Abstract
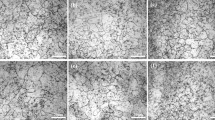
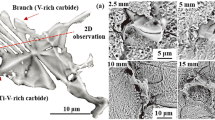
The effects of rare earths (RE)-Mg-Ti compound modification on the structures and properties of high-carbon high speed steel (HSS) were researched. The impact toughness (αk), the fracture toughness (K1c) and threshold of fatigue crack growth (ΔKth) are tested. The thermal fatigue test is done on a self-straining thermal fatigue tester, the wear test is done on a high temperature wear test machine. The results show that the matrix can be refined by the RE-Mg-Ti compound modification, the eutectic carbides are inclined to spheroidicize and are distributed evenly, the morphology and distribution of eutectic carbides are unproved by appropriate RE-Mg-Ti complex modification. After RE-Mg-Ti compound modification, a little effects can be found on the strength, hardness and red hardness, but the fracture toughness (K1c) and threshold of fatigue crack growth (ΔKth) are improved in the meantime, the impact toughness (αk) is increased by over one time, and the resistance to thermal fatigue and wear resistance at an elevated temperature are remarkably improved.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hashimoto M, Otomo S, Oshida K,et al. Development High-toughness Roll by CPC Process.Seitetsu Kenkyu, 1990, 338: 62
Shimizu M, Shitamura, O Matsuo S,et al. Development of High Perfonnance New Composite Roll.ISIJ Ira., 1992, 32: 1244
Kang Y J, Oh J C, Lee H C,et al. Effects of Carbon and Chromium Additions on the Wear Resistance and Surface Roughness of Cast High-speed Steel Rolls.Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2001, 32A: 2515
Fu H G, Zhao A M, Xing J D,et al. Centrifugal Casting of High Speed Steel/Nodular Cast Iron Compound Roll Collar.J. Iron & Steel Res. Int., 2002, (9): 32
Kononov A A, Salmanov N S, Salmanov M N. The Effect of Modifiers on the Structure of S6-5-2 High-speed Steel.Liteinoe Proizcodstvo, 2001, (2):5
Song Y P, Li B Z, Zhu J Z,et al. Effects of RE Compound Modificator on Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of High Carbon High Speed Steel.Journal of Iron and steel Research, 2001, (13): 31
Liu H F, Liu Y H, Yu S R. The Effect of Alloy Elements on Formation and Morphology of Carbide in High Carbon High Speed Steel.Foundry, 2000, 49: 17
Frost R H, Majewski T, Krauss G. Impact Fracture Behavior of High Chromium-Molybdenum White Cast Irons.AFS Trans., 1986, 94: 297
Guo X C, Ceng Q M, Su D L. Hot Wear and Thermal Fatigue Properties of Some Hot Roll Materials.Iron & Steel, 1992, 27: 37
Yang Q X, Wang A R, Ren X J. Effect of Rare Earth Elements on Thermal Fatigue of High Ni-Cr Alloy Cast Iron.J. Rare Earths, 1996, 14: 286
Liu Z M. Friction and Wear Characteristics of M50 High Speed Steel at Elevated Temperature.Tribology, 1997, 17: 38
Chen J B, Liu S G, Su D L. High Temperature Wear Characteristics of Paste Boron-aluminized Layer on 5CrMnMo Steel.Heat Treatment of Metals, 2001, (2): 8
Zum-Gahr K H. How Microstructure Affects Abrasive Wear Resistance.Metal Progress, 1979, 116: 46
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fu, Hg., Fu, Dm., Zou, Dn. et al. Structures and properties of high-carbon high speed steel by RE-Mg-Ti compound modification. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology-Mater. Sci. Ed. 19, 48–51 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03000167
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03000167