Abstract
Objective
To compare histological findings of FDG-PET false-positive and true-negative hilar and mediastinal lymph nodes.
Methods
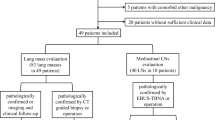
Sixty-seven lymphnode areas in 11 patients who were diagnosed to have N3 lymph nodes by FDG-PET and underwent surgery were histologically examined, and the histopathological findings in false-positive and true-negative lymph nodes were compared. Lymph nodes with higher accumulation of FDG than the surrounding mediastinum level were judged as positive. On histological sections, proportions of macrophages and lymphocytes, amount of coal dust deposit, presence of silicotic nodules, long- and short-axes of the largest node, and volume of macrophages and lymphocytes were evaluated. Correlations between the above-mentioned factors and FDG accumulation were evaluated.
Results
FDG uptake was not correlated with the proportion of macrophages and lymphocytes, coal dust amounts, or the presence of silicotic nodules. The long- and short-axes of the largest node in the false-positive areas were significantly longer than those in the true-negative areas (p = 0.01, and 0.001, respectively). Volumes of lymph nodes (mean ± SD: 150 ± 190 mm3) and macrophages (78 ± 71 mm3) in false-positive areas were markedly larger than those in true-negative areas (68 ± 87 mm3, p = 0.0009 and 34 ± 54 mm3, p = 0.0001, respectively). The volume of lymphocytes was also larger in false-positive areas but less markedly.
Conclusion
Our study suggested that false-positive results of FDG-PET in hilar and mediastinal lymph nodes were closely related to the size of lymph node and the volume of macrophages.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Steinert HC, Hauser M, Allemann F, Engel H, Berthold T, von Schulthess GK, et al. Non-small cell lung cancer: nodal staging with FDG PET versus CT with correlative lymph node mapping and sampling.Radiology 1997; 202: 441–446.
Wahl RL, Quint LE, Greenough RL, Meyer CR, White RI, Orringer MB. Staging of mediastinal non-small cell lung cancer with FDG PET, CT, and fusion images: preliminary prospective evaluation.Radiology 1994; 191: 371–377.
Scott WJ, Gobar LS, Terry JD, Dewan NA, Sunderland JJ. Mediastinal lymph node staging of non-small-cell lung cancer: a prospective comparison of computed tomography and positron emission tomography.J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 1996; 111:642–648.
Guhlmann A, Storck M, Kotzerke J, Moog F, Sunder-Plassmann L, Reske SN. Lymph node staging in non-small cell lung cancer: evaluation by [18F]FDG positron emission tomography (PET).Thorax 1997; 52: 438–441.
Vansteenkiste JF, Stroobants SG, De Leyn PR, Dupont PJ, Verschakelen JA, Nackaerts KL, et al. Mediastinal lymph node staging with FDG-PET scan in patients with potentially operable non-small cell lung cancer: a prospective analysis of 50 cases. Leuven Lung Cancer Group.Chest 1997; 112: 1480–1486.
Farrell MA, McAdams HP, Herndon JE, Patz EF Jr. Related non-small cell lung cancer: FDG PET for nodal staging in patients with stage I disease.Radiology 2000; 215: 886–890.
Chin R Jr, Ward R, Keyes JW, Choplin RH, Reed JC, Wallenhaupt S, et al. Mediastinal staging of non-small-cell lung cancer with positron emission tomography.Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1995; 152 (6 Pt 1): 2090–2096.
Patz EF Jr, Lowe VJ, Goodman PC, Herndon J. Thoracic nodal staging with PET imaging with18FDG in patients with bronchogenic carcinoma.Chest 1995; 108 (6): 1617–1621.
Vansteenkiste JF, Stroobants SG, De Leyn PR, Dupont PJ, Bogaert J, Maes A, et al. Lymph node staging in non-small-cell lung cancer with FDG-PET scan: a prospective study on 690 lymph node stations from 68 patients.J Clin Oncol 1998; 16 (6): 2142–2149.
