Abstract
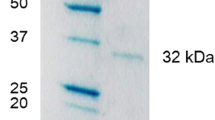
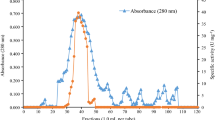
Among 30 species of filamentous fungi isolated from Brazilian soil,Aspergillus caespitosus produced and secreted the highest levels of alkaline phosphatase in culture medium supplemented with xylan. The extracellular alkaline phosphatase was purified by DEAE-cellulose and concanavalin A-sepharose chromatography. The enzyme was a glycoprotein containing up to 56 % sugar with molar mass of 134.8 kDa, according to gel filtration in Sepharose CL-6B, and 57 kDa according to SDS-PAGE. Non-denaturing electrophoresis (6 % PAGE) of the purified enzyme produced a single band, suggesting that the native enzyme was a homodimer. Optima of temperature and pH were 75 °C and 8.5, respectively. The enzyme was stable at 50 °C and its activity was enhanced by 95 % in the presence of Mg2+ (1 mmol/L). 4-Nitrophenyl phosphate was the preferentially hydrolyzed substrate withK m andv lim values of 74 µmol/L and 285 µmol/s, in the absence, and 90 µmol/L and 418 µmol/s, in the presence of Mg2+, respectively. The enzyme also hydrolyzed other phosphorylated amino acids (O-phosphothreonine,O-phosphotyrosine,O-phosphoserine).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aquino A.C.M.M., Jorge J.A., Terenzi H.F., Polizeli M.L.T.M.: Thermostable glucose-tolerant glucoamylase produced by the thermophilic fungusScytalidium thermophilum.Folia Microbiol. 46, 11–16 (2001).
Blum H., Beier H., Gross H.J.: Improved silver staining of plant protein, RNA and DNA in polyacrylamide gels.Electrophoresis 81, 93–99 (1987).
Buainain L.B., Kadowaki M.K., Polizeli M.L.T.M., Terenzi H.F., Jorge J.A.: Characterization of a conidial alkaline phosphatase from the thermophilic fungusHumicola grisea var.thermoidea.J.Basic Microbiol. 38, 85–94 (1998).
Davis B.J.: Disc electrophoresis: II. Method and application to human serum proteins.Ann.N.Y.Acad.Sci. 121, 407–427 (1964).
Denison S.H.: pH regulation of gene expression in fungi.Fungal Gen.Biol. 29, 61–71 (2000).
Dickman M.B., Yarden O.: Serine/threonine protein kinases and phosphatases in filamentous fungi.Fungal Gen.Biol. 26, 99–117 (1999).
Dong G., Zeikus G.: Purification and characterization of alkaline phosphatase fromThermotoga neapolitana.Enzyme.Microbiol.Technol. 21, 335–340 (1997).
Dubois M., Gilles K.A., Hamilton J.K., Rebers P.A., Smith F.: Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances.Analyt.Chem. 28, 350–356 (1956).
Elzainy T.A., Ali T.H.: Participation of a proton-translocating plasma membrane ATPase degradation byAspergillus niger extracts.Biochim.Biophys.Acta 1239, 91–97 (1995).
Guimarães L.H.S., Jorge J.A., Terenzi H.F., Polizeli M.L.T.M.: Thermostable conidial and mycelial alkaline phosphatases from the thermophilic fungusScytalidium thermophilum.J.Industr.Microbiol.Biotechnol. 27, 265–270 (2001).
Guimarães L.H.S., Jorge J.A., Terenzi H.F., Jamur M.C., Oliver C., Polizeli M.L.T.M.: Effect of carbon source on phosphatase production inAspergillus caespitosus.J.Basic Microbiol. 43, 200–207 (2003).
Heinonen J.K., Lahti R.J.: A new and convenient colorimetric determination of inorganic orthophosphate and its application to the assay of inorganic pyrophosphatase.Analyt.Biochem. 113, 313–317 (1981).
Laemmli U.K.: Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head bacteriophage T4.Nature 227, 680–685 (1970).
Leone F.A., Degreve L., Baranauskas J.A.: SIGRAF: a versatile computer program for fitting assay kinetics data.Biochem.Educ. 20, 94–96 (1992).
Leone F.A., Baranauskas J.A., Ciancaglini P.: Enzyplot: a microcomputer-assisted program for teaching enzyme kinetics.Biochem.Educ. 23, 35–37 (1995).
MacKintosh C., MacKintosh R.W.: Inhibitors of protein kinases and phosphatases.Trends Biochem.Sci. 19, 444–448 (1994).
McComb R.B., Bowers G.N. Jr.,Posen S.:Alkaline Phosphatase, pp. 229–287. Plenum Press, New York 1979.
Morales A.C., Nozawa S.R., Thedei-Jr. G., Maccheroni W., Rossi A.: Properties of a constitutive alkaline phosphatase from strain 74A of moldNeurospora crassa.Braz.J.Med.Biol.Res. 33, 905–912 (2000).
Negrete-Urtasun S., Reiter W., Diez E., Denison S.H., Tilburn J., Espeso E.A., Peñalva M.A., Arst H.N. Jr.: Ambient pH signal transduction inAspergillus: completion of gene characterization.Mol.Microbiol. 33, 994–1003 (1999).
Oshima Y.: The phosphatase system inSaccharomyces cerevisiae.Gen.Genet.Syst. 72, 323–334 (1997).
Pereira M., Pereira-Jr. H., Thedei-Jr. G., Rossi A., Martinez-Rossi N.M.: Purification ofNeurospora crassa alkaline phosphatase without DNAse activity for use in molecular biology.World J.Microbiol.Biotechnol. 11, 505–507 (1995).
Raper K.B., Fennell D.I.:The Genus Aspergillus. Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore 1965.
Rizzatti A.C.S., Jorge J.A., Terenzi H.F., Rechia C.G.V., Polizeli M.L.T.M.: Purification and properties of a thermostable extracellular β-d-xylosidase produced by thermotolerantAspergillus phoenicis.J.Industr.Microbiol.Biotechnol. 26, 156–160 (2001).
Say J.C., Furriel R.P.M., Ciancaglini P., Jorge J.A., Polizeli M.L.T.M., Pizauro J.M., Terenzi H.F., Leone F.A.: Conidial alkaline phosphatase fromNeurospora crassa.Phytochemistry 41, 71–75 (1996).
Vincent J.B., Crowder M.W., Averill B.A.: Hydrolysis of phosphate monoesters: a biological problem with multiple chemical solutions.Trends Biol.Sci. 17, 105–110 (1992).
Watanabe T., Takeuchi T., Otsuka M., Tanaka S., Umezawa K.: Synthesis and protein tyrosine phosphatase inhibitory activity of dephostatin analogs.J.Antibiot. 48, 1460–1466 (1995).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by grants fromFundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (FAPESP) andConselho de Desenvolvimento Cientifico e Tecnológico (CNPq). This work is part of the DSc Thesis of the first author who is a recipient of a fellowship from CNPq. The other authors are research fellows of CNPq.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guimarães, L.H.S., Terenzi, H.F., Jorge, J.A. et al. Extracellular alkaline phosphatase from the filamentous fungusAspergillus caespitosus: Purification and biochemical characterization. Folia Microbiol 48, 627–632 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02993469
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02993469