Abstract
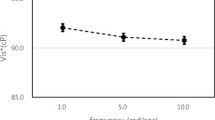
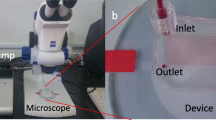
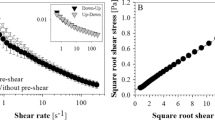
A newly designed pressure-scanning slit viscometer is developed to combine an optical device without refraction while measuring blood viscosity over a range of shear rates. The capillary tube in a previously designed capillary viscometer was replaced with a transparent slit, which is affordable to mount optical measurement of flowing blood cells. Using a pressure transducer, we measured the change of pressure in a collecting chamber with respect to the time, p(t), from which the viscosity and shear rate were mathematically calculated. For water, standard oil and whole blood, excellent agreement was found between the results from the pressure-scanning slit viscometer and those from a commercially available rotating viscometer. This new viscometer overcomes the drawbacks of the previously designed capillary viscometer in the measuring whole blood viscosity. First, the pressure-scanning slit viscometer can combine an optical instrument such as a microscope. Second, this design is low cost and simple (i.e., ease of operation, no moving parts, and disposable).
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- h:
-
Half slit gap (mm)
- L:
-
Slit length (m)
- P:
-
Pressure (Pa)
- Q:
-
Flow rate (m3/s)
- t:
-
Time (s)
- V:
-
Volume (m3)
- v:
-
Voltage (V)
- w:
-
Slit width (mm)
- ρ:
-
Density (kg/m3)
- \(\dot \gamma \) :
-
Shear rate (s-1)
- η:
-
Non-Newtonian viscosity (Pa·s)
- τ:
-
Shear stress (Pa)
- A:
-
Atmospheric condition
- h:
-
Head
- i:
-
Initial
- w:
-
Wall
References
Bird, R., Amstrong, R. C. and Hassager, O., 1987,Dynamics of Polymeric Liquids, Vol. 1, New York: John Wiley & Son.
Chandler, W. L. and Schmer, G., 1986, “Evaulation of a New Dynamic Viscometer for Measuring the Viscosity of Whole Blood and Plasma, ”Clin. Chem., Vol. 32, pp. 505–507.
Dintenfass, L., 1969, “ Blood Rheology in Pathogenesis of the Coronary Heart Deseases, ” Am. Heart J. Vol. 77, pp. 139–147.
Fahraeus, R. and Lindquist, T., 1931, The Viscosity of the Blood in Narrow Capillary Tubes,Am. J. Physio., Vol. 96, No. 562, pp. 1931–1939.
Fossum, E., Høieggen, A. and Moan, A., 1997, “ Whole Blood Viscosity, Blood Pressure and Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Healthy Blood Donors, ”Blood Press., Vol. 6, pp. 161–165.
Kim, S., Cho, Y. I., Kensey, K. R., Pellizzari, R. O. and Stark, P. R. H., 2000, “ A Scanning Dual-Capillary-Tube Viscometer, ”Review of Scientific Instruments, Vol. 71, pp. 3188–3192.
Lide, D. R.(Ed), 1994, CRC handbook of chemistry and physics, 75th ed.CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL.
Macosko, W., 1993,Rheology: Principles, Measurements, and Applications, VCH, New York.
Ogawa, K., Okawara, S., Ito, S. and Taniguchi, K., 1991, “ Blood Viscometer with Vacuum Glass Suction Tube and Needle, ”J. Chemical Eng. of Japan, Vol.24, p. 215–221.
Reinhart, W. H., Haeberli A., Stark, J. and Straub, P. W., 1990, “ Influence of Blood Withdrawal and Anticoagulant on Clotting Activity, Hematologic Data, and Certain Rheologic Measurements, ”J. Lab. Clinical Med., Vol. 115, pp. 98–103.
Shin, S. and Keum, D. Y., 2002a, “ Continuous Viscosity Measurement of Polymer Solutions over a Range of Shear Rates Using a Mass-Detecting Capillary Viscometer, ”KSME Int. J., Vol. 16, pp. 255–261.
Shin, S. and Keum, D. Y., 2002b, “ A New Mass-Detecting Capillary Viscometer, ”Biosensor and Bioelectronics, Vol. 17, pp. 383–388.
Shin, S., Keum, D. Y. and Ku, Y. H., 2002c, “Blood Viscosity Measurement Using a Pressure-Scanning Capillary Viscometer, ”KSME Int. J., Vol. 16, pp. 1719–1724.
Singh, M. and Coulter, A., 1973, “ Rheology of Blood Effect of Dilution with Various Dextrans, ”Microvasc. Res., Vol. 5, pp. 123–135.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shin, S., Lee, SW. & Ku, YH. Measurements of blood viscosity using a pressure-scanning slit viscometer. KSME International Journal 18, 1036–1041 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02990876
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02990876