Abstract
Objective
To calculate héaring handicap in textile mill employees with noise induced hearing loss.
Design
Cross-sectional study.
Setting
Model Mills, Nagpur and Govt. Medical College, Nagpur.
Participants
77 employees with noise induced hearing loss.
Study Variables
Noise levels (by sound level meter), Noise Induced Hearing Loss (by audiometry), Hearing handicap (AAOO guidelines).
Statistical Analysis
Chi square test, Odds ratios, ANOVA.
Results
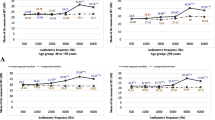
NIHL was significantly higher (76.6%) in employees exposed to >85 dB(A) than to 70-85 dB(A) (35.2%) and to <70 dB(A) (10.7%) (x2=60.6, df=2, p<0.001). Hearing handicap in employees with NIHL increased in severity as the noise level increased. Average hearing handicap was significantly higher (12.5%) in >85 dB(A) exposure group than 70-85 dB(A) (7.9%) and <70 dB(A) (4.9%) exposure groups (F=5.17, p <0.05). The risk of having hearing handicap >10% was 5.2 times higher in > 85 dB(A) exposure group than in <85 dB(A) exposure group (OR = 5.22, 95% C.I. 1.76-15.44).
Conclusion
One third of textile mill employees had hearing handicap. Noise levels >85 dB(A) are associated with high proportion as well as greater severity of hearing handicap.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alberti P.W. (1988): Noise and the ear. In : Stephens Dafydd, ed, Scott Brown’s Otolaryngology, Adult Audiology, Vol. 2. London : Butterworth International Edition, 594–641.
Allen R.W. Ells M.D., Hart A.W. (1976): Industrial Hygiene. New Jersy : Prentice Hall, Inc Englewood Cliffs, 206–239.
Bartsch R, Dicroff HG, Bruekner C. (1977): High frequency audiometry in evaluation of critical noise intensity. International Archieves of Occupational and Environmetal Health; 61: 347–351.
Catlin F.I. (1979) : Guide for the evaluation of hearing handicap. In : Cantrell R.W. ed, Symposium on noise—its effect and control. Otolaryngologic Clinics of North America; 12.
Hartman P.W. (1979): An Introduction to the Measurement of Sound. In : Cantrell R.W. ed, Symposium on noise—Its effect and control. Otolaryngol Clinics of North America; 12 : 551–561.
Hughes Lewis. (1974): Occupational exposure to noise. Journal of Occupational Medicine; 16 : 38.
Sataloff Joseph. (1957); Industrial deafness-hearing testing and noise measurement. USA: The Blackiston division, McGgaw Hill Book Company, Inc; 181–224.
World Health Organisation. (1980): Environmental Health Criteria 12 Noise. Geneva : WHO.
Yerg R.A. (1975): Protocol of interindustry noise study. Journal of Occupational Medicine; 17 : 760–764.
Yerg R.A., Sataloff J., Glorig A., Menduke H. (1978): Interindustry noise study, the effects upon hearing of steady state noise between 82 and 92 dB (A). Journal of Occupational Medicine; 20 351–358.
Guide for the Evaluation of Hearing Hadicap. Amer. Acad. Otol. Comm. on Hearing and Eqilibrium and Amer. Council of Otolaryngology Comm. on the Medical Aspects of Noise. (1979) : Journal of the American Medical Association : 241 : 2055–2059.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ruikar, M.M., Motghare, D.D. & Vasudeo, N.D. Evaluation of hearing handicap in textile mill employees with noise induced hearing loss. IJO & HNS 49, 97–100 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03023782
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03023782