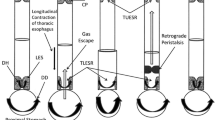
Conclusions
Our experimental investigations indicate that the change in the hydrogen-ion concentration of gall bladder bile is an important factor in the etiology of gall stones.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Morrison, Samuel and Feldman, Maurice: An Experimental Study on the Effect of Vitamins Upon the Dissolution of Gall Stones.Rev. of Gastroenterology, 1937.
Krantz, John C., Jr., Feldman, Maurice, Morrison, Samuel and Carr, D. Jelleff: Hydrogen-ion Concentration of the Bile of the Guinea Pig.Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. and Med., 35:48–49, 1936.
Morrison, Samuel, Feldman, Maurice and Krantz, John C., Jr.: The Correlation of the Hydrogen-ion Concentration of Bile to the Formation of Gall Stones. (To be published).
Feldman, Maurice, Morrison, Samuel and Krantz, John C., Jr.: Etiology of Gall Stones; The Relationship of pH. of Bile to the Formation and the Dissolution of Gall Stones.Am. J. Digest. Dis. and Nutrit., 4, 1937.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
From the research section of the Department of Gastro-Enterology and the Department of Pharmacology, School of Medicine, University of Maryland.
The expense of this work was defrayed in part by the Julius Friedenwald Experimental Fund.
Read before the American Association for the Advancement of Science. Atlantic City, N. J., December 28, 1936.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feldman, M., Morrison, S., Carr, C.J. et al. A contribution to the etiology of gall stones. American Journal of Digestive Diseases and Nutrition 4, 223–225 (1937). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02999901
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02999901