Abstract
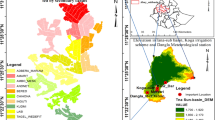
Water Utilisation Index (WUI) defined as area irrigated per unit volume is a measure of water delivery performance and constitutes one of the important spatial performance indicators of an irrigation system. WUI also forms basis for evaluating the adequacy of seasonal irrigation supplies in an irrigation system (inverse of WUI is delta, i.e. depth of water supplied to a given irrigation unit). In the present study WUI and adequacy indicators were used in benchmarking the performance of Nagarjunasagar Left Canal Command (NSLC) in Andhra Pradesh. Optimised temporal satellite data of rabi season during the years 1990–91 and 1998–99 was used in deriving irrigated crop areas adopting hierarchical classification approach. Paddy is the predominant crop grown and cotton, chillies, sugarcane etc. are the other crops grown in the study area. Equivalent wet area (paddy crop area) was estimated using the operationally used project specific conversion factors. WUI was estimated at disaggregated level viz., distributary, irrigation block, irrigation zone level using the canal discharge data. At project level, WUI estimated to be 65 ha/MCM and 92 ha/MCM during rabi season of 1990–91 and 1998–99 years respectively. A comparison of total irrigated area and discharges corresponding to both the years indicate that irrigation service is extensive and sub optimal during 1998–99 and it is intensive and optimal in 1990–91. It was also observed that WUI is lesser in blocks of with higher Culturable Command Area (CCA) compared to the blocks of lower CCA. All the disaggregated units were ranked into various groups of different levels of water distribution performance. The study demonstrates the utility of WUI as spatial performance indicator and thus useful for benchmarking studies of irrigation command areas. The WUI together with satellite data derived spatial irrigation intensity, crop productivity constitutes important benchmarking indices in irrigation command areas.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bastiaanssen, W.G.M. (1998). Remote sensing in water resources management: the state of the art. Report: International Water Management Institute (IWMI), Colombo, Sri Lanka, pp. 1–118.
Bastiaanssen, W.G.M. and Bos, M.G. (1999). Irrigation performance indicators based on remotely sensed data: a review of literature.Irrigation and Drainage Systems,13:291–311.
Bastiaanssen, W.G.M., Thiruvengadachari, S., Sakthivadivel, R. and Molden, D.J. (1999b). Satellite remote sensing for estimating productivities of land and water.Int. J. Water Resources Development,15(2): 181–186.
Bos, M.G. (1997). Performance indicators for irrigation and drainage.Irrigation and Drainage Systems,11: 119–137.
Dadhwal, V.K. (1999). Remote sensing and GIS for agricultural crop acreage and yield estimation.Int. Arch.Photogram. Rem. Sens.,32(7-W9): 58–67.
INCID (2001). Indicators for irrigation performance assessment. Indian Committee on Irrigation and Drainage, New Delhi.
NSP (1998). Annual Report. Nagarjunasagar left canal irrigation command, Andhra Pradesh State.
NRSA (2005). Satellite remote sensing based evaluation study of Nagarjunasagar left canal irrigation command, Andhra Pradesh State. National Remote Sensing Agency (NRSA), Hyderabad.
Perry, C.J. (1999). The IWMI water resources paradigm- definitions and implications.Agriculture and Water Management,40(1): 45–50.
Rao, P.S. (1993). Review of selected literature on indicators of irrigation performance. IIMI Research Paper No. 13. Colombo, Sri Lanka: International Management Institute, Colombo, Sri Lanka, pp. 1–75.
Rao, N.P.P. and Mohankumar, A. (1994). Cropland inventory in the command area of Krishnarajasagar project using satellite data.Int. J. Remote Sensing,15(6): 1295–1305.
Ray, S.S., Dadhwal, V.K. and Navalgund, R.R. (2002). Performance Evaluation of an irrigation command area using remote sensing: A case study of Mahi command, Gujarat, India.Agricultural Water Management,56: 81–91.
Sakthivadivel, R., Thiruvengadachari, S., Amerasinghe, U., Bastiaanssen, W.G.M. and Molden, D.J. (1999a). Performance evaluation of the Bhakra irrigation system, India, using remote sensing and GIS techniques. Research Report: 28. International Water Management Institute. Colombo, Sri Lanka, pp. 1–22.
Shanker, M., Venkateshwar Rao, V., Suresh Babu, A.V and Chakraborti. A.K. (2001). Satellite remote sensing application to major irrigation projects in Andhra Pradesh. Workshop on Water Resources of Andhra Pradesh: Optimal Utilisation held at Visakhapatnam, Andhra Pradesh.
Sarma, P.B.S. and V. Venkateshwar Rao (1997). Evaluation of an Irrigation Water Management Scheme-A case study.J. of Agricultural Water Management,32: 181- 195.
Tennakoon, Murthy and Eiumnoh, 1992. Estimation of cropped area and grain yield of rice using remote sensing data.Int. J. Remote Sensing,13: 427–439.
Rao, V.V. and Chakraborthi, A.K. (2000). Water balance study and conjunctive water use planning in an irrigation canal command area: a remote sensing perspective.Int. J. Remote Sensing,21: 3227–3238.
Venkateshwar Rao. V., Shanker, M., Thiruvengadachari, S. and Sharma, S. (1997). Irrigation status in Tungabhadra project command-satellite sensing of field realities. Proc. Workshop on Remote Sensing and GIS applications in Water Resources Engineering, held at Bangalore from September 17- 19, 1997, pp.116–124.
Thiruvengadachari, S. and Sakthivadivel, R. (1997). Satellite remote sensing techniques to aid irrigation system performance assessment: A case study in India. Research Report 9, International Water Management Institute, Colombo, Sri Lanka, pp. 1–23.
Wolters, W., Zevenbergen, A.W. and Bos, M.G. (1991). Satellite remote sensing in irrigation.Irrigation and Drainage Systems,5: 307–323.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Suresh Babu, A.V., Venkateshwar Rao, V. & Muralikrishna, I.V. Satellite remote sensing derived spatial water utilisation index (wui) for benchmarking of irrigation systems. J Indian Soc Remote Sens 35, 81–91 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02991836
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02991836