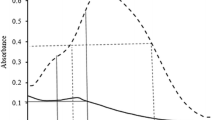
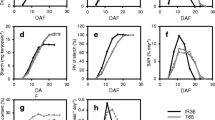
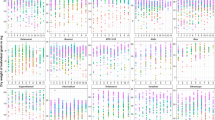
Abstract
Amylose and amylopectin are determinants of the physicochemical properties for starch and grain quality in rice. Their biosynthesis is catalyzed by the interplay of ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase (AGPase), granule-bound starch synthase (GBSS), soluble starch synthase (SSS), a starch branching enzyme (SBE), and a starch debranching enzyme (SDE). In this study, the genes for these enzymes were highly expressed 7 to 28 days after flowering during grain development, and their expression closely matched increases in both starch content and grain weight Among all the tested cultivars, amylose contents in the rice grains remained essentially constant throughout their development The AGPase gene was highly expressed in the high-yield cultivars of both glutinous and non-glutinous rice. The SSS gene was actively expressed when mature GBSS mRNA decreased. Genes responsible for amylopectin biosynthesis were simultaneously expressed in the late stage of grain development. We have now demonstrated that the expression patterns of starch biosynthetic genes differ between glutinous and non-glutinous rice, and between Tongil (a Japonica/ Indica hybrid) and Japonica types.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Baba T, Nishihara M, Mizunp K, Kawasaki T, Shimada H, Kobayashi E, Ohnishi S, Tanaka Kl, Arai Y (1993) Identification, cDNA cloning, and gene expression of soluble starch synthase in rice(Oryza sativa L.) immature seeds. Plant Physiol103: 565–573
Burton RA, Jenner H, Carrangis L, Fahy B, Fipcher GB, Hylton C, Laurie DA, Parker M, Waite D, Wegen SV, Verhoeven T, Denyer K (2002) Starch granule initiation and growth are altered in barley mutants that lack isoamylase activity. Plant J31: 97–112
Chen CL, Li CC, Sung LM (1994) Carbohydrate metabolism enzymes in CO2-enriched developing rice grains of cultivars varying in grain size. Physiol Plant90: 79–85
Chirgwin JM, Przybyla AE, Mac Donala RJ, Rutter WJ (1979) Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochem18: 5294–5304
Dry I, Smith A, Edwards A, Bhattacharyya M, Dunn P, Martin C (1992) Characterization of cDNAs encoding two isoforms of granule-bound starch synthase which show differential expression in developing storage organs of pea and potato. Plant J2: 193–202
Jane J, Chen YY, Lee LF, McPherson AE, Wong KS, Radosavljevic M, Kasemsuwan T (1999) Effects of amylopectin branch chain length and amylose content on the gelatinization and pasting properties of starch (1). Cereal Chem76: 629–637
Kim AK, Kim SK, Lee AR (1995) Comparison of chemical composition and gelatinization property of mung bean flour and starch. Kor J Soc Food Sci11: 30–36
Kim SK, Rhee CO (2004) Analysing and improving the texture of cooked rice,In D Kilkast, ed, Texture in Food, Vol 2. Solid Foods. Woodhead Publishing, Cambridge, pp 451–474
Kubo A, Fujita N, Harada K, Matsuda T, Satoh H, Nakamura Y (1999) The starch debranching enzymes isoamylase and pullulanase are both involved in amylopectin biosynthesis in rice endosperm. Plant Physiol121: 399–499
Lloyd JR, Springer F, Bulcon A, Mueller-Rowber B, Willmitzer L, Kossmann J (1999) The influence of alterations in ADP-glucose pyrophosphatase activities on starch structure and composition in potato tubers. Planta209: 230–238
Manners DJ (1989) Recent developments in our understanding of amylopectin structure. Carbohyd Polym11: 87–112
Mizuno K, Kimura K, Arai Y, Kawasaki T, Shimada H, Baba T (1992) Starch branching enzymes from immature rice seeds. J Biochem112: 643–651
Nakamura Y, Sakurai A, Inaba Y, Kimura K, Iwasawa N, Nagamine T (2002) The fine structure of amylopectin in endosperm from Asian cultivated rice can be largely classified into two classes. Starch54: 117–131
Ong MH, Blanshard JMV (1995) Texture determinants in cooked, parboiled rice. I. Rice starch amylose and the fine structure of amylopectin. J Cereal Sci21: 251–260
Preiss J (1991) Biology and molecular biology of starch synthesis and its regulation. Oxford Surv Plant Mol Cell Biol7: 59–114
Reddy KR, Ali SZ, Bhattacharya KR (1993) The fine structure of rice-starch amylopectin and its relation to the texture of cooked rice. Carbohyd Polym22: 267–275
Safford R., Jobling SA, Sidebottom CM, Westcott RJ, Cooke D, Tober KJ, Strongitharm BM, Russel AL, Gidley MJ (1998) Consequences of antisense RNA inhibition of starch branching enzyme activity on properties of potato starch. Carbohyd Polym35: 155–168
Smidansky ED, Martin JM, Hannah LC, Fischer AM, Giroux MJ (2003) Seed yield and plant biomass increases in rice are conferred by deregulation of endosperm ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase. Planta216: 656–664
Su J-C (2000) Starch synthesis and grain filling in rice,In AK Gupta, N Kaur, eds, Developments in Crop Science, Vol 26. Elsevier Science, Amsterdam, pp 107–124
Umemoto T, Terachima K, Nakamura Y, Satoh H (1999) Differences in amylopectin structure between two rice varieties in relation to the effects of temperature during grain-filling. Starch51: 58–62
van den Koornhuyse N, Libessart N, Delrue B, Zabawinski C, Decq A, Iglesias A, Carton A, Preiss J, Ball S (1996) Control of starch composition and structure through substrate supply in the monocellular algaClamydomonas reinhardtii. J Biol Chem271: 16281–16287
Wang L, Wang YJ, Porter R (2002) Structures and physico-chemical properties of six wild rice starches. J Agric Food Chem50: 2695–2699
Wang ZY, Zheng FQ, Shen GZ, Gao JP, Snustad DP, Li MG, Zhang JL, Hong MM (1995) The amylose content in rice endosperm is related to the post-transcriptional regulation of the waxy gene. Plant J7: 613–622
Williams PC, Kuzina FD, Hylnka I (1970) A rapid colorimetric procedure for estimating the amylase content of starches and flours. Cereal Chem47: 411–420
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hwang, JW., Kim, SK., Lee, JS. et al. Gene expression of the biosynthetic enzymes and biosynthesis of starch during Rice Grain development. J. Plant Biol. 48, 448–455 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03030587
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03030587