine neurotoxicity by the antioxidant ascorbic acid.Neuropharmacology 24, 1257–1259.
Shoulson, I. (1998) Where do we stand on neuroprotection? Where do we go from here?Mov. Disord. 13(Suppl. 1), 46–48.
Sian, J., Gerlach, M., Youdim, M.B.H. and Riederer, P. (1999) Parkinson’s disease: A major hypokinetic basal ganglia disorder.J. Neural Transm. 106, 443–476.
Siesjö, B.K. (1990) Calcium in the brain under physiological and pathological conditions.Eur. Neurol. 30(Suppl. 2), 3–9.
Sohal, R.S., Farmer, K.J. and Allen, R.G. (1987) Correlates of longevity in two strains of the housefly,Musca domestica.Mech. Ageing Dev. 40, 171–179.
Sonsalla, P.K., Zeevalk, G.D., Manzino, L., Giovanni, A. and Nicklas, W.J. (1992) MK-801 fails to protect against the dopaminergic neuropathology produced by systemic l-methyl-4-phenyl-l,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine in mice or intranigral l-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium in rats.J. Neurochem. 58, 1979–1982.
Steiner, J.P., Hamilton, G.S., Ross, D.T., Valentine, H.L., Guo, H.Z., Connolly, M.A., Liang, S., Ramsey, C, Li, J.H.J., Huang, W., Howorth, P., Soni, R., Fuller, M., Sauer, H., Nowotnik, A.C., and Suzdak, P.D. (1997) Neurotrophic immunophilin ligands stimulate structural and functional recovery in neurodegenerative animal models.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94, 2019–2024.
Szabo, L. and Hofmann, H.P. (1989) (S)-Emopamil, a novel calcium and serotonin antagonist for the treatment of cerebrovascular disorders. 3rd Communication: Effect on postischemic cerebral blood flow and metabolism, and ischemic neuronal cell death.Arzneim.-Forsch./Drug Res. 39, 314–319.
Tatton, N.A. and Kish, S.J. (1997)In situ detection of apoptotic nuclei in the substantia nigra compacta of l-methyl-4- phenyl-l,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine-treated mice using terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase labelling and acridine orange staining.Neuroscience 77, 1037–1048.
Tatton, W.G., Chalmers-Redman, R.M.E., Ju, W.Y.H., Wadia, J. and Tatton, N.A. (1997) Apoptosis in neurodegenerative disorders: Potential for therapy by modifying gene transcription.J. Neural Transm. 49(Suppl.), 245–268.
Temlett, J.A., Landsberg, J.P., Watt, F. and Grime, G.W. (1994) Increased iron in the substantia nigra compacta of the MPTP-lesioned hemiparkinsonian african green monkey: Evidence from proton microprobe elemental microanalysis.J. Neurochem. 62, 134–146.
Tolmasoff, J.M., Ono, T. and Cutler, R.G. (1980) Superoxide dismutase: Correlation with lifespan and specific metabolite rate in primate species.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 77, 2777–2781.
Trump, B.F. and Berezesky, I.K. (1995) Calcium-mediated cell injury and cell death.FASEB J. 9, 219–228.
Tsukahara, T., Takeda, M., Shimohama, S., Ohara, O. and Hashimoto, N. (1995) Effects of brain-derived neurotrophic factor on l-methyl-4-phenyl-l,2,3,6-tetrahydro- pyridine-induced parkinsonism in monkeys.Neurosurgery 37, 733–739.
Turski, L., Bressler, K., Rettig, K.-J., Löschmann, P.-A. and Wachtel, H. (1991) Protection of substantia nigra from MPP+ neurotoxicity by N-methyl-D-aspartate antagonists.Nature 349, 414–418.
Wagner, G.C., Jarvis, M.F. and Carelli, R.M. (1985) Ascorbic acid reduces the dopamine depletion induced by MPTP.Neuropharmacology 24:1261–1262.
Whitehouse, P.J., Price, D.L., Clark, A.W., Coyle, J.T. and DeLong, M.R. (1981) Alzheimer disease: Evidence for selective loss of cholinergic neurons in the nucleus basalis.Ann. Neurol. 10, 122–126.
Yoshikawa, T., Minamiyama, Y, Naito, Y and Kondo, M. (1994) Antioxidant properties of bromocriptine, a dopamine agonist.J. Neurochem. 62, 1034–1038.
Zang, L.Y and Misra, H.P. (1992) EPR kinetic studies of Superoxide radicals generated during the autoxidation of l-methyl-4-phenyl-2,3-dihydropyridinium, a bioactivated intermediate of Parkinsonian-inducing neurotoxin l-methyl-4-phenyI-l,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine.J. Biol. Chem. 267, 23601–23608.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gerlach, M., Double, K.L., Youdim, M.B.H. et al. Strategies for the protection of dopaminergic neurons against neurotoxicity. neurotox res 2, 99–114 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03033788
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03033788