Abstract
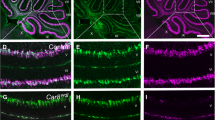
Leaner mice carry a homozygous, autosomal recessive mutation in the mouse CACNA1A gene encoding the α1A subunit of P/Q-type calcium channels, which results in an out-of-frame splicing event in the carboxy terminus of the α1A protein. Leaner mice exhibit severe ataxia, paroxysmal dyskinesia and absence seizures. Functional studies have revealed a marked decrease in calcium currents through leaner P/Q-type channels and altered neuronal calcium ion homeostasis in cerebellar Purkinje cells. Histopathological studies of leaner mice have revealed extensive postnatal cerebellar Purkinje and granule cell loss. We examined the temporospatial pattern of cerebellar granule cell death in the leaner mouse between postnatal days (P) 10 and 40. Our observations clearly indicate that leaner cerebellar granule cells die via an apoptotic process and that the peak time of neuronal death is P20. We did not observe a significant increase in microglial and astrocytic responses at P20, suggesting that glial responses are not a cause of neuronal cell death. We propose that the leaner cerebellar granule cell represents anin vivo animal model for low intracellular [Ca2+]-induced apoptosis. Since intracellular [Ca2+] is critical in the control of gene expression, it is quite likely that reduced intracellular [Ca2+] could activate a lethal cascade of altered gene expression leading to the apoptotic granule cell death in the leaner cerebellum.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott LC and DM Jacobowitz (1995) Development of calretinin-immunoreactive unipolar brush-like cells and an afferent pathway to the embryonic and early postnatal mouse cerebellum.Anat. Embryol. 191, 541–559.
Abbott LC and C Sotelo (2000) Ultrastructural analysis of cate-cholaminergic innervation in weaver and normal mouse cerebel-lar cortices.J. Comp. Neurol. 426, 316–329.
Alavez S, D Pedroza and J Moran (2003) Mechanisms of cell death by deprivation of depolarizing conditions during cerebellar granule neurons maturation.Neurochemistry 43, 581–590.
Annunziato L, S Amoroso, A Pannaccione, M Cataldi, G Pignataro, A D’Alessio, R Sirabella, A Secondo, L Sibaud and GF Di Renzo (2003) Apoptosis induced in neuronal cells by oxidative stress: role played by caspases and intracellular calcium ions.Toxicol. Lett. 139, 125–133.
Cassia P, H Peluffo, M Pehar, L Martinez-Palma, A Ressia, JS Beckman, AG Estevez and L Barbeito (2002) Peroxynitrite triggers a phenotypic transformation in spinal cord astrocytes that induces motor neuron apoptosis.J. Neurosci. Res. 67, 21–29.
Dove LS, LC Abbott and WH Griffith (1998) Whole-cell and single-channel analysis of P-type calcium currents in cerebellar Purkinje cells of leaner mutant mice.J. Neurosci. 18, 7687–7699.
Dove LS, SS Nahm, D Murchison, LC Abbott and WH Griffith (2000) Altered calcium homeostasis in cerebellar Purkinje cells of leaner mutant mice.J. Neurophysiol. 84, 513–524.
Enari M, H Sakahira, H Yokoyama, K Okawa, A Iwamatsu and S Nagata (1998) A caspase-activated DNase that degrades DNA during apoptosis, and its inhibitor ICAD.Nature 391, 43–50.
Fiskum G, A Starkov, BM Polster and C Chinopoulos (2003) Mitochondrial mechanisms of neural cell death and neuroprotec-tive interventions in Parkinson’s disease.Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 991, 111–119.
Fletcher CF, CM Lutz, TN O’Sullivan, JD Shaughnessy Jr, R Hawkes, WN Frankel, NG Copeland and NA Jenkins (1996) Absence epilepsy in tottering mutant mice is associated with calcium channel defects.Cell 87, 607–617.
Frank TC, M Nunley, R Ramon and LC Abbott (2003) Fluoro-Jade identification of cerebellar granule cell and Purkinje cell death in the ?1A calcium ion channel mutant mouse, leaner.Neuroscience 118, 667–680.
