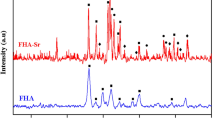
Abstract
The surface of implantable biomaterials is in direct contact with the host tissue and plays a critical role in determining biocompatibility. In order to improve the integration of implants, some attempts have been made to coat the surface of the biomaterial with calcium phosphate. In this investigation pure Ti, Ti-6A1-4V alloy and alkali treated specimens were used as implanted materials in the abdominal wall of mice. The implants were kept there for 3 months and then their biocompatibility was evaluated by optical microscope. Surface structural changes of specimens due to the alkali treatment and soaking in Hank’s solution were analyzed by XRD, SEM and XPS. Alkali treated specimens formed a dense and uniform bone-like apatite layer on the specimen surface when they were soaked in Hank’s solution. The average thickness of the fibrous capsule formed around the implant was much thinner for the alkali-treated specimens than the others. The number of macrophages was much less for the alkali-treated specimens than the others. The results of this evaluation indicate that alkali treated pure Ti and the Ti-6A1-4V alloy have better biocompatibility compared to the other metals tested.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Van Noort,J. Mater. Sci. 22, 3801 (1987).
H. Zitter and H. Plenk,J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 21, 881 (1987).
C. M. Cotell,Appl. Surf. Sci. 69, 140 (1993).
T. Brendel, A. Engel and C. Russel,J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med.3, 175 (1992).
D. F. Williams, I. N. Askill and R. Smith,J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 19, 313 (1985).
R. E. Baier,Adv. Chem. Ser. 145, 1 (1975).
L. Tang and J. W. Eaton,Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 103, 466 (1995).
H. Schreiber, F. Keller, HP. Kinzl, H. Hunger, W. Knofler, U. Rubling and W. Merten,Z Exp. Chir. Transplant Kunstliche Organe. 23, 23 (1990).
C. C. Mery, G. Grunert, J. C. Plaza and T. Pizzi,Biol. Res. 29, 361 (1996).
Xu Zhang, Fumiaki Miyaji, Takeshi Yao, Tadashi Kokubo and Chikara Ohtsuki,J. Japan. Soc. Powder. Powder Metall. 4, 664 (1994).
H. M. Kim, F. Miyaji and T. Kokubo,J. Jpn. Inst. of Metals 62, 1102 (1998).
T. Hanawa and M. Ota,Biomater. 12, 767 (1991).
W. J. Landis and J. K Martin,J. Vac. Sci. Tech A 2, 1108 (1984).
J. M. Anderson,ASAIO Trans. 34, 101 (1988).
T. N. Salthouse,J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 18, 395 (1984).
J. M. Morehead and G. R. Holt,Otolaryngology Clin. North Am. 27, 195 (1994).
J. F. Wolfaardt, P. Cleaton-Jones, J. Lownie, G. Ackermann and J. Prosthet,Dent. 68, 331 (1992).
R. F. Turner, D. J. Harrison and RV. Rajotte,Biomater. 12, 361 (1991).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, MH. Biocompatibility of a modified metallic surface of pure Ti and Ti-6Al-4V alloy with the connective tissue of mouse. Metals and Materials 6, 373–379 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03028085
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03028085