Abstract
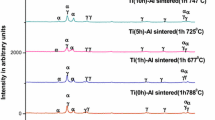
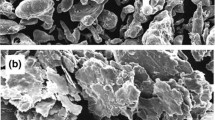
The effect of compact structure both on phase transition kinetics and on the densification during sintering of n-TiO2 compacts has been investigated. The compact structures varied from loose powder pack to very high density using different compaction pressures. The compact structure is verified to significantly affect phase transition kinetics and densification during sintering. The onset temperature of anatase -> rutile phase transition decreased with the increase of the compact density. The highest density compact of 86.9% showed phase transition at the lowest temperature and no detrimental effect on densification. The compact structure, i.e., the coordination number of particles in the compacts, is considered to significantly affect both the phase transition kinetics and the subsequent densification during the sintering of n-TiO2 compacts.
Access this article
We’re sorry, something doesn't seem to be working properly.
Please try refreshing the page. If that doesn't work, please contact support so we can address the problem.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Gleiter,Prog, in Mater. Sci. 33, 233 (1989).
H. Gleiter,Nanostruct. Mater. 1, 1 (1992).
H. Gleiter,Adv. Mater. 44, 474 (1992).
W. H. Rhodes,J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 64, 19 (1981).
F. W. Dynys and J. W. Halloran,J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 66, 655 (1983).
F. W. Dynys and J. W. Halloran,J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 67, 596 (1984).
T. S. Yeh and M. D. Sacks,J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 71, C484 (1988).
M. M. Yoshida, S. Tehuacanero and M. J. Yacaman,Surf. Sci. Lett. 274, L569 (1992).
R. C. Garvie,J. Phys. Chem. 69, 1238 (1965).
Y. Ishitobi, M. Shimada, and M. Koizumi,Ceram. Bull. 59, 1208 (1980).
F. W. Dynys and J.W. Halloran,J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 64, 442 (1982).
M. Kumakai and G. L. Messing,J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 68, 500 (1985).
T. C. Chou and T. G. Nieh,J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 74, 2270 (1991).
T. C. Chou and T. G. Nieh,Thin Solid Films 221, 89 (1992).
G. Skandan, C. M. Foster, H. Frase, M. N. AH, J. C. Parker, and H. Hahn,Nanostruct. Mater. 1, 313 (1992).
S. J. Wu and L. C. DeJonghe,J. Am Ceram. Soc. 79, 2207 (1996).
S. C. Nordahl and G. L. Messing,J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 79, 3149 (1996).
F. N. Rhines, inDynamic Particle Stacking in Ceramic Processing before Firing(eds., G.Y. Onoda and L. L. Hench), p. 321, A. Wiley-International Science Publ (1978).
C. S. Smith,Metall. Rev. 9, 1 (1964).
J. P. Ahn, M. Y. Huh and J. K. Park,Nanostruct. Mater. 8, 637 (1997).
J. P. Ahn, J. K. Park and M. Y. Huh,J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 80, 2165 (1997).
J. P. Ahn, J. K. Park and H. W. Lee,Nanostruct. Mater. (in press).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, JK., Ahn, JP. & Kim, G. Effect of compact structure on phase transformation kinetics from anatase phase to rutile phase and microstructure evolution during sintering of ultrafine titania powder compacts. Metals and Materials 5, 129–134 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03026042
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03026042