Abstract
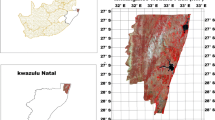
Sustainable management of wetland ecosystem is necessary as it serves the important functions such as food storage, water quality maintenance and providing habitat for different species of wildlife. Hence, an inventory of wetlands in any given area is a pre-requisite for their conservation and management. A study has been carried out to delineate the wetlands of east Champaran district of Bihar, India, using IRS ID LISS III data. The data for the pre and post monsoon seasons have been analysed and the wetlands have been qualitatively characterized based on the turbidity and aquatic vegetation status. The extent of water logging problem in the study area was inferred from the seasonal variation of waterspread during both the seasons. The three categories of wetlands (ponds/lakes, water logged areas and oxbow lakes) have been identified. From the analysis, it has been observed that the inland wetlands constitute 2.7% of the study area, of which 1.8% is subjected to water logging. Thus, this study highlights the usefulness of remotely sensed data for wetland mapping, seasonal monitoring and characterization.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carpenter, D.J. and Carpenter, S.M. (1983). Modelling inland water quality using Landsat data. Remote Sensing Environ.,13: 345–352.
Chopra, R., Verma, V.K. and Sharma, P.K. (1999). Mapping, monitoring and conservation of Harike ecosystem, Punjab, India, through remote sensing. Int. J. Remote Sensing,18: 1637–1651.
Garg, J.K., Singh, T.S. and Murthy, T.V.R. (1998). Wetlands of India. Scientific Note: RSAM/SAC/ RESA/PR/01/98. Space Applications Centre, Ahmedabad, India.
Hollis, G. E. and Acreman, M. C. (1994). The functions of wetlands within integrated river basin development: international perspectives. In: Integrated River Basin Development (Eds.: C. Kirby and W. R. White) Wiley, Chichester, pp. 351–365.
Loveland, T.R., Merchant, J.W., Ohlen, D.O. and Brown, J.R. (1991). Development of a land cover characteristics database for the conterminus U.S., Photogrammetric Engg. & Remote Sensing,57:1453–1463.
Murthy, T.V.R., Muley, M.V., Chakraborty, M., Tamilarasan, V., Amminedu, E., Mehar Baba, G., Krishnan, A. and Rama Krishna, S. (1988). Water quality studies in the Chilka Lake using LANDSAT data. Workshop of remote sensing applications in water resources management, Bhubaneswar.
Nagarajan, R., Marathe, G.T. and Collins, W.G. (1993). Identification of flood prone regions of Rapti river using temporal remotely sensed data. Int. J. Remote Sensing,14(7): 1297–1303.
Palria, S., Singh, T. C, Chakraborty, M., Tamilarasan. V. and Chaws, M.A. (1994). Mapping of turbidity levels and aquatic vegetation in the Wular Lake using IRS-1A data. Proc. ISRS Silver Jubilee Symposium, 1994–95.
Perry, C. and Lautenschlager, L. (1984). Functional equivalence of spectral vegetation indices. Remote Sensing Environ.,14: 169–182.
RRSSC (2000). Manual for mapping of inland wetlands. RRSSC, Dehradun, India.
Sharma, P.K., Chopra, R., Verma, V.K. and Thomas, A. (1996). Flood management using remote sensing technology: the Punjab (India) experience. Int. J. Remote Sensing,17(17): 3511–3521.
Tucker, C.J. and Sellers, P.J. (1986). Satellite remote sensing of primary production. Int. J. Remote Sensing,7: 1395–1416.
Tucker, C. (1979). Red and photographic near infra-red linear combination for monitoring green vegetation. Remote Sensing Environ.,8: 127–150.
Wani, M.M., Choubey, V.K. and Joshi, H. (1996). Quantification of suspended sediments in Dal Lake, Srinagar using Remote Sensing Technology. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sensing,24: 25–32.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Manju, G., Chowdary, V.M., Srivastava, Y.K. et al. Mapping and characterization of inland wetlands using remote sensing and GIS. J Indian Soc Remote Sens 33, 51–61 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02989990
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02989990