Abstract
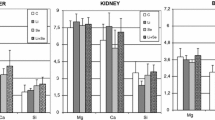
References to individual trace minerals in hypertensive rats have been made; however, data on multiple minerals in SHR hypertensive rats is lacking. The purpose of this study was to investigate five trace minerals in normotensive, chronic renal and SHR hypertensive rats. Blood samples were drawn to measure serum levels of Ca, Fe, K, Mg, and Na. Serum K values were elevated in the chronic renal hypertensive animals. Iron levels were decreased in both the renal and SHR hypertensive animals. No difference was observed in levels of Ca, Mg, and Na between normotensive and chronic renal or SHR hypertensive rats. Further study of multiple trace minerals in experimental hypertension is recorded in order to extend these deviations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. A. McCarron,Hypertension 4, 27–33 (1982).
A. Grollman,Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 57, 102 (1944).
Y. Yamori, R. Horve, H. Tanase, K. Fujiwara, Y. Nera, and W. Lovenberg,Hypertension 6, 49–53 (1984).
H. J. Gitelman,Anal. Biochem. 18, 520–531 (1967).
W. J. Price,Spectrochemical analysis by atomic absorption, Heyden, London, 1979, 265, 266.
H. J. Gitelman, C. Hurt, and L. Lutwak,Anal. Biochem. 14, 106–120 (1966).
L. Tobian, J. Lange, K. Ulm, L. Wold, and J. Twai,Hypertension,7, suppl. I, 110–114 (1985).
D. B. Gordon and D. R. Drury,Circ. Res. 4, 167–172 (1956).
H. F. Loyke,JEPTO 7, 1–8 (1986).
H. F. Loyke,Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 35, 608–611 (1985).
B. M. Altura, B. T. Altura, and A. Geberwold,Science 223, 1315–1317 (1984).
D. Pette, K. Simpson, A. Rogers, and O. B. Holland,Exp. Pathophysiol. 6, 413–417 (1988).
D. A. McCarron, N. N. Yung, B. A. Ugoretz, S. Krutzik,Hypertension (Part 3),2, 162–167 (1981).
S. Ayach,Metabolism 28, 1234–1238 (1979).
L. A. Sapirstein, W. L. Brandt, and D. R. Drury,Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 73, 82–85 (1950).
J. F. Vondraska and R. A. Greco,Bull. Am. Soc. Vet. Clin. Pathol. 2, 3–17 (1973).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Loyke, H.F. Minerals in renal and SHR hypertensive rats. Biol Trace Elem Res 25, 47–50 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02990263
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02990263