Abstract
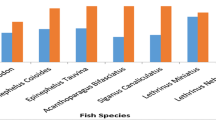
Concentrations of mono- (MBT), di- (DBT), and tri-(TBT) butyltin compounds were measured in eggs, liver, and muscle of nine species of fish from four regions of the Baltic Sea - the Firth of Vistula, the Gulf of Gdańsk, Puck Bay, and the mouth of the Vistula River. The overall concentration ranges among all the fish sampled from the four sites were: < 7 to 79 ng/g for MBT, 6 to 1100 ng/g for DBT, 7 to 3600 ng/g for TBT, and 16 to 4800 ng/g for total BTs, on a wet wt basis. The highest concentration of total BTs was found in herring liver from the Firth of Vistula (4800 ng/g, wet wt) and in roach muscle from Puck Bay (3300 ng/g, wet wt), while the least concentration was found in burbot eggs and liver from the Vistula River (39 and 32 ng/g, wet wt, respectively). TBT was the major form of BTs present in most samples analyzed. Sediment samples collected from shipyards in the Gulf of Gdańsk contained butyltin concentrations ranging from 1.2 to 46 μg/g (dry wt) for MBT, 2.0 to 42 μg/g for DBT, and 2.6 to 40 μg/g for TBT. As with the fish, the majority of the BTs in sediment were present as TBT, which suggested recent exposure of the aquatic environment of the region to TBT.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alzieu, C.;Sanjuan, J.;Michael, P.;Borel, M.;Dreno, J.P. (1989): Monitoring and Assessment of Butyltins in Atlantic Coastal Waters. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 20, 22–26
Beaumont, A.R.;Newman, P.B. (1986): Low Levels of Tributyltin Reduce Growth of Marine Micro-algae. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 17, 457–461
Becker-Van Slooten, K.;Tarradellas, J. (1995): Organotins in Swiss Lakes after Their Ban: Assessment of Water, Sediment, andDreissena polymorpha Contamination over a Four-Year Period. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 29, 384–392
Bryan, G.W.;Gibbs, P.E.;Hummerstone, L.G.;Burt, G.R. (1986): The Decline of the GastropodNucella lapillus around South-west England: Evidence for the Effect of Tributyltin from Antifouling Paints, J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 66, 611–640
Bushong, S.J.;Hall, JR,L.W.;Hall, W.S.;Johnson, W.E.;Herman, R.L. (1988): Acute Toxicity of Tributyltin to Selected Chesapeake Bay Fish and Invertebrates. Water Res. 22, 1027–1032
Chau, Y.K.;Maguire, R.J.;Brown, M.;Yang, F.;Batchelor, S.P. (1997): Occurrence of Organotin Compounds in the Canadian Aquatic Environment Five Years after the Regulation of Antifouling Uses of Tributyltin. Water Qual. Res. J. Canada 32, 453–521
Chwir-Golebiowska, A. (1999): Mercury in Edible Species of Fish from the Gulf of Gdansk and the Firth of Vistula: Concentrations, Epidemiological Studies and Risk Assessment of Selected Sites Along the Gulf of Gdansk. Ph.D. Thesis, in preparation, University of Gdansk, Gdansk, Poland
Cortez, L.;Quevauviller, P.;Martin, F.;Donard, O.F.X. (1993): Survey of Butyltin Contamination in Portuguese Coastal Environments. Environ. Pollut. 82, 57–62
De Mora, S.J.;Stewart, C.;Phillips, D. (1995): Sources and Rate of Degradation of Tri(n-butyl)tin in Marine Sediments Near Auckland, New Zealand. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 30, 50–57
Falandysz, J.;Kannan, K.;Tanabe, S.;Tatsukawa, R. (1993): Persistent Organochlorine Residues in Canned Cod Livers of the Southern Baltic Origin. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 50, 929–934
FAO (1991): Food Balance Sheets: 1984–86 Average. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations
Fent, K. (1991): Bioconcentration and Elimination of Tributyltin Chloride by Embryos and Larvae of MinnowsPhoxinus phoxinus. Aquat. Toxicol. 20, 147–158
Fent, K. (1992): Embryotoxic Effects of Tributyltin on the Minnow,Phoxinus phoxinus. Environ. Pollut. 76, 187–194
Fent, K. (1996): Ecotoxicology of Organotin Compounds. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 26, 1–117
Fent, K.;Hunn, J. (1995): Organotins in Freshwater Harbors and Rivers: Temporal Distribution, Annual Trends and Fate. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 14, 1123–1132
Fent, K.;Stegeman, J.J. (1993): Effects of Tributyltinin vivo on Hepatic Cytochrome P450 Forms in Marine Fish. Aquat. Toxicol. 24, 219–240
Kan-Atireklap, S.;Tanabe, S.;Sanguansin, J. (1997): Contamination by Butyltin Compounds in Sediments from Thailand. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 34, 894–899
