Abstract
The respiratory burst reaction (RBR) of neutrophilic granulocytes of the peripheral blood was estimated by means of the luminol reaction in 10 smokers and in 10 nonsmokers. Compared to the nonsmokers, the RBR of smokers' granulocytes showed a significantly higher rate of RBR.
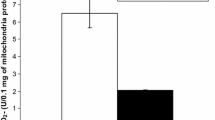
RBR consists of two enzymatic systems, i.e., NADPH-oxidase generating superoxide anions and myeloperoxidase, generating hypochlorous acid. Furthermore the superoxide anion may undergo dismutation to oxygen and peroxide. Thus, since the RBR may cause an oxidative stress, the smokers were supplemented for 10 d with antioxidants, i.e., 200 μg L-Se-methionine and 1000 mg vitamin E/d.
After 10 d of supplementation with the antioxidants, the RBR of the smokers was significantly decreased by 20–75 percent. Since the oxidative stress associated with RBR may cause autodigestive reactions in the lungs of smokers, it may be beneficial for smokers to use relatively high doses of such antioxidants in order to hamper the pathological processes associated with smoking.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
B. Harriwell and M. C. Gutteridge,Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine, 2d ed., Clarendon Press, Oxford (1989).
Y. Sibille, J. S. Lwebuga-Mukasa, L. Polomski, W. W. Merril, D. H. Ingbar, and J. B. L. Gee,Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 134, 134 (1986).
J. Michaelis, M. C. M. Vissers, and C.V. C. Wintherbourn,Biochem. J. 270, 809 (1990).
J. Clausen, S. A. Nielsen, and M. Kristensen,Biol. Trace Element Res. 20, 135 (1989).
B.-L. Zhao, X. J. Li, and W. J. Win,Cell Biol. Int. Rep. 13, 529 (1989).
G. Carlin, R. Djursäter, and G. Smedegård,Pharmacol. & Toxicol. 65, 121 (1989).
J. Uetrecht,Toxicol. 20, 213 (1990).
H. Sayo and M. Saito,Xenobiot. 20, 957 (1990).
J. R. Hoidal, R. B. Fox, P. A. Lemarbe, R. Perri, and J. E. Repine,Am. Rev. Resp. Dis. 123, 85 (1981).
J. R. Hoidal and D. E. Niewoehner,Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 126, 548 (1982).
D. E. Niewoehner, F. J. Peterson, and J. R. Hoidal,Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 127, 227 (1983).
P. W. Ludwig and J. R. Hoidal,Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 126, 977 (1982).
R. Anderson, A. J. Theron, and G. J. Ras,Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 135, 1027 (1987).
M. N. Gillespie, J. O. Owasoju, S. Kojima, and M. Jay,Toxicol. 45, 45 (1987).
S. E. Hannan, J. O. Harris, N. P. Sheridan, and J. M. Patel,Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 140, 1668 (1989).
M. Corn,Air Pollution, A. C. Stern, ed., Academic, NY, p. 47 (1968).
F. P. Perera, K. Hemminki, T. L. Young, D. Brenner, G. Kelly, and R. M. Santella,Cancer Res. 48, 2288 (1988).
D. H. Phillips, B. Schoket, A. Hewer, E. Bailey, S. Kostic, and I. Vincze,Int. J. Cancer 46, 569 (1990).
H. E. Jasin,J. Clin. Invest. 81, 6 (1988).
I. U. Schraufstatter, D. B. H. Hinshaw, P. A. Hyslop, R. G. Spragg, and C. G. Cocrane,J. Clin. Invest. 77, 1312 (1986).
P. Leanderson and C. Tagesson,Chem. Biol. Interactions 75, 71 (1990).
W. A. Engle, M. C. Yoder, J. L. Baurley, and P.-L. Yu,Pediat. Res. 23, 245 (1988).
P. A. Southorn and G. Powis,Mayo Clin. Proc. 63, 381 (1988).
C. E. J. van Rensburg, A. Theron, G. A. Richards, C. A. van der Merwe, and R. Anderson,Mut. Res. 215, 167 (1989).
E. R. Pacht, K. Kaseki, J. R. Hohammed, D. G. Cornwelle, and W. B. Davis,J. Clin. Invest. 77, 789 (1986).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Clausen, J. The influence of selenium and vitamin E on the enhanced respiratory burst reaction in smokers. Biol Trace Elem Res 31, 281–291 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02990197
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02990197