Nettelbladt OS, Sundin AE, Valind SO, Gustafsson GR, Lamberg K, Langstrom B, et al. Combined fluorine-18-FDG and carbon-11-methionine PET for diagnosis of tumors in lung and mediastinum.J Nucl Med 1998; 39: 640–647.
Kutlu CA, Pastorino U, Maisey M, Goldstraw P. Selective use of PET scan in the preoperative staging of NSCLC.Lung Cancer 1998; 21 (3): 177–184.
Valk PE, Pounds TR, Hopkins DM, Haseman MK, Hofer GA, Greiss HB, et al. Staging non-small cell lung cancer by whole-body positron emission tomographic imaging.Ann Thorac Surg 1995; 60 (6): 1573–1581.
Sazon DA, Santiago SM, Soo Hoo GW, Khonsary A, Brown C, Mandelkern M, et al. Fluorodeoxyglucose-positron emission tomography in the detection and staging of lung cancer.Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1996; 153: 417–421.
Schiepers C. Related articles, role of positron emission tomography in the staging of lung cancer.Lung Cancer 1997; 17(Suppl 1): S29–35.
Liewald F, Grosse S, Storck M, Guhlmann A, Halter G, Reske S, et al. How useful is positron emission tomography for lymphnode staging in non-small-cell lung cancer?J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2000; 48: 93–96.
Shreve PD, Anzai Y, Wahl RL. Pitfalls in oncologic diagnosis with FDG PET imaging: physiologic and benign variants.Radiographics 1999; 19: 61–77.
Hara M, Shiraki N, Iida A, Tamaki T, Itoh M, Arakawa T. A problem of FDG-PET in patients with lung cancer diagnosed as N3: False positive.Radiology 2001; 221 (P): 409.
Armstrong P. Mediastinum and Hilar Disorders In: Armstrong P, Wilson AG, Dee P, eds.Imaging of Diseases of the Chest, 3rd ed. London; Mosby, 2000: 789–892.
Rosai J.Ackerman’s Surgical Pathology. 8th ed. St. Louis; Mosby-Year Book, 1996; 2: 1670–1671.
Johansson A, Camner P. Are alveolar macrophage translocated to the lymph nodes?Toxicology 1980; 15: 157–162.
Kubota R, Yamada S, Kubota K, Ishiwata K, Tamahashi N, Ido T. Related intratumoral distribution of fluorine-18-fluorodeoxyglucosein vivo: high accumulation in macrophages and granulation tissues studied by microautoradiography.J Nucl Med 1992; 33: 1972–1980.
Yamada S, Kubota K, Kubota R, Ido T, Tamahashi N. High accumulation of fluorine-18-fluorodeoxyglucose in turpentine-induced inflammatory tissue.J Nucl Med 1995; 36: 1301–1306.
Boisellef PM, Patz EF Jr., Vining DJ, Weissleder R, Shephard JA, McLoud TC. Imaging of mediastinal lymph nodes: CT, MR, and FDG PET. 1998; 18: 1061–1069.
Marom EM, McAdams HP, Erasmus JJ, Goodman PC, Culhane DK, Coleman RE. Staging non-small cell lung cancer with whole-body PET.Radiology 1999; 212: 803–809.
Lowe VJ, Duhaylongsod, Patz EF, Delong DM, Hoffman JM, Wolfe WG, et al. Pulmonary abnormalities and PET data analysis: A retrospective study.Radiology 1997; 202: 435–439.
Inoue K, Matoba S. Counterattack of re-emerging tuberculosis after 38 years.Int J Tuberc Lung Dis 2001; 5: 873–875.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shiraki, N., Hara, M., Ogino, H. et al. False-positive and true-negative hilar and mediastinal lymph nodes on FDG-PET —Radiological-pathological correlation—. Ann Nucl Med 18, 23–28 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02985610
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02985610