Abstract
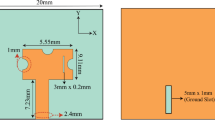
This paper presents a synthesis of linear standingwave arrays of microstrip antennas such as transverse dipoles, series-fed by a proximity coupled microstrip line. Each radiating element is characterized by its self-admittance and mutual coupling admittance. The self-admittance depends on geometrical parameters and on the nature of the substrate, while the mutual coupling admittance is related to the presence of the other radiating elements. These values are computed exactly using an integral equation technique combined with a two-port model of the element. The synthesis procedure is validated with measurements of the radiation pattern and a return loss of a 20-dipole array. The importance of mutual coupling in the design process is clearly demonstrated.
Résumé
Cet article présente une synthèse de réseaux rectilignes à ondes stationnaires ďéléments microrubans du type doublets transverses, alimentées en série par couplage de proximité. Le principe consiste à caractériser chaque élément rayonnant unitaire par son admittance propre, fonction de sa géométrie et du substrat employé, et par son admittance de couplage mutuel traduisant ľinfluence des autres éléments composant le réseau. Ces données sont calculées grâce à un simulateur électromagnétique reposant sur la résolution ďéquations intégrales par la méthode des moments, associé à un modèle quadripolaire de ľ élément rayonnant. Cette synthèse est validée par des mesures réalisées sur le diagramme de rayonnement ďune part et sur ľadaptation ďautre part ďun réseau de 20 doublets transverses. LĽimportance de la prise en compte du couplage mutuel dans une telle structure est clairement démontrée.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stern (G. J.), Elliott (R. S.). The design of microstrip dipole arrays including mutual coupling, part 1: theory.IEEE Trans. AP (1981),29, pp. 757–760.
Stern (G. J.), Elliott (R. S.). The design of microstrip dipole arrays including mutual coupling, part 2: experiment.IEEE Trans. AP (1981),29, pp. 761–765.
Yang (H. Y.), Alexopoulos (N. G.), Lepeltier (Ph.). Design of transversaly fed EMC microstrip dipole arrays including mutual coupling.IEEE Trans. AP (1990),38, pp. 145–151.
Ghali (H. A.),Citerne (J.),Drissi (M.),Fouad Hanna (V.). Simulation numérique ďune charge adaptée en vue de la caractérisation des discontinuités planaires.Recueil des 7 es Journées Nationales Microondes (1991), pp. 319–320.
Legay (H.), Floc’h (J. M.), Citerne (J.), Piton (G.). Etude théorique et expérimentale ďantennes plaques alimentées par couplage de proximité à une ligne microruban.Ann. Télécommunic. (1990),45, n° 3–4, pp. 192–202.
Tessereau (S.), Floc’h (J. M.), Legay (H.), Citerne (J.). Analysis and measurement of mutual coupling between two series-fed electromagnetically coupled transverse dipoles.Micro. & Optic. Techn. Letters (1992),5, pp. 265–267.
Elliott (R. S.). Antenna theory and design.Prentice Hall (1981).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tessereau, S., Floc’h, JM. & Citerne, J. Synthesis of linear arrays of series fed proximity-coupled microstrip antennas. Ann. Télécommun. 48, 573–581 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02995493
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02995493
Key words
- Antenna array
- Linear antenna
- Patch antenna
- Microstrip line
- Antenna feed
- Antenna synthesis
- Mutual coupling
- Modeling, Dipole