Abstract
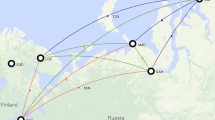
A propagation experiment at the frequencies of 1.7, 11.5 and 34.5 GHz using Engineering Test Satellite Type IIEts-II was conducted at the Kashima earth station of the Radio Research Laboratories (Rrl).Several meteorological parameters were also measured simultaneously at the station using rain gauge networks, a C-band rain radar, a 35 GHz radiometer and meteorological instruments.
The whole data for one year in this experiment were classified into three rain types such as stratus, cumulusand others by using radar data along the path mainly to determine the size of precipitation area and whether the radar bright band existed or not.
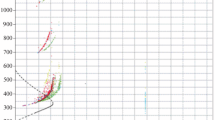
Rainfall classified as stratus occurred for 45 % of the total rainfall time, whilst rainfall classified as cumulus occurred for 10 %, and others for 45 % of the total rainfall time. For the co-polar attenuation, a prediction method based upon an assumption of spatial homogeneity is found to be applicable to the Earth-space path for the stratus type, though the method is not applicable for the cumulus type. On the contrary, in the degradation ofXpd,a prediction method based upon an assumption of deformed raindrops is not applicable to the path for the stratustype, while the method is applicable for the cumulus type.
Analyse
Une expérience de propagation à des fréquences de 1.7, 11.5 et 34.5 GHz utilisant le satelliteEts-II a été réalisée à la station de Kashima du Radio Research Laboratories. Quelques paramètres météorologiques ont simultanément été mesurés à la station, à l’aide de pluviomètres, d’un radar météorologique dans la bande C, d’un radiomètre à 35 GHz et de divers instruments météorologiques. Tous les résultats de l’expérience pour une année ont été classés suivant trois types de précipitations: stratus, cumuluset autres cas;ceci, grâce aux enregistrements du radar qui ont permis de déterminer l’aire couverte par la précipitation et l’existence ou non-existence de la bande brillante du radar. L’occurrence de précipitations du type stratus est observée durant 45% de la durée totale de précipitation, le type cumulusdurant 10% et le type autres cas45%. On trouve pour l’atténuation copolaire une méthode de prévision basée sur l’hypothèse d’homogénéité spatiale qui est utilisable sur un trajet Terre-espace pour une précipitation du type stratus mais ne l’est pas pour le cas cumulus.Par contre, pour la dégradation du découplage de polarisation croisée, une méthode de prévision supposant les gouttes déformées n’est pas applicable au type stratusmais l’est au type cumulus.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fugono (N.). Summary of millimeter wave propagation experiments using Japan’s First geostationary Satellite « Kiku-2 ».Ann. Télécommunic., Fr. (mai–juin 1979),34, n∘ 5–6, pp. 299–318.
***ETS-II Experiments. Fugono (N.), Hayashi (R.), Ishizawa (Y.). Part I: Japan’s First Geostationary Satellite. Hayashi (R.), Teshirogi (T.), Kimura (S.), Komuro (H.), Yoshimura (K.), Suzuki (Y.), Aoyama (S.). Part II: Earth Station Facilities. Tanaka (H.), Shinozuka (T.), Nakamura (K.), Koike (K.), Kuroiwa (H.). Part III: Weather Radar System. Fujita (M.), Shinozuka (T.), IHARA (T.), FURUHAMA (Y.), Inuki (H.). Part IV: Characteristics of millimeter and centimeter wave length propagation. Awaka (J.), Ogawa (T.), Fujita (M.), Shinno (K.), Kan (M.). Part V: Effects of the ionosphere.IEEE Trans. AES, USA (sep. 1980),16, n∘ 5 pp. 549–603.
Morita (K.),Yamada (M.). Radio wave propagation through precipitation.J. IECE, Jap. (Apr. 1977),E60, n∘ 4, pp. 375–382.
Furuhama (Y.),Ihara (T.),Inuki (H.),Fugono (N.). Radar reflectivity profile classified by rain types.Trans. IECE, Jap. (Jun. 1980),E63, n∘ 6, pp. 437–438.
Sato (K.), Sakagami (S.), Hosoya (Y.). Statistical analyses of rainfall intensity data. 1978. Nat. Conf. on light and radio waves.IECE, Jap. (Oct. 1978), p. 41.
Morita (K.),Higuchi (I.). Statistical studies on rain attenuation and site diversity effect on earth to satellite links in microwave and millimeter wavebands.Trans. IECE, Jap. (Jun. 1978),E61, n∘ 6, pp. 425–432.
Oguchi (T.). Scattering properties of Pruppacher-and-Pitter form raindrops and cross polarization due to rain: calculations at 11, 13, 19.3 and 34.8 GHz.Radio Sci., USA (Jan.–Feb. 1977),12, n∘ 1, pp. 41–51.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Furuhama, Y., Ihara, T., Fujita, M. et al. Propagation characteristics of millimetre and centimetre waves of ETS-II classified by rainfall types. Ann. Télécommun. 36, 24–32 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02997000
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02997000