Abstract
Background
Rest thallium-201 (201T1) myocardial perfusion imaging has been widely used for evaluation of myocardial ischemia/viability after myocardial infarction, but the ideal timing for imaging after injection to maximally estimate viability is not well established.
Methods
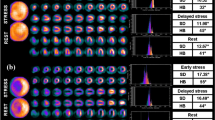
Thirty-six patients with myocardial infarction underwent the initial, 3 h, and 24 h redistribution imaging after intravenous injection of 148–185 MBq201T1. The initial and 3 h images, the initial and 24 h images, and the 3 and 24 h images were compared double-blinded. Results: Out of the 184 abnormal segments based on the initial imaging, 56 (30%) segments improved by at least 1 grade on the 3 h imaging while 78 (42%) segments improved by at least 1 grade on the 24 h imaging. The 24 h late imaging detected more viable myocardium than the 3 h imaging did, with a significant difference (χ2= 5.680, p = 0.017). There were 158 abnormal segments on the 3 h imaging, with average 28% (44) segments improved by at least 1 grade on the 24 h imaging. There were 128 initial abnormal segments with no improvement on the 3 h imaging. Out of these segments, the 24 h late redistribution imaging detected additional redistribution in 26 segments, taking up 20%.
Conclusions
Twenty-four hour late201T1 imaging will demonstrated additional redistribution in patients who have incompletely reversible defects on early redistribution imaging at 3h.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allman KC, Shaw LJ, Hachamovitch R, et al. Myocardial viability testing and impact of revascularization on prognosis in patients with coronary artery disease and left ventricular dysfunction: a meta-analysis.J Am Coll Cardiol 2002; 39: 1151–1158.
Dilsizian V, Rocco TP, Freedman MNT, et al. Enhanced detection of ischemic but viable myocardium by the reinjection of thallium after stress-redistribtution imaging.N Engl J Med 1990; 323: 141.
Ohtani H, Tamaki N, Yonekura Y, et al. Value of thallium-201 reinjection after delayed SPECT imaging for predicting reversible ischemia after coronary artery bypass grafting.Am J Cardiol 1990; 66: 394.
Coll C, Gonzalez P, Massardo T, et al. Performance of Thallium 201 rest-redistribution SPECT to predict viability in recent myocardial infarction.Revista Medica de Chile 2002; 130: 243–250. (in Spanish)
Cerqueira MD, Weissman NJ, Dilsizian V, et al. Standardized myocardial segmentation and nomenclature for tomo-graphic imaging of the heart.Circulation 2002; 105: 539–542.
Klocke FJ, Baird MG, Bateman TM, et al. ACC/AHA/ ASNC guidelines for the clinical use of cardiac radionuclide imaging: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines (ACC/AHA/ASNC Committee to Revise the 1995 Guidelines for the Clinical Use of Cardiac Radionu-clide Imaging).Circulation 2003; 108: 1404–1418.
Kiat H, Berman DS, Maddahi J, et al. Late reversibility of tomographic myocardial thallium-201 defects: an accurate marker of myocardial viability.J Am Coll Cardiol 1988; 12: 1456–1463.
Gutman J, Berman DS, Freeman M, et al. Time to completed redistribution of thallium-201 in exercise myocardial scintigraphy: relationship to the degree of coronary artery stenosis.Am Heart J 1983; 106: 989–995.
Matsuno K, Kuwabara Y, Watanabe S, et al. Detection of myocardial viability using rest-redistribution thallium-201 imaging in a stress99Tcm-tetrofosmin/rest thallium-201 dual-isotope protocol.Nucl Med Comm 2001; 22: 165–173.
Wagdy HM, Christian TF, Miller TD, et al. The value of 24-hour images after rest thallium injection.Nucl Med Comm 2002; 23: 6296–37.
Matsunari I, Fujino S, Taki J, et al. Significance of late redistribution thallium-201 imaging after rest injection for detection of viable myocardium.J Nucl Med 1997; 38: 1073–1078.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, XJ., He, YM., Zhang, B. et al. Assessment of myocardial viability in patients with myocardial infarction using twenty-four hour thallium-201 late redistribution imaging. Ann Nucl Med 20, 23–28 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02985586
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02985586