Abstract
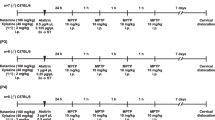
To explore a recently established association between histaminergic and dopaminergic neuronal phenotypic systems in brain, we determined the effect of the respective histaminergic H3 receptor agonist and antagonist/inverse agonist, imetit and thioperamide, on L-DOPA — derived tissue and extracellular dopamine (DA) and metabolite levels in the striatum of 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA) - lesioned rats (i.e., parkinsonian rats). We also examined the influence of histamine H3 ligands on L-DOPA evoked behavioral responses (locomotor activity, number of rearings, stereotyped behavior and motor coordination). Using HPLC/ED andin vivo microdialysis technique, imetit (5 mg/kg, i.p.) but not thioperamide (5 mg/kg, i.p.) was shown to attenuate an L-DOPA-evoked (15 mg/ kg, i.p.; carbidopa, 30 min pretreatment) increase in extracellular DA in the neostriatum of 6-OHDA-lesioned rats. However, both imetit and thioperamide increased microdialysate levels of DOPAC and HVA, probably by enhancing intraneuronal DA utilization. As indicated by neurochemical analysis of the striatum imetit produced a decrease in tissue DA content. These findings support the hypothesis that central H3 histaminergic receptors have a modulatory role in the storage, metabolism and release of DA derived from exogenous L-DOPA challenge. Furthermore, evidence from behavioral studies indicate that histamine H3 receptor block markedly improved motor coordination. Conversely, histamine H3 receptor stimulation, being without effect on motor coordination, enhanced vertical activity in rats. From the above we conclude that histamine H3 agonism may augment motor dyskinesia in Parkinson’s disease (PD) patients and presumably worsen L-DOPA therapy. Consequently, the histaminergic system represents a viable target for modulating the effectiveness of L-DOPA therapy in Parkinson’s disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anichtchik OV, N Peitsaro, JO Rinne, H Kalimo and P Panula (2001) Distribution and modulation of histamine H3 receptors in basal ganglia and frontal cortex of healthy controls and patients with Parkinson’s disease.Neurobiol. Dis. 8, 707–716.
Arias-Monatano JA, B Floran, M Garcia, J Aceves and JM Young (2001) Histamine H3 receptor-mediated inhibition of depolarization-induced, dopamine D1 receptor-dependent release of [3H]-γ-aminobutryic acid from rat striatal slices.Br. J. Pharmacol. 133, 165–171.
Arrang JM, B Devaux, JP Chodkiewicz and JC Schwartz (1988) H3-receptors control histamine release in human brain.J. Neurochem. 51, 105–108.
Brown RE, DR Stevens and HL Haas (2001) The physiology of brain histamine.Prog. Neurobiol. 63, 637–672.
Brus R, P Nowak, A Sokola, RM Kotrzewa and J Shani (2002) Behavioral and biochemical effects of new central dopamine D3 and D4 receptor antagonists in rats.Pharmacol. Rev. Comm. 12, 39–59.
Brus R, RM Kostrzewa, P Nowak, KW Perry and JP Kostrzewa (2003) Ontogenetic quinpirole treatments fail to prime for D2 agonist-enhancement of locomotor activity in 6-hydroxydopamine- lesioned rats.Neurotox. Res. 5, 329–338.
Clapham J and GJ Kilpatrick (1994) Thioperamide, the selective histamine H3 receptor antagonist, attenuates stimulantinduced locomotor activity in the mouse.Eur. J. Pharmacol. 259, 107–114.
Creese I and SD Iversen (1975) Behavioral sequel of dopaminergic degeneration: post-synaptic supersensitivity, In: Modern Pharmacology - Toxicology (Ellsodin JR and JR Buney, Eds.) (Marcel Dekker Publ.) 3, 171–190.
Cumming P, C Shaw and SR Vincent (1991) High affinity histamine binding site is the H3 receptor: characterization and autoradiographic localization in rat brain.Synapse 8, 144–151.
Farzin D and M Attarzadeh (2000) Influence of different histamine receptor agonists and antagonists on apomorphineinduced licking behavior in rat.Eur. J. Pharmacol. 404, 169–174.
Ganellin CR, SK Hosseini, YS Khalaf, W Tertiuk, JM Arrang, M Garbarg, X Ligneau and JC Schwartz (1995) Design of potent non-thiourea H3-receptor histamine antagonists.J. Med. Chem. 38, 3342–3350.