Gastard MC, JC Troncoso and VE Koliatsos (2003) Caspase activation in the limbic cortex of subjects with early Alzheimer’s disease.Ann. Neurol. 54, 393–398.
Gillard SE, SG Volsen, W Smith, RE Beattie, D Bleakman and D Lodge (1997) Identification of the pore-forming subunit of calcium channels: an antisense study on rat cerebellar Purkinje cells in culture.Neuropharmacology 36, 405–409.
Haughey NJ, A Nath, SL Chan, AC Borchard, MS Rao and MP Mattson (2002) Disruption of neurogenesis by amyloid beta-pep-tide, and perturbed neural progenitor cell homeostasis, in models of Alzheimer’s disease.J. Neurochem. 83, 1509–1524.
Heckroth JA and LC Abbott (1994) Purkinje cell loss from alternating sagittal zones in the cerebellum of leaner mutant mice.Brain Res. 658, 93–104.
Hengartner MO (2000) The biochemistry of apoptosis.Nature 407, 770–776.
Herrup K and SLWilczynski (1982) Cerebellar cell degeneration in the leaner mouse.Neuroscience 7, 2185–2196.
Hu J, A Ferreira and LJ Van Eldik (1997) S100beta induces neu-ronal cell death through nitric oxide release from astrocytes.J. Neurochem. 69, 2294–2301.
Ichikawa D, A Tabuchi, A Taoka, T Tsuchiya and M Tsuda (1998) Attenuation of cell death mediated by membrane depolarization different from that by exogenous BDNF in cultured cerebellar granule cells.Mol. Brain Res. 56, 218–226.
Isaacs KR and LC Abbott (1992) Development of the paramedian lobule of the cerebellum in wild type and tottering mice.Dev. Neurosci. 14, 386–393.
Jouvenceau A, LH Eunson, A Spauschus, V Ramesh, SM Zuberi, DM Kullmann and MG Hanna (2001) Human epilepsy associated with dysfunction of the brain P/Q-type calcium channel.Lancet 358, 801–807.
Juurlink B and LHertz (1993) Ischemia-induced death of astrocytes and neurons in primary culture: pitfalls in quantifying neuronal cell death.Dev. Brain Res. 71, 239–246.
Kerr JF, AH Wyllie and AR Currie (1972) Apoptosis: a basic biological phenomenon with wide-ranging implications in tissue kinetics.Br. J. Cancer 26, 239–257.
Kim JY, AL Nelson, SA Algon, O Graves, LM Sturla, LC Goumnerova, DH Rowitch, RA Segal and SLPomeroy (2003) Medulloblastoma tumorigenesis diverges from cerebellar granule cell differentiation in patched heterozygous mice.Dev. Biol. 263, 50–66.
Lau FC, LC Abbott, IJ Rhyu, DS Kim and HM Chin (1998) Expression of calcium channel ?1A mRNA and protein in the leaner mouse (tgla/tgla) cerebellum.Mol. Brain Res. 59, 93–99.
Lee JW, JH Richburg, SC Younkin and K Boekelheide (1997) The Fas system is a key regulator of germ cell apoptosis in the testis.Endocrinology 138, 2081–2988.
Li SY, JH Ni, DS Xu and HT Jia (2003) Down-regulation of GluR2 is associated with Ca2+-dependent protease activities in kainate-induced apoptotic cell death in cultured rat hippocampal neurons.Neurosci. Lett. 352, 105–108.
Liu B, K Wang, HM Gao, B Mandavilli, JY Wang and JS Hong (2001) Molecular consequences of activated microglia in the brain: overactivation induces apoptosis.J. Neurochem. 77, 182–189.
Lorenzon NM, CM Lutz, WN Frankel and KG Beam (1998) Altered calcium channel currents in Purkinje cells of the neurological mutant mouse leaner.J. Neurosci. 18, 4482–4489.
Lossi L, S Mioletti and A Merighi (2002) Synapse-independent and synapse-dependent apoptosis of cerebellar granule cells in postnatal rabbits occur at two subsequent but partly overlapping developmental stages.Neuroscience 112, 509–523.
Lubec G and E Engidawork (2002) The brain in Down syndrome (TRISOMY 21).J. Neurol. 249, 1347–1356.
