Abstract
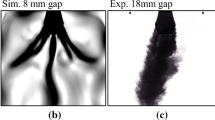
This study presents a simple and robust algorithm for the optimal design of the system with coupled complex transport phenomena: the transport phenomena comprise fluid flow, heat and mass transfer. The (1+1)-Evolution Strategy method is adopted as the optimization method. In order to analyze the transport phenomena in the complex geometry generated during the optimization procedure, thefinite volume method with a boundary fitted curvilinear coordinate system is used. To confirm the validity of the present method, the optimal design for the inner shape of the simplified two-dimensionalSubmerged Entry Nozzle in the continuous slab caster is conducted. It is shown that the resulting design of the nozzle is consistent with the purpose and constraints of the design.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. A. Schmit,Proc. 2nd Conf. on Electronic Computation, ASCE, New York (1960).
D. A. Tortorelli, M. M. Tiller and J. A. Dantzig,Comput. Meth. Appl. Mech. Eng. 113, 141 (1994).
Z. X. Wang, D. A. Tortorelli and J. A. Dantzig,Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 23, 991 (1996).
A. Törn and A. Zilinskas,Lecture Notes in Computer Science 350, Springer (1989).
T. Bäck,Evolution Algorithms in Theory and Practice, Oxford University Press, New York (1996).
H. P. Schwefel,Kybernetische Evolution als Strategie der Experimentellen Forschung in der Strömungstechnik, Diplomarbeit, Technishe Universität Berlin (1965).
I. Rechenberg,Evolution Strategie—Optimierung Technischer Systeme nach Prinzip-ien der Biologischen Evolution, Stuttgart (1973).
H. P. Schwefel,Numerische Optimierung von Computer-Modellen Mittels der Evo-lutionsstrategie, vol. 26, Interdisciplinary Systems Research, Birkbäuser, Basel (1977).
K. Y. Kim,Ph.D. Dissertation, Seoul National Univ. (1993).
P. R. Cha, Y. S. Hwang, Y. J. Oh, S. H. Chung and J. K. Yoon,ISIJ Int. 36, 1157 (1996).
P. R. Cha, Y. S. Hwang, H. S. Nam, S. H. Chung and J. K. Yoon,ISIJ Int. 38, 403 (1998).
S. V. Patankar,Numerical Heat Transfer and Fluid Flow, vol. 116, p. 16, McGraw-Hill, New York (1980).
A. W. Date,Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 36, 1913 (1993).
C. M. Rhie and W. L. Chow,AIAA J. 21, 1525 (1983).
J. O. Hinze,Turbulence, McGraw-Hill, New York (1975).
F. M. Najjar, B. G. Thomas and D. E. Hershey,Metall. Mater. Trans. B 26, 749 (1995).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cha, PR., Nam, HS., Jeon, DY. et al. Numerically optimal design for the system with coupled complex transport phenomena-application to the Submerged EntryNozzle in continuous slab caster. Met. Mater. Int. 8, 119–127 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03027038
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03027038