Garbarg M, JM Arrang, A Rouleau, X Ligneau, MD Tuong, JC Schwartz and CR Ganellin (1992) S-[2-(4-imidazolyl) ethyl] isothiourea, a highly specific and potent histamine H3 receptor agonist.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 263, 304–310.
Garcia M, B Floran, JA rias-Monatano, JM Young and Aceves (1997) Histamine H3 receptor activation selectively inhibits dopamine D1 receptor-dependent [3H]GABA release from depolarization-stimulated slices of rat substantia nigra pars reticulata.Neuroscience 80, 241–249.
Garcia-Ramirez M, J Aceves and JA Arias-Montano (2004) Intranigral injection of the H3 agonist immepip and systemic apomorphine elicit ipsilateral turning behaviour in naive rats, but reduce contralateral turning in hemiparkinsonian rats.Behav. Brain Res. 154, 409–415.
Gibb WR (1997) Functional neuropathology in Parkinson’s disease.Eur. Neurol. 38, 21–25.
Huotari M, K Kukkonen, N Liikka, T Potasev, A Raasmaja and PT Mannisto (2000) Effects of histamine H3-ligands on the levodopa-induced turning behavior of hemiparkinsonian rats.Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 6, 159–164.
Johnston TH, J Lee, J Gomez-Ramirez, SH Fox and JM Brotchie (2005) A simple rodent assay for thein vivo identification of agents with potential to reduce levodopa-induced dyskinesia in Parkinson’s disease.Exp. Neurol. 191, 243–250.
Kannari K, H Yamato, H Shen, M Tomiyama, T Suda and M Matsunaga (2001) Activation of 5-HT1A but not 5-HT1B receptors attenuates an increase in extracellular dopamine derived from exogenously administered L-DOPA in the striatum with nigrostriatal denervation.J. Neurochem. 76, 1346–1353.
Kostrzewa RM and L Gong (1991) Supersensitized D1 receptors mediate enhanced oral activity after neonatal 6-OHDA.Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 39, 677–682.
Kostrzewa RM, JP Kostrzewa, P Nowak, RA Kostrzewa and R Brus (2004) Dopamine D2 agonist priming in intact and dopamine-lesioned rats.Neurotox. Res. 6, 457–462.
Kostrzewa RM, P Nowak, JP Kostrzewa, RA Kostrzewa and R Brus (2005) Peculiarities of L-DOPA treatment of Parkinson’s disease.Amino Acids 28, 157–164.
Kostrzewa RM, JP Kostrzewa, R Brus, RA Kostrzewa and P Nowak (2006) Proposed animal model of severe Parkinson’s disease: neonatal 6-hydroxydopamine lesion of dopaminergic innervation of striatum.J. Neural. Transm. (Suppl.)70, 277–279.
Kostrzewa RM, NY Huang, JP Kostrzewa, P Nowak and R Brus (2007) Modeling tardive dyskinesia: predicitive 5-HT2C receptor antagonist treatment.Neurotox. Res. 11, 41–50.
Maeda T, K Kannari, T Suda and M Matsunaga (1999) Loss of regulation by presynaptic dopamine D2 receptors of exogenous L-DOPA-derived dopamine release in the dopaminergic denervated striatum.Brain Res. 817, 185–191.
Magnusson O, LB Nilsson and D Westerlund (1980) Simultaneous determination of dopamine, DOPAC and homovanillic acid. Direct injection of supernatants from brain tissue homogenates in a liquid chromatography--electrochemical detection system.J. Chromatogr. 221, 237–247.
Martinez-Mir MI, H Pollard, J Moreau, JM Arrang, M Ruat, E Traiffort, JC Schwartz and JM Palacios (1990) Three histamine receptors (H1, H2 and H3) visualized in the brain of human and non-human primates.Brain Res. 526, 322–327.
Moore DJ, AB West, VL Dawson and TM Dawson (2005) Molecular pathophysiology of Parkinson’s disease.Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 28, 57–87.
Nowak P, R Brus, J Oswiecimska, A Sokola and RM Kostrzewa (2002) 7-Nitroindazole enhances amphetamine-evoked dopamine release in rat striatum. Anin vivo microdialysis and voltammetric study.J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 53, 251–263.
Nowak P, RM Kostrzewa, A Kwiecinski, A Bortel, L Labus and R Brus (2005) Neurotoxic action of 6-hydroxydopamine on the nigrostriatal dopaminergic pathway in rats sensitized with D-amphetamine.J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 56, 325–333.