Mark MD, S Whittemann and S Herlitze (2000) G protein modulation of recombinant P/Q-type calcium channels by regulators of G protein signaling proteins.J. Physiol. 528, 65–77.
Marx J (2001) Neuroscience. New leads on the ’how’ of Alzheimer’s.Science 293, 2192–2194.
Mattson MP (2000) Apoptosis in neurodegenerative disorders.Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 1, 120–129.
Meacham, CA, LD White, S Barone Jr and TJ Shafer (2003) Ontogeny of voltage-sensitive calcium channel 1A and 1E sub-unit expression and synaptic function in rat central nervous system.Brain Res. Dev. Brain Res. 142, 47–65.
Meier H and AD McPike (1971) Three syndromes produced by two mutant genes in the mouse. Clinical, pathological, and ultrastruc-tural bases of tottering, leaner, and heterozygous mice.J. Heredity 62, 297–302.
Meier P, A Finch and G Evan (2000) Apoptosis in development.Nature 407, 796–801.
Migheli A, A Attanasio, WH See, SA Bayer and B Ghetti (1995) Detection of apoptosis in weaver cerebellum by electron microscopicin situ end-labeling of fragmented DNA.Neurosci. Lett. 199, 53–56.
Murchison D, LS Dove, LC Abbott and WH Griffith (2002) Homeostatic compensation maintains Ca2+ signaling functions in Purkinje neurons in the leaner mutant mouse.Cerebellum 1, 119–127.
Norman DJ, L Feng, SS Cheng, J Gubbay, E Chan and N Heintz (1995) The lurcher gene induces apoptotic death in cerebellar Purkinje cells.Development 121, 1183–1193.
Ophoff RA, GM Terwindt, MN Vergouwe, R van Eijk, PJ Oefner, SM Hoffman, JE Lamerdin, HW Mohrenweiser, DE Bulman, M Ferrari, J Haan, D Lindout, G-JB van Ommen, MH Hofker, MD Ferarri and RR Frants (1996) Familial hemiplegic migraine and episodic ataxia type-2 are caused by mutations in the Ca2+ channel gene CACNL1A4.Cell 87, 543–552.
Oppenheim RW (1991) Cell death during development of the nervous system.Ann. Rev. Neurosci. 14, 453–501.
Penkowa M, A Molinero, J Carrasco and J Hidalgo (2001) Interleukin-6 deficiency reduces the brain inflammatory response and increases oxidative stress and neuroprotection after kainic acid-induced seizures.Neuroscience 102, 805–818.
Polazzi E, ET Gianni and A Contestablile (2001) Microglial cells protect cerebellar granule neurons from apoptosis: evidence for reciprocal signaling.Glia 36, 271–280.
Portera-Caillaiu C, JC Hedreen, DL Price and VE Koliatsos (1995) Evidence for apoptotic cell death in Huntington disease and exci-totoxic animal models.J. Neurosci. 15, 3775–3787.
Raff MC (1992) Social controls on cell survival and cell death.Nature 356, 397–400.
Raff MC, BA Barres, JF Burn, HS Coles, Y Ishizaki and MD Jacobson (1993) Programmed cell death and the control of cell survival: lessons from the nervous system.Science 262, 695–700.
Rakic P and RLSidman (1973) Weaver mutant mouse cerebellum: defective neuronal migration secondary to abnormality of Bergmann glia.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 70, 240–244.
Sastry PS and KS Rau (2000) Apoptosis and the nervous system.J. Neurochem. 74, 1–20.
Schmued LC, C Albertson and W Slikker Jr (1997) Fluoro-Jade: a novel fluorochrome for the sensitive and reliable histochemical localization of neuronal degeneration.Brain Res. 751, 37–46.
Sidman RL, MC Green and SH Appel (Eds.) (1965)Catalogue of the Neurological Mutants of the Mouse (Harvard University Press: Cambridge).
Smale G, NR Nichols, DR Brady, CE Finch and WE Horton Jr (1995) Evidence for apoptotic cell death in Alzheimer’s disease.Exp. Neurol. 133, 225–230.
