Abstract
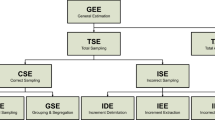
Heavy Metal data from a measurement program at a municipal incinerator in Vienna, Austria are analysed. The experimental design had a nested structure, and analysis of variance is used to break down the total variability into several components; (1) variability between mean hourly concentrations, (2) variability between mean sample concentrations within intervals of an hour and (3) variability due to “measurement” errors. Results of a pre-experiment show, that if grab samples are taken, within hour variation is dominant. The results of analysis of variance were used to calculate an optimal number of samples, which ensure a predetermined accuracy for the mean concentrations. In two main measuring periods with different incinerated waste types, slag and fly ash (ESP dust and boiler ash) data are produced and analysed. For both slag and fly ash, significant differences in measures of location and dispersion between the data sets of the main experiment are found. This proves, that differences in the chemical set up of waste can be detected via incineration residues.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agenend F.J., Trondt L. (1990), Bilanzierung bei der Müllverbrennung am Beispiel des Müllheizkraftwerkes Essen-Karnap, VGB Kraftwerkstechnik 1/90 p. 36–42
Bauer G. (1995), Die Stoffflußanalyse von Prozesses der Abfallwirtschaft unter Berücksichtigung der Unsicherheit, PhD Thesis (to be published), Technical University, Vienna
Bergström J., Sundquist J. (1984), Emission control for municipal solid waste incineration in Sweden, EWPCA-ISWA, München
Brunner P.H., Mönch H. (1986), The flux of metals through a municipal solid waste incinerator, Waste Manag. & Res.4, p. 105–119
Brunner P.H., Ernst W. (1986), Alternative Methods for the Analysis of Municipal Solid Wastes, Waste Manag. & Res.4, p. 147–160
Burdick R.K., Graybill F.A. (1992), Confidence Intervals on Variance Components, Statistics, textbooks and monographs, vol.127, New York
Dean R.B. (1987), Incineration of Municipal Waste, Academic Press, London
Eawag (1982), Metallgehalte in der Kehrichtschlacke und Elektrofilterasche der Kehrichtverbrennungsanlage Biel, Projekt Nr. 30-4658
Holcome L. (1988), Relations of Sampling Design to Analytical Precision Estimates, In: Principles of Environmental Sampling, Ed. by Keith L.H., American Chemical Society, p. 395–408
Reinmann D.O. (1989), Heavy Metals in Domestic Refuse and their Distribution in Incinerator Residues, Waste Manag. & Res. 1, p. 57–62
SAS/STAT (1990), User’s Guide, Version 6, Fourth Edition, Volume 2, Cary, NC SAS Institute Inc.
Schachermayer E., Bauer G., Ritter E., Brunner P.H. (1995), Messung der Güter und Stoffbilanz einer MVA, Monographien Bd. 56, UBA, Wien
Schaeffer D.J., Kerster H.W., Janardan K.G. (1980), Grab Versus Composite Sampling: A Primer for the Manager und Engineer, Enviro. Manag. 4, 2, p. 157–163
Scheffe H. (1957), The Analysis of Variance, John Wiley & Sons, London
Welch B.L. (1947), The Generalization of ‘Student’s’ problem, when Several Different Population Variances are involved, Biometrica, 34 p. 28–35
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bauer, G., Schachermayer, E. Statistical analysis of heavy metal data from municipal waste incineration residues. Environ. Sci. & Pollut. Res. 3, 10–16 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02986804
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02986804