Abstract
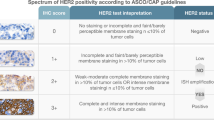
Breast cancer is an increasingly important cause of illness and death among women. In recent years several novel prognostic determinants of breast cancer have been identified, including c-ErbB-2. In this study, expression of c-ErbB-2 in breast carcinoma was correlated with axillary lymph node metastases and disease outcome. The expression of c-ErbB-2 oncoprotein was analysed in 315 tumor specimens of infiltrating ductal carcinoma of breast. They were categorized according to the modified Bloom and Richardson criteria into three histological grades. These patients also had axillary lymph nodes sampling. The expression of c-ErbB-2 oncoprotein was analysed immunohistochemically. Over expression of c-ErbB-2 were observed in 39.36% tumors. Axillary lymph node metastasis had significant correlation with intensified positivity of c-ErbB-2. C-ErbB-2 positive patients did show resistance to chemotherapy when compared for recurrence and distant metastases following surgery (p< 0.05). At a median follow-up of 48 months in c-ErbB-2 positive patients, the overall survival was 3.0 years and disease free survival was 2.5 years. c-ErbB-2 negative tumor patients showed a far better survival. In this group the overall survival was 4.44 years and the disease free survival was 3.78 years. These findings reinforce the view that c-ErbB-2 immunohistochemical detection is of help in detecting a subgroup of breast carcinoma patients who are at high risk. This may also be of particular relevance in decisions regarding adjuvant chemotherapy to these patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Guido S, Georg F, Joachim T; Fluorescence in Situ Hybridization for detecting C-ErbB-2 amplification in breast tumor fine needle aspiration biopsies. Acta Cytologica 40:164–173, 1996.
Muss HB, Thor AD, Berry DA; Cerb-B-2 expression and response to adjuvant therapy in women with node-positive early breast cancer. N Engl J Med 330:1260–1266, 1994.
William C; More than one way to look for HER-2. Cap Today 13:31–54, 1999.
Perren TJ; C-ErbB-2 oncogene as a prognostic marker in breast cancer. Br J Cancer 63:328–332, 1991.
van de Vijver MJ, Peterse JL, Mooi WJ; Neu-protein over expression in breast cancer. Association with comedo-type ductal carcinoma in situ and limited prognostic value in stage II breast cancer. N Engl J Med 319:1239–1245, 1988.
Aryandono-T, Harijadi, Ghozali-A; Correlation of clinical, pathological status, hormone receptor and C-ErbB-2 oncoprotein in breast cancer patients. Gan-To-Kagaku-Ryoho Suppl 2:600–606, 2000.
Looi-LM, Cheah-PL; C-ErbB-2 oncoprotein amplification in infiltrating ductal carcinoma of breast relates to high histological grade and loss of oestrogen receptor protein. Malays J Pathol. 20:19–23, 1998.
Wright C, Angus B, Nicholson S; Expression of c-ErbB-2-oncoprotein: a prognostic indicator in human breast cancer. Cancer Res 49:2087–2090, 1989.
Walker RA, Gullick WJ, Varley JM; An evaluation of immunoreactivity for C-ErbB-2 protein as a marker of poor short-term prognosis in breast cancer. Br J Cancer 60:426–429, 1989.
Barnes DM, Lammie GA, Millis RR; An immunohistochemical evaluation of C-ErbB-2 gene expression in human breast carcinoma. Br J Cancer 58:448–452, 1988.
Gusterson BA, Gelber RD, Goldhirsch A; Prognostic significance of C-ErbB-2 expression in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 10:1046–1049, 1992.
Tandon AK, Clark GM, Chamness GC; HER-2/neu oncogene protein and prognosis in breast cancer. J Clin Onco 1989; 17:1120–1128, 1989.
Tsuda H, Hirohashi S, Shimasto Y; Correlation between longterm survival in breast cancer patients and amplification of two putative oncogene-coamplification units, hst-1 / int-2 and CErbB-2 / ear-1. Cancer Res 49:3104–3110, 1989.
Borg A, Tandon AK, Sigurdsson H; HER-2/ neu amplification predicts poor survival in node-negative breast cancer. Cancer Res 50:4332–4337, 1990.
Slamon DJ, Clark GM, Wong SG; Human breast cancer: Correlation of relapse and survival with amplification of HER-2/neu oncogene. Science 235:177–183, 1987.
Wright C, Angus B, Nicholson S; Expression of c-ErbB-2-oncoprotein: a prognostic indicator in human breast cancer. Cancer Res 49:2087–2090, 1989.
Gullick WL, Wright C, Barnes D; C-ErbB-2 protein overexpression in breast carcinoma is a risk factor in patients with involved and uninvolved lymph nodes. Br J Cancer 63:434–438, 1991.
Cobleigh MA, Vogel CL, Tripathy D: Efficacy and safety of herceptin as a single agent in 222 women with HER-2 over expression who relapsed following chemotherapy for metastatic breast cancer. ASCO, Los Angeles California 1998; Abstract 376.
Slamon D, Leyland-Jones B, Shak S: Addition of herceptin to first line chemotherapy for HER-2 over expression metastatic breast cancer markedly increases anticancer activity; A randomised multinational controlled phase III trial. ASCO, Los Angeles California 1998; Abstract 377.
Jakic-Razumovic J, Petrovecki M, Uzarevic B; Mutual predictive value of c-ErbB-2 over expression and various prognostic factors in ductal invasive breast carcinoma. Tumori 86:30–36, 2000.
King CR, Kraus MH, Aaronson SA; Amplification of a v-erbB related gene in human mammary carcinoma. Science 229:974–976, 1985.
Berger MS, Locher GW, Saurer S; Correlation of C-ErbB-2 gene amplification and protein expression in human breast carcinoma with nodal status and nuclear grading. Cancer Res 48:1238–1243, 1985.
Slamon DJ, Godolphin W, Lones LA; Studies of HER-2/neu proto-oncogene in human breast and ovarian cancer. Science 244:707–712, 1989.
Ali IU, Campbell G, Lidereau R; Amplification of C-ErbB-2 and aggressive human breast tumors. Science 235:1795–1798, 1988.
Bernard T, Jacques B; Prognostic significance of HER-2 /neu oncoprotein expression in node-positive breast cancer. Cancer 73:2359–2365, 1994.
Sharma BK, Ray A, Kaur S; Immunohistochemical co-expression of c-ErbB-2/Neu oncoprotein, altered tumor suppressor (p53) protein, EGF-R and EMA in histological subtypes of infiltrating duct carcinoma of the breast. Indian J Exp Biol 37: 223–227, 1999.
Shimizu C, Fukutomi T, Tsuda H; c-ErbB-2 protein over expression and p53 immunoreaction in primary and recurrent breast cancer tissues. J Surg Oncol 73:17–20, 2000.
Baselga J, Tripathy D, Mendelsohn J; Phase II study of weekly intravenous trastuzumab (Herceptin) in patients with HER2/neu-overexpressing metastatic breast cancer. Semin Oncol 26 (Suppl 12): 78–83, 1992.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aziz, S.A., Pervez, S., Khan, S. et al. Significance of immunohistochemical c-ErbB-2 product localisation pattern for prognosis in human breast cancer. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 7, 190–196 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03032348
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03032348