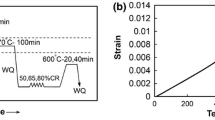
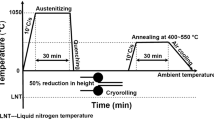
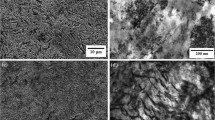
Abstract
Low carbon steels containing carbon less than 0.2 wt.% are the most widely used ferrous alloys in structural application. These steels consist of ferrite of large volume fraction with pearlite as the remainder and exhibit a strength of ∼400 MPa. To date, considerable effort has been devoted to enhancing the strength of these steels. However, existing methods of improving their strength are limited by the counter effect of loss of ductility and toughness. To overcome this deficiency, a new low carbon steel microstructure and its processing route are reported in this study. The steel with the new microstructure-submicrometer scale equiaxed ferrite grains with fine cementite particles distributed uniformly—was manufactured by imposing severe plastic deformation to introduce ultrafine ferrite grains and subsequent static annealing for uniform precipitation of nanosized cementite particles. The strength of the steel with the new microstructure increased nearly 100%, over 800 MPa, without significant loss of ductility.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. Gladman,The Physical Metallurgy of Microalloyed Steels, p. 63, The University Press, IOM, Cambridge, UK (1997).
R. Z. Valiev, R. K. Islamgaliev and I. V. Alexandrov,Prog. Mater. Sci. 45, 103 (2000).
Z. Horita, D. J. Smith, M. Furukawa, M. Nemoto, R. Z. Valiev and T. G. Langdon,J. Mater. Res. 11, 1880 (1996).
D. H. Shin, K. H. Oh, W. J. Kim, S. W. Lee and W. Y. Choo,J. Kor. Inst. Met. & Mater. 37, 1048 (1999).
D. H. Shin, W. J. Kim and W. Y. Choo,Scripta mater. 41, 259 (1999).
D. H. Shin, C. W. Seo, J. Kim, K. T. Park and W. Y. Choo,Scripta mater. 42, 695 (1999).
D. H. Shin, B. C. Kim, Y. S. Kim and K. T. Park,Acta mater. 48, 2247 (2000).
V. M. Segal,Mater. Sci. Eng. A 197, 157 (1995).
M. Nemoto, Z. Horita, M. Furukawa and T. G. Langdon,Metall. Mater. 4, 1181 (1998).
D. H. Shin, B. C. Kim, K. T. Park and W. Y. Choon,Acta mater. 48, 3245 (2000).
K. T. Park, Y. S. Kim, J. G. Lee and D. H. Shin,Mater. Sci. Eng. A 293, 165 (2000).
T. Oyama, O.D. Sherby, J. Wadsworth and B. Walser,Scripta metall. 18, 799 (1984).
E. M. Taleff, C. K. Syn, D. R. Lesuer and O. D. Sherby,Metall. Mater. Trans. A 27, 111 (1996).
C. Garcia-Mateo, B. Lopez and J. M. Rodriguez-Ibabe,Scripta mater. 42, 139 (2000).
C. Garcia-Mateo, B. Lopez and J. M. Rodriguez-Ibabe,Mater. Sci. Eng. A 303, 216 (2001).
J. Languillaume, G. Kapelski and B. Baudelet,Acta mater. 45, 1201 (1997).
M. H. Hong, W. J. Reynolds Jr., T. Tauri and K. Hono,Metall. Mater. Trans. A 30, 717 (1999).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shin, D.H., Kim, J. & Park, KT. A new low carbon steel microstructure: Ultrafine ferrite grains with homogeneously distributed fine cementite particles. Met. Mater. Int. 7, 431–435 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03027083
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03027083