Nowak P, J Dabrowska, G Szczerbak, I Biedka, R Brus and RM Kostrzewa (2006a) Effect of the central H3 histamine receptor agonist and antagonist on D1 evoked behavioral responses in rats with dopaminergic system denervation.Eur. J. Pharmacol. 552, 46–54.
Nowak P, G Szczerbak, I Biedka, M Drosik, RM Kostrzewa and R Brus (2006b) Effect of ketanserin and amphetamine on nigrostriatal neurotransmission and reactive oxygen species in Parkinsonian rats.In vivo microdialysis study.J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 57, 583–597.
Ossowska K, J Wardas, M Smialowska, K Kuter, T Lenda, JM Wieronska, B Zieba, P Nowak, J Dabrowska, A Bortel, A Kwiecinski and S Wolfarth (2005) A slowly developing dysfunction of dopaminergic nigrostriatal neurons induced by long-term paraquat administration in rats: an animal model of preclinical stages of Parkinson’s disease?Eur. J. Neurosci. 22, 1294–1304.
Perez-Garcia C, L Morales, MV Cano, I Sancho and LF Alguacil (1999) Effects of histamine H3 receptor ligands in experimental models of anxiety and depression.Psychopharmacology (Berl.) 142, 215–220.
Pollard H, J Moreau, JM Arrang and JC Schwartz (1993) A detailed autoradiographic mapping of histamine H3 receptors in rat brain areas.Neuroscience 52, 169–189.
Ryu JH, K Yanai and T Watanabe (1994) Marked increase in histamine H3 receptors in the striatum and substantia nigra after 6-hydroxydopamine-induced denervation of dopaminergic neurons: an autoradiographic study.Neurosci. Lett. 178, 19–22.
Ryu JH, K Yanai, XL Zhao and T Watanabe (1996) The effect of dopamine D1 receptor stimulation on the up-regulation of histamine H3-receptors following destruction of the ascending dopaminergic neurones.Br. J. Pharmacol. 118(3), 585–592.
Sanchez-Lemus E and JA Arias-Montano (2004) Histamine H3 receptor activation inhibits dopamine D1 receptor-induced cAMP accumulation in rat striatal slices.Neurosci. Lett. 364, 179–184.
Schlicker E, K Fink, M Detzner and M Gothert (1993) Histamine inhibits dopamine release in the mouse striatum via presynaptic H3 receptors.J. Neural. Transm. Gen. Sect. 93, 1–10.
Song YN, HZ Li, JN Zhu, CL Guo and JJ Wang (2006) Histamine improves rat rota-rod and balance beam performances through H2 receptors in the cerebellar interpositus nucleus.Neuroscience 140, 33–43.
Takeda H, T Matsumiya and T Shibuya (1990) Detection and identification modes for the highly sensitive and simultaneous determination of various biogenic amines by coulometric high-performance liquid chromatography.J. Chromatogr. 515, 265–278.
Tanaka H, K Kannari, T Maeda, M Tomiyama, T Suda and M Matsunaga (1999) Role of serotonergic neurons in L-DOPAderived extracellular dopamine in the striatum of 6-OHDAlesioned rats.Neuroreport 10, 631–634.
Threlfell S, SJ Cragg, I Kallo, GF Turi, CW Coen and SA Greenfield (2004) Histamine H3 receptors inhibit serotonin release in substantia nigra pars reticulata.J. Neurosci. 24, 8704–8710.
Toyota H, C Dugovic, M Koehl, AD Laposky, C Weber, K Ngo, Y Wu, DH Lee, K Yanai, E Sakurai, T Watanabe, C Liu, J Chen, AJ Barbier, FW Turek, WP Fung-Leung and TW Lovenberg (2002) Behavioral characterization of mice lacking histamine H3 receptors.Mol. Pharmacol. 62, 389–397.
Widnell K (2005) Pathophysiology of motor fluctuations in Parkinson’s disease.Mov. Disord. 20, S17-S22.
Wieland K, G Bongers, Y Yamamoto, T Hashimoto, A Yamatodani, WM Menge, H Timmerman, TW Lovenberg and R Leurs (2001) Constitutive activity of histamine H3 receptors stably expressed in SK-N-MC cells: display of agonism and inverse agonism by H3 antagonists.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 299, 908–914.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nowak, P., Bortel, A., Dabrowska, J. et al. Histamine H3 receptor ligands modulate L-dopa-evoked behavioral responses and L-dopa-derived extracellular dopamine in dopamine-denervated rat striatum. neurotox res 13, 231–240 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03033506
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03033506