Abstract
In the ten past years, the telecommunication industry has experienced an unprecedented growth rate. To follow the exponential Bandwidth demand, new transmission technologies have emerged. Amongst them, we find Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) technology. Its appearance coinciding with the emergence of key optical functions.
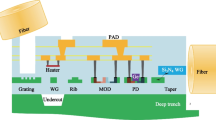
This paper addresses one of these key optical functions, today an absolute must: wavelength demultiplexing. This function can be realized thanks to a demultiplexer, also named AWG, the acronym for Arrayed Waveguide Gratings. It took only ten years to transform the first research experiments into real commercial products: demultiplexers using a silica on silicon planar platform.
This platform allowed yesterday the realization of demultiplexer AWG-products, managing high channels count at a relatively low cost, today this same platform allows the integration of complex optical functions with a more drastic cost reduction. As for tomorrow, transmission systems will continue to require new signal processing functions to permit high bit rate transmission. Once again, the AWG can play a key role.
Résumé
Ces dix dernières années, l’industrie des télécommunications a connu une croissance sans précédent. Afin de satisfaire la demande exponentielle en bande passante, de nouvelles technologies de transmission ont vu le jour. Parmi elles, se trouve la technologie de multiplexage en longueur d’onde, diteWDM (Wavelength Division Multiplexing). Son apparition s’est accompagnée de l’émergence de fonctions optiques clés.
Cet article a pour objet de faire un point sur l’une de ces fonctions optiques clés aujourd’hui incontournable: le démultiplexage en longueur d’onde. Cette fonction peut être réalisée grâce à un démultiplexeur autrement appelé AWG, cet acronyme reprenant l’anglais Arrayed Waveguide Grating (réseaux de guides d’onde). Il a fallu dix ans seulement pour que les premières expériences de laboratoires se transforment en véritables produits commerciaux: des démultiplexeurs utilisant une plate-forme planaire en silice sur silicium.
Si cette plate-forme planaire permettait hier de réaliser des produits AWG démultiplexeurs gérant un grand nombre de canaux pour un coût relativement faible, aujourd’hui, cette même plate-forme permet l’intégration de fonctions optiques complexes et une réduction encore plus drastique des coûts. Quant à demain, les systèmes de transmission continueront de requérir de nouvelles fonctions de traitement optique du signal pour permettre la transmission à très haut débit. Une fois encore, l’AWG peut jouer un rôle primordial.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Castelli (R.),Krause (T.), Market Trends and Evolution for Optical Transmission Systems,Alcatel Telecommunications Review, 3rd Quarter 1998,photonics — fiat lux.
Ollivier (F.-X.),Thompson (S.),Zugno (C.), Evolution of high speeddwdm backbone networks,Alcatel Telecommunications Review, 3rd Quarter 2000, optinexTM.
Borella (M.S.), Jue (J.P.);Banerjee (D.), Ramamurthy (B.), Mukherjee (B.),Optical components for WDM lightwave networks, Proceedings of the IEEE,85, Issue 8, Aug 1997, pp. 1274–1307.
Lebby (M.), Optical components and their role in optical networks,Electronic Components and Technology Conference, 2001. Proceedings., 51st, 2001, pp. 444–447.
Kato (K.), Tohmori (Y.), PLC hybrid integration technology and its application to photonic components, IEEE Journal on Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics,6, Issue 1, Jan/Feb 2000, pp. 4–13.
Smit (M. K.), New focusing and dispersive planar component based on an optical phased array,Electronics Letters,24, Issue 7, 31 Mar 1988, pp. 385–386.
Kawachi (M.) Recent progress in silica-based planar lightwave circuits on silicon,Optoelectronics, IEEProceedings,143, Issue 5, Oct 1996, pp. 257–262.
Okuno (M.), Recent progress on silica-based planar lightwave circuit technology,Lasers and Electro-Optics, 1999. CLEO/Pacific Rim ’99. The Pacific Rim Conference on,3, 1999, pp. 583–584.
Smit (M.K.), Van Dam (C.), PHASAR-basedWDM-devices: Principles, design and applications,Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics, IEEE Journal on,2, Issue 2, Jun 1996, pp. 236–250.
http://www.opsitech.com/pdf/AWG%20specifications.pdf.
Chen (J.C.), Dragone (C.), A proposed design for ultralow-loss waveguide grating routers,IEEE Photonics Technology Letters,10, Issue 3, Mar 1998, pp. 379–381.
Okuno (M.),Sugita (A.),Jinguji (K.),Kawachi (M.), Birefringence control of silica waveguides on Si and its application to a polarization-beam splitter/switch,Journal of Lightwave Technology,12, Issue 4, Apr 1994.
Amersfoort (M.R.), Soole (J.B.D.), Leblanc (H.P.), Andreadakis, (N.C.), Rajhel (A.), Caneau (C.), Passband broadening of integrated arrayed waveguide filters using multimode interference couplers,Electronics Letters,32, Issue 5, 29 Feb 1996, pp. 449.
Dragone (C.), Efficient techniques for widening the passband of a wavelength router,Journal of Lightwave Technology,16, Issue 10, Oct 1998, pp. 1895–1906.