Kannan, K.;Tanabe, S.;Iwata, H.;Tatsukawa, R. (1995a): Butyltins in Muscle and Liver of Fish Collected from Certain Asian and Oceanian Countries. Environ. Pollut. 90, 279–290
Kannan, K.;Yasunaga, Y.;Iwata, H.;Ichihashi, H.;Tanabe, S.;Tatsukawa, R. (1995b): Concentrations of Heavy Metals, Organochlorines, and Organotins in Horseshoe Crab,Tachypleus tridentatus, from Japanese Coastal Waters. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 28, 40–47
Kannan, K.;Tanabe, S.;Tatsukawa, R.;Williams, R.J. (1995c): Butyltin Residues in Fish from Australia, Papua New Guinea and the Solomon Islands. Intern. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 61, 263–273
Kannan, K.;Corsolini, S.;Focardi, S.;Tanabe, S.;Tatsukawa, R. (1996): Accumulation Pattern of Butyltin Compounds in Dolphin, Tuna and Shark Collected from Italian Coastal Waters. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 31, 19–23
Kannan, K.;Falandysz, J. (1997): Butyltin Residues in Sediment, Fish, Fish-Eating Birds, Harbour Porpoise and Human Tissues from the Polish Coast of the Baltic Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 34, 203–207
Kannan, K.;Senthilkumar, K.;Loganathan, B.G.;Takahashi, S.;Odell, D.K.;Tanabe, S. (1997a): Elevated Accumulation of Tributyltin and Its Breakdown Products in Bottlenose Dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) Found Stranded along the U.S. Atlantic and Gulf Coasts. Environ. Sci. Technol. 31, 296–301
Kannan, K.;Senthilkumar, K.;Sinha, R.K. (1997b): Sources and Accumulation of Butyltin Compounds in Ganges River Dolphin,Platanista gangetica. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 11, 223–230
Kannan, K.;Guruge, K.S.;Thomas, N.J.;Tanabe, S.;Giesy, J.P. (1998): Butyltin Residues in Southern Sea Otters (Enhydra lutris nereis) Found Dead along California Coastal Waters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 32, 1169–1175
Kannan, K.;Grove, R.A.;Senthilkumar, K.;Henny, C.J.;Giesy, J.P. (1999): Butyltin Compounds in River Otters (Lutra canadensis) from the Northwestern United States. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 36, 462–468
Kim, G.B.;Tanabe, S.;Koh, C.H. (1998): Butyltins in Surface Sediments of Kyeonggi Bay, Korea. J. Korean Soc. Oceano. 33, 64–70
Lau (Wong), M.M. (1991): Tributyltin Antifoulings: A Threat to the Hong Kong Marine Environment. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 20, 299–304
Lee, R.F. (1985): Metabolism of Tributyltin oxide by Crabs, Oysters and Fish. Mar. Environ. Res. 17, 145–148
Lee, R.F. (1993): Passage of Xenobiotics and Their Metabolites from Hepatopancreas into Ovary and Oocytes of Blue Crabs,Callinectus sapidus: Possible Implications for Vitellogenesis. Mar. Environ. Res. 35, 181–187
Page, D.S.;Ozbal, C.C.;Lanphear, M.E. (1996): Concentration of Butyltin Species in Sediments Associated with Shipyard Activity. Environ. Pollut. 91, 237–243
Penninks, A.H. (1993): The Evaluation of Data-derived Safety Factors for Bis(tri-n-buryltin) Oxide. Food. Addit. Contam. 10, 351–361
Stab, J.A.;Trass, T.P.;Stroomberg, G.;Van Kesteren, J.;Leonards, P.;Van Hattum, B.;Brinkman, U.A. TH.;Cofino, W.P. (1996): Determination of Organotin Compounds in the Foodweb of a Shallow Freshwater Lake in The Netherlands. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 31, 319–328
Szpunar, J.;Falandysz, J.;Schmitt, V.O.;Obrebska, E. (1997): Butyltins in Marine and Freshwater Sediments of Poland. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 58, 859–864
Uhler, A.D.;Durell, G.S.;Steinhauer, W.G.;Spellacy, A.M. (1993): Tributyltin Levels in Bivalve Mollusks from the East and West Coasts of the United States: Results from the 1988–1990 National Status and Trends Mussel Watch Project. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 12, 139–153
Wade, T.L.;Garcia-Romero, B.;Brooks, J.M. (1990): Butyltins in Sediments and Bivalves from U. S. Coastal Areas. Chemosphere 20, 647–662
Yonezawa, Y.;Nakata, K.;Miyakozawa, Y.;Ochi, A.;Kowata, T.;Fukawa, H.;Sato, Y.;Masunaga, S.;Urushigawa, Y. (1993): Distributions of Butyltins in the Surface Sediment of Ise Bay, Japan. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 12, 1175–1184
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Senthilkumar, K., Duda, C.A., Villeneuve, D.L. et al. Butyltin compounds in sediment and fish from the Polish Coast of the Baltic Sea. Environ. Sci. & Pollut. Res. 6, 200–206 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02987327
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02987327