Abstract
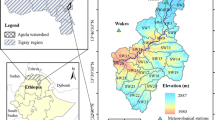
Drainage channels as represented over the topographical maps of the Survey of India on scale 1:50,000 and depicted over the IRS-IB imageries (May 1993) and limited photographs are characterized in view of its areal, linear and abstract properties associated with the Archean gneissic plate of the Sur catchment spread over 983 km2. Morphological characteristics of the drainage lines as appear in shape, size, number and order, length, Dd, Sf, Rb, Is, II, Re, It and infiltration number are derived to trace its usefulness for surface water development. Chiefly dendritic, sub-dendritic and sub-parallel drainage patterns evolved out of the dissected hills, undulating plateau, pediplain and the gently sloping plain persisting under dry sub-humid climatic conditions at an elevation ranging from 246 to 580 m above MSL have given rise to situations suitable for good bunding sites mostly occurring at 3rd and 4th orders of streams for water resource development. Detailed analysis of dominant V order segments (Total 7) suggests high intensity of flood occurrence at a time at the outlet point of the streams indicated along the increased values of Dd, Sf, Rb and Re thereby cautioning proper bunding structure at sites marked on the map for irrigation of crops beyond rainy season.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Athavale, R.N. (2003). Water harvesting and sustainable supply in India. Prem Rawat for Prem Rawat Publications, Jawahar Nagar, Jaipur, pp. 110–113.
Gregory, K.J. and Walling, D.E. (1973). Drainage basin form and process — A geomorphological approach. Edward Arnold (Publishers) Ltd., London, pp.38- 39.
Hirekerur, L.R., Batta, R.K., Pofali, R.M., Singh, S.R. and Swaminathan, M. (1984). Evaluation of hydrological, fluvial and morphometric characteristics of the Upper Wunna watershed in relation to water and sediment yield under different land uses. Unpublished Report.
Horton, R.E. (1945). Erosional development of streams and their drainage basin, hydrophysical approach to quantitative morphology.Bull. Geological Soc. of America,56: 275–370.
Singh, S.R., Pofali, R.M. and Batta, R.K. (1985). Quantitative analysis of the Hiran catchment for land resources development and management: A case study based on aerial photo interpretation.National Geographical J. ofIndia,31: 10–12.
Singh, S.R., Gajbhiye, K.S. and Kolte, K.T. (1998). Application of cartographic techniques for mapping and management of land resources of the Sur catchment in Ramtek and Bhandara tahsils of Maharashtra, India.Pub. Indian Cartographer,18: 163p.
Small, R.J. (1978). The study of landforms — a text book of geomorphology. Cambridge University Press, 217p.
Strahler, A.N. (1958). Dimensional analysis applied to fluvially eroded landforms.Bull. Geological Soc. of America,69: 279–300.
Verstappen, H.Th. (1983). Applied Geomorphology — Geomorphological surveys for Environmental Development. Ealsevier Science Publishers B.V. Amsterdam, The Netherlands, pp. 66–71.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, S.R. A drainage morphological approach for water resources development of the sur catchment, Vidarbha region. J Indian Soc Remote Sens 34, 79–88 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02990749
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02990749