Rigny (A.), Bruno (A.), Sik (H.), Multigrating method for flattened spectral response wavelength multi/demultiplexer,Electronics Letters,33, Issue:20, 25 Sep 1997, pp. 1701–1702.
Okamoto (K.), Takiguchi (K.), Ohmori (Y.), Eight-channel flat spectral response arrayed-waveguide multiplexer with asymmetrical Mach-Zehnder filters,IEEE Photonics Technology Letters,8, Issue 3, Mar 1996, pp. 373–374.
Inoue (Y.), Kaneko (A.), Hanawa (F.), Takahashi (H.), Hattori (K.), Sumida (S.), Athermal silica-based arrayed-waveguide grating multiplexer,Electronics Letters,33, Issue 23, 6 Nov 1997, pp. 1945–1947.
Ooba (N.), Hibino (Y.), Inoue (Y.), Sugita (A.), Athermal silica-based arrayed-waveguide grating multiplexer using bimetal plate temperature compensatorElectronics Letters,36, Issue 21, 12 Oct 2000, pp. 1800–1801
Heise (G.), Schneider (H.W.), Clemens (P.C.), Optical phased array filter module with passively compensated temperature dependence,24th European Conference on Optical Communication, 1998,1, 20–24 Sep 1998, pp. 319–320.
http://www.alcatel.com/optronics
http://www.jdsu.com
http://www.hitachi-cable.co.jp/en/optical/plc
http://www.nel-world.com/products/photonics
Lee (C.-H.),Zhong (S.),Lin (X.),Chen (Y. J.), Proposed planar lightwave circuit design of programmable opticalcdma spectral encoder/decoder using array-waveguide grating,Nanostructures and Quantum Dots/WDM Components/vcsels and Microcavaties/RF Photonics for catv and hfc Systems, 1999 Digest of the leos Summer Topical Meetings, 1999, pp. II39–II40.
Bainbridge (J.D.),Sharafi (A.R.),White (I.H.),Cowin (M.A.),Stephens (M.F.C.),Owen (M.),Penty (R.V.),Guild (K.M.),Tzanakaki (A.),O’mahony (M.J.),Thompson (G.H.B.),Clements (S.J.),Rogers (C.B.), All-optical routing using a 12_12 passive InP wavelength selective router and tuneable wavelength conversion,IEEE Colloquium on Multiwavelength Optical Networks: Devices, Systems and Network Implementations (Ref. No. 1998/257), 17 Jun 1998, pp. 8/1–8/5.
Mestric (R.), Porcheron (C.), Martin (B.), Pommereau (F.), Guillemot (I.), Gaborit (F.), Fortin (C.), Rotte (J.), Renaud (M.), Sixteen-channel wavelength selector monolithically integrated on InP,Optical Fiber Communication Conference, 2000,1, 2000, pp. 81–83.
McGreer (K.A.), Arrayed waveguide gratings for wavelength routing,IEEE Communications Magazine, 36, Issue 12, Dec 1998, pp. 62–68.
Tachikawa (Y.), Inoue (Y.), Ishii (M.), Nozawa (T.), Arrayed-waveguide grating multiplexer with loop-back optical paths and its applications,Journal of Lightwave Technology,14, Issue 6, Jun 1996, pp. 977–984.
Menezo (S.), Rigny (A.), Talneau (A.), Delorme (F.), Grosmaire (S.), Nakajima (H.), Vergnol (E.), Alexandre (F.), Gaborit (F.), Design, realization, and characterization of a ten-wavelength monolithic source forWDM applications integrating DBR lasers with a PHASAR,IEEE Journal on Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics,6, Issue 1, Jan/Feb 2000, pp. 185–190.
Zirngibl (M.), Joyner (C.H.), Glance (B.), Digitally tunable channel dropping filter/equalizer based on waveguide grating router and optical amplifier integration,IEEE Photonics Technology Letters,6, Issue 4, Apr 1994, pp. 513–515.
Doerr (C.R.), Multiwavelength semiconductor lasers using waveguide grating routers,Lasers and Electro-Optics, 1999, CLEO, Pacific Rim’99,4, 1999, pp. 1159–1160.
Kurokawa (T.), Takenouchi (H.), Tsuda (H.), Time-space-conversion optical signal processing using arrayed-waveguide grating,The Pacific Rim Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics, 1999. CLEO/Pacific Rim ’99,3, 1999, pp. 809–810.
Takenouchi (H.), Ishii (T.), Goh (T.), 8 THZ bandwidth dispersion-slope compensator module for multiband 40 Gbit/sWDM transmission systems using an AWG and spatial phase filter,Electronics Letters,37, Issue 12, Jun 2001, pp. 777–778.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rigny, A. A key component in optical systems: the silica-based arrayed waveguide grating (de)multiplexer. Overview and perspectives. Ann. Télécommun. 58, 1307–1341 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03001733
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03001733
Key words
- Optical telecommunication
- Wavelength multiplexing
- Multiplexer
- Demultiplexer
- Planar technology
- Optical waveguide
- System design
- Transmission characteristic
- Commercial product
- Optical component
- State of the art