Abstract
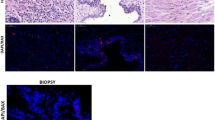
Cellular proliferation programmed cell death (apoptosis) are associated with tumor growth in general, and prostate cancer growth in particular. The aim of this study was to examine the expression of the apoptosis regulating genes bcl-2 and p53 and Gleason score in core needle biopsy specimens of prostate cancer using immunohistochemistry. We studied bcl-2 and p53 expression in 12 cases of low grade (Gleason score 2–5), 12 cases of intermediate grade (Gleason score 6–7) and 8 cases of high grade (Gleason score 8–10) prostate cancer. Overexpression of bcl-2 was noted in 3 of 32 patients (9.32%). One of them was high grade; others were intermediate grades. Expression of p53 was observed in 3 of low grades; others were high grade. The statistical analysis of present data suggest that there is no significant relation between p53 and bcl-2 expression and Gleason score in prostate cancer.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bauer JJ, Sesterhenn IA, Mostofi FK, et al; Elevated levels of apoptosis regulator proteins p53 and bcl-2 are independent prognostic biomarkers in surgically treated clinically localized prostate cancer. J Urol 156:1511–1516, 1996.
Boring CC, Squires T; Cancer statistics 1994. CA Cancer J Clin 44:7, 1994.
Bubendorf L, Sauter G, Moch H, et al; Prognostic significance of bcl-2 in clinically localized prostate cancer. Am J Pathol 148:1557, 1996.
Cheng L, Leibovich BC, Bergstralh EJ, et al; P53 Alteration in regional lymph node metastases from prostate carcinoma. Cancer 85:2455–2459, 1999.
Cheng L, Sebo JT, Pisansky T, et al; P53 Protein Overexpression Is Associated with Increased Cell Proliferation in Patients with Locally Recurrent Prostate Carcinoma after Radiation Therapy. Cancer 85:1293–1299, 1999.
Fox SB, Persad RA, Royds J, et al; p53 and c-myc expression in stage A1 prostatic adenocarcinoma: Useful prognostic determinants? J Urol 150:490–494, 1993.
Grignon DJ, Hammond EH; Collage of American pathologists conferance XXVI on clinical relevance of prognostic markers in solid tumors: Report of prostate cancer working group. Arch Pathol Lab Med 119:1122–1126, 1995.
Grossfeld GD, Olumi AF, Connolly JA, et al; Locally recurrent prostate tumors following either radiation therapy or radical prostatectomy have changes in Ki-67 labelling index, p53 and bcl-2 immunoreactivity. J Urology 159:1437–1443, 1998.
Hockenbery D, Nunez G, Milliam C, et al; Bcl-2 is an inner mitochondrial membrane protein that blocks programmed cell death. Nature 348:334, 1990.
Issacs JT; Molecular markers for prostate cancer metastasis: Devoloping diagnostic methods for predicting the aggressiveness of prostate cancer. Am J Pathol 150:1511–1521, 1997.
Kallakury BV, Figge J, Ross JS, et al; Association of p53 immunoreactivity with high Gleason tumor grade in prostatic adenocarcinoma. Human Pathol 25:92, 1994.
Levine AJ; P53, the cellular gatekeeper for growth and division. Cell88:323, 1997.
Masuda M, Takano Y, Iki M, et al; Prognostic Significance of Ki-67, p53 and bcl-2 expression in prostate cancer patients with lymph node metastases: A retrospective immunohistochemical analysis. Pathol Int:48:41–46, 1998.
Matsushima H, Kitamura T, Goto T, et al; Combined anaysis with bcl-2 and p53 immunostaining predicts poorer prognosis in prostatic carcinoma. J Urology 158:2278–2283, 1997.
Prendergest NJ, Atkins MR, Schatte EC, et al; p53 immunohistochemical and genetic alterations are associated at high incidence with post-irradiated locally persistent prostate carcinoma. J Urol 155:1685–92, 1996.
Piris MA, Pezzella F, Martinez-Montero JC, et al; p53 and bcl-2 expression in high grade B-cell lymphomas. Br J Cancer, 69:337, 1994.
Shurbaji MS, Kalbfleisch JH, Thurmond S; Immunohistochemical detection of p53 protein as a prognostic indicator in prostate cancer. Human Path 26:106–109, 1995.
Soini Y, Paakko P; Extent of Apoptosis in Relation to p53 and bcl-2 Expression in Germ Cell Tumors. Hum Pathol 27:1221–1226, 1996.
Von Eschenbach AC; The biologic dilemma of early carcinoma of prostate. Cancer 78:326–329, 1996.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paker, S.K., Kilicarslan, B., Ýftcýoglu, A.M.C. et al. Relationship between apoptosis regulator proteins (bcl-2 and p53) and Gleason score in prostate cancer. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 7, 209–212 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03032351
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03032351