Sortwell CE, BF Daley, MR Pitzer, SO McGuire, JR Sladek Jr and TJ Collier (2000) Oligodendrocyte-type 2 astrocyte-derived trophic factors increase survival of developing dopamine neurons through the inhibition of apoptotic cell death.J. Comp. Neurol. 426, 143–153.
Stoica G, O Illanes, SI Tasca and PKY Wong (1993) Temporal central and peripheral nervous system changes induced by a paraly-togenic mutant of moloney murine leukemia virus TB.Lab. Invest. 69, 724–735.
Su JH, G Deng and CW Cotman (1997) Bax protein expression is increased in Alzheimer’s brain: correlations with DNA damage, bcl-2 expression, and brain pathology.J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 56, 86–93.
Su JH, AJ Anderson, DH Cribbs, C Tu, L Tong, P Kesslack and CW Cotman (2003) Fas and Fas ligand are associated with neuritic degeneration in the AD brain and participate in beta-amyloid-induced neuronal death.Neurobiol. Dis. 12, 182–193.
Sugimoto A, PA Friesen and JH Rothman (1994) Baculovirous p35 prevents developmental programmed cell death and rescues a ced-9 mutant in the nematodeCaenorhabditis elegans.EMBO J. 13, 2023–2028.
Tabuchi A, E Funaji, J Nakatsubo, M Fukuchi, T Tsuchiya and M Tsuda (2003) Inactivation of aconitase during the apoptosis of mouse cerebellar granule neurons induced by a deprivation of membrane depolarization.J. Neurosci. Res. 71, 504–515.
Toescu EC (1999) Activity of voltage-opened calcium channels in rat cerebellar granule neurons and neuronal survival.Neuroscience 94, 561–570.
Vaudry D, A Falluel-More, S Leuillet, H Vaudry and BJ Gonzalez (2003) Regulators of cerebellar granule cell development act through specific signaling pathways.Science 300, 1532–1534.
Verhage M, AS Maia, JJ Plomb, AB Brussaard, JH Heeroma, H Vermeer, F Toonen Ruud, RE Hammer, TK van den Berg, M Missler, HJ Geuze and TC Sudhof (2000) Synaptic assembly of the brain I the absence of neurotransmitter secretion.Science 287, 864–869.
Westenbroek RE, T Sakurai, EM Elliott, JW Hell, TVB Starr, TP Snutch and WA Catterall (1995) Immunochemical identification and subcellular distribution of the ?1A subunits of brain calcium channels.J. Neurosci. 15, 6403–6418.
Wullner U, PA Loschmann, M Weller and T Klockgether (1995) Apoptotic cell death in the cerebellum of mutant weaver and lurcher mice.Neurosci. Lett. 200, 109–112.
Yoon WJ, SJ Won, RB Ryu and BJ Gwag (2003) Blockade of ionotropic glutamate receptors produces neuronal apoptosis through the Bax-cytochrome C-caspase pathway: the causative role of Ca2+ deficiency.J. Neurochem. 85, 525–533.
Yuan J and BA Yanker (2000) Apoptosis in the nervous system.Nature 407, 802–809.
Yuan J, M Lipinski and A Degterev (2003) Diversity in the mechanisms of neuronal cell death.Neuron 40, 401–413.
Zhang W, B Ghetti and WH Lee (1997) Decreased IGF-I gene expression during the apoptosis of Purkinje cells in pcd mice.Dev. Brain Res. 98, 164–176.
Zhou YD, TJ Turner and K Dunlap (2003) Enhanced G protein-dependent modulation of excitatory synaptic transmission in the cerebellum of the Ca2+ channel-mutant mouse, tottering.J. Physiol. 547, 497–507.
Zhuchenko O, J Bailey, P Bonnen, T Ashizawa, DW Stockton, C Amos, WB Dobyns, SH Subramony, HY Zoghbi and CC Lee (1997) Autosomal dominant cerebellar ataxia (SCA6) associated with small polyglutamine expansions in the? 1A-voltage-depend-ent calcium channel.Nat. Genet. 15, 62–69.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lau, F.C., Frank, T.C., Nahm, SS. et al. Postnatal apoptosis in cerebellar granule cells of homozygous leaner (tg la/tg la) mice. neurotox res 6, 267–280 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03033437
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03033437