Abstract
Objective
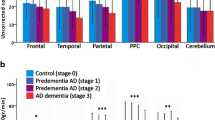
Treatment with donepezil improves cognitive function of patients with Alzheimer’s disease (AD) when compared to a placebo-controlled group. The purpose of this study was to investigate changes in regional cerebral blood flow (rCBF) of AD patients in short-term and long-term treatment with donepezil.
Methods
rCBF was measured byN-isopropyl-p-123I-iodoamphet-amine (IMP) autoradiography method. CBF measurements were performed in 17 AD patients before treatment and after 3 months (short-term therapy) and 1 year (long-term therapy). Regions of interest were set at cerebral cortex and cerebellar hemisphere. We used absolute CBF and relative CBF expressed as ratio to cerebellar CBF.
Results
Significant increases in relative rCBF were noted in the frontal, parietal and temporal lobes at the end of short-term therapy. rCBF was decreased after the long-term therapy, whereas rCBF was still increased to a slight extent, as compared with the pre-treatment levels. Absolute rCBF showed minimal change and a tendency to decline.
Conclusion
Relative rCBF significantly increased in the short-term donepezil therapy, while following the long-term therapy, rCBF decreased to the pre-treatment level.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kasa P, Papp H, Kasa P Jr, Torok I. Donepezil dose-dependently inhibits acetylcholinesterase activity in various areas and in the presynaptic cholinergic and the postsynaptic cholinoceptive enzyme-positive structures in the human and rat brain.Neuroscience 2000; 101:89–100.
Kaasinen V, Nagren K, Jarvenpaa T, Roivainen A, Yu M, Oikonen V, et al. Regional effects of donepezil and rivastigmine on cortical acetylcholinesterase activity in Alzheimer’s disease.J Clin Psychopharmacol 2002; 22: 615–620.
Rogers SL, Farlow MR, Doody RS, Mohs R, Friedhoff LT. A 24-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of donepezil in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Donepezil Study Group.Neurology 1998; 50: 136–145.
Ceravolo R, Volterrani D, Tognoni G, Dell’Agnello G, Manca G, Kiferle L, et al. Cerebral perfusional effects of cholinesterase inhibitors in Alzheimer disease.Clin Neuropharmacol 2004; 27: 166–170.
Nakano S, Asada T, Matsuda H, Uno M, Takasaki M. Donepezil hydrochloride preserves regional cerebral blood flow in patients with Alzheimer’s disease.J Nucl Med 2001; 42: 1441–1445.
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders,Fourth Edition (DSM-IV). Washington, DC; American Psychiatric Association, 1994: 123–163.
McKhann G, Drachman D, Folstein M, Katzman R, Price D, Stadlan EM. Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: report of the NINCDS-ADRDA working group under the auspices of the Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer’s Disease.Neurology 1984; 34: 939–944.
Iida H, Itoh H, Nakazawa M, Hatazawa J, Nishimura H, Onishi Y, et al. Quantitative mapping of regional cerebral blood flow using iodine-123-IMP and SPECT.J Nucl Med 1994; 35: 2019–2030.
Ichihara T, Ogawa K, Motomura N, Kubo A, Hashimoto S. Compton scatter compensation using the triple-energy window method for single- and dual-isotope SPECT.J Nucl Med 1993; 34: 2216–2221.
Minoshima S, Frey KA, Koeppe RA, Foster NL, Kuhl DE. A diagnostic approach in Alzheimer’s disease using three-dimensional stereotactic surface projections of fluorine-18-FDG PET.J Nucl Med 1995; 36: 1238–1248.
Minoshima S, Koeppe RA, Frey KA, Kuhl DE. Anatomic standardization: linear scaling and nonlinear warping of functional brain images.J Nucl Med 1994; 35: 1528–1537.
Whitehouse PJ, Price DL, Clark AW, Coyle JT, DeLong MR. Alzheimer disease: evidence for selective loss of cholinergic neurons in the nucleus basalis.Ann Neurol 1981; 10: 122–126.
Sugimoto H, Iimura Y, Yamanishi Y, Yamatsu K. Synthesis and structure-activity relationships of acetylcholinesterase inhibitors: l-benzyl-4-[(5,6-dimethoxy-l-oxoindan-2-yl)methyl]piperidine hydrochloride and related compounds.J Med Chem 1995; 38: 4821–4829.
Homma A, Takeda M, Imai Y, Udaka F, Hasegawa K, Kameyama M, et al. Clinical efficacy and safety of donepezil on cognitive and global function in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. A 24-week, multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled study in Japan. E2020 Study Group.Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 2000; 11: 299–313.
Burns A, Rossor M, Hecker J, Gauthier S, Petit H, Moller HJ, et al. The effects of donepezil in Alzheimer’s disease —results from a multinational trial.Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 1999; 10:237–244.
Rogers SL, Friedhoff LT. Long-term efficacy and safety of donepezil in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease: an interim analysis of the results of a US multicentre open label extension study.Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 1998; 8:67–75.
Nobili F, Koulibaly M, Vitali P, Migneco O, Mariani G, Ebmeier K, et al. Brain perfusion follow-up in Alzheimer’s patients during treatment with acetylcholinesterase inhibitors.J Nucl Med 2002; 43: 983–990.
Staff RT, Gemmell HG, Shanks MF, Murray AD, Venneri A. Changes in the rCBF images of patients with Alzheimer’s disease receiving Donepezil therapy.Nucl Med Commun 2000; 21: 37–41.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ushuima, Y., Okuyama, C., Mori, S. et al. Regional cerebral blood flow in Alzheimer’s disease: Comparison between short and long-term donepezil therapy. Ann Nucl Med 20, 425–429 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03027378